As a BetterHelp affiliate, we receive compensation from BetterHelp if you purchase products or services through the links provided
Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT) has emerged as a powerful tool in addressing various mental health challenges, including anxiety disorders. Initially developed to treat individuals with borderline personality disorder, DBT has proven effective in alleviating anxiety symptoms and fostering emotional stability. By incorporating mindfulness, emotion regulation, and distress tolerance techniques, DBT has helped many people regain control over their anxiety and improve their overall quality of life.
At its core, DBT is a cognitive-behavioral therapy that focuses on enhancing the individual’s ability to manage emotions and navigate challenging situations. It achieves this through a unique blend of acceptance-based and change-based strategies, providing clients with the skills to establish more positive thought patterns and behaviors. With a strong emphasis on the therapeutic relationship, DBT practitioners work collaboratively with their clients to achieve lasting change.
Key Takeaways
- DBT is an effective treatment for anxiety, offering a unique blend of acceptance and change-based strategies
- The core components of DBT, such as mindfulness and emotional regulation, equip clients with skills to manage their anxiety more effectively.
- A strong therapeutic relationship plays an essential role in the success of DBT in addressing anxiety-related issues.
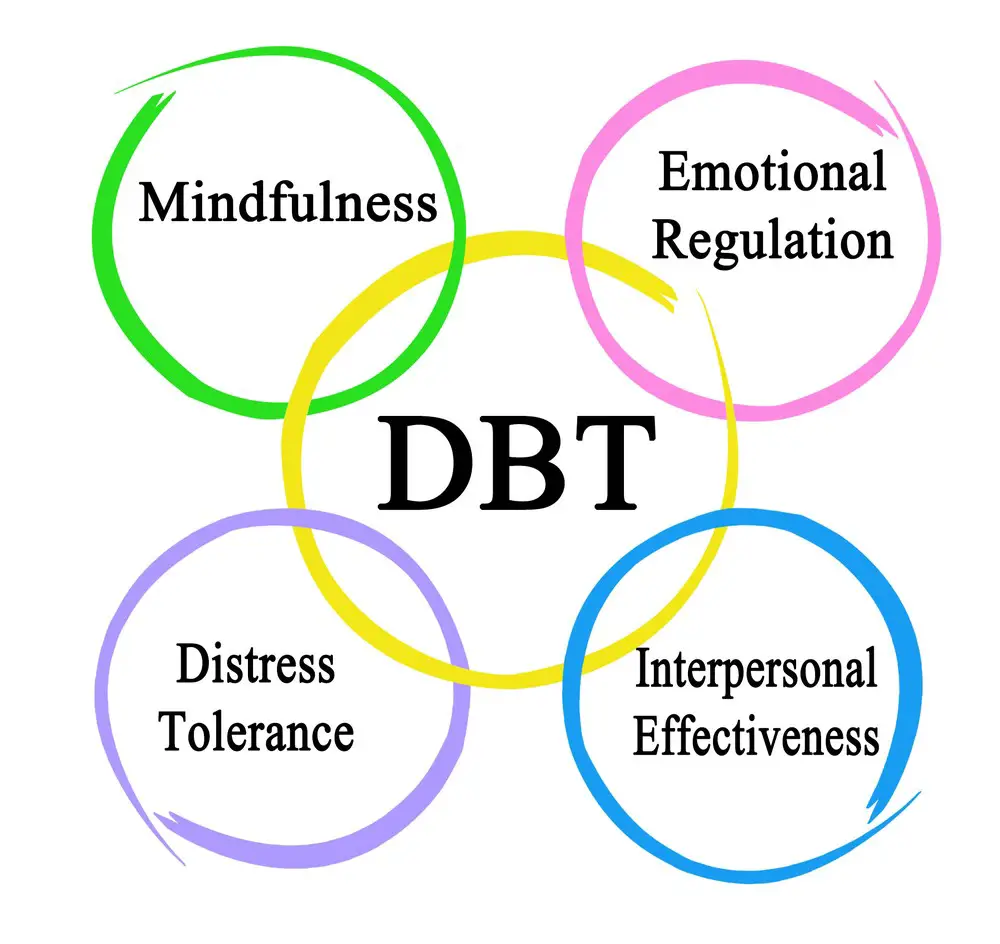
Understanding DBT
Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT) is a groundbreaking approach to help people manage overwhelming emotions and improve their mental well-being. Developed by psychologist Marsha Linehan, DBT has gained recognition as an effective therapy for coping with anxiety and other emotional difficulties.
At its core, DBT aims to strike a balance between acceptance and change. It acknowledges that the struggle to manage one’s emotions is real while providing the necessary tools and skills to navigate those turbulent times. DBT teaches patients how to regulate their feelings, communicate assertively, and engage in mindfulness practices.
A key aspect of DBT is its systematic approach. This therapy encompasses four modules: mindfulness, distress tolerance, emotion regulation, and interpersonal effectiveness. Each module addresses specific emotional challenges and provides practical guidance for overcoming them.
For instance, mindfulness helps individuals remain present and aware of their thoughts and emotions. By practicing mindfulness, people can learn to observe their anxiety without getting caught up in it, paving the way for a more grounded and rational response.
Regarding distress tolerance, DBT emphasizes the importance of navigating through emotional crises without resorting to destructive behaviors. By developing coping strategies, patients can learn to tolerate emotional distress and emerge from it with resilience intact.
The emotion regulation component equips individuals with skills to manage their emotions effectively. DBT helps them identify triggers, understand emotional patterns, and develop strategies to reduce the intensity and frequency of anxiety episodes.
Lastly, interpersonal effectiveness focuses on honing one’s communication abilities, setting boundaries, and nurturing healthy relationships. This module teaches people to assert their needs in a non-confrontational yet firm manner, reducing conflict-induced anxiety.
In summary, Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT) offers a comprehensive approach to managing anxiety. DBT has proven itself a worthwhile therapy for those seeking to regain control over their emotional health by providing valuable skills and strategies in its four key modules.
DBT and Anxiety
Dealing with anxiety can be challenging, especially when it feels overwhelming and all-consuming. That’s where Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT) swoops in to save the day! Originally designed to treat Borderline Personality Disorder, DBT has expanded its reach and proven effective for anxiety disorders.
So, what exactly is this wonder therapy? In a nutshell, DBT is a type of cognitive-behavioral therapy that focuses on developing skills for emotion regulation, interpersonal effectiveness, distress tolerance, and mindfulness. When anxiety kicks in big time, these skills are vital for regaining control and taming the whirlwind of fear, worry, and panic attacks.
Take mindful breathing, for example. One of the key components of mindfulness in DBT is learning to focus on the breath as an anchor when anxiety takes over. It becomes easier to detach from the chaos and keep a level head by tuning into the steady pace of inhaling and exhaling. It’s a fantastic skill for navigating those tumultuous waves of worry.
But wait, there’s more! DBT isn’t a one-trick pony. Another valuable tactic it teaches us how to challenge those pesky negative thoughts that fuel anxiety. Individuals learn to identify, assess, and alter these unhelpful beliefs through cognitive restructuring. It is a relief to break free from irrational fear and finally find clarity!
And let’s not forget about the importance of interpersonal effectiveness in managing anxiety. For many people, anxiety creates a rift in their relationships as they struggle to express their needs or set boundaries. DBT offers a set of skills to build stronger connections and feel more secure in interactions with others, which can be a real game-changer in reducing anxiety.
In short, DBT is a powerful tool in the battle against anxiety disorders. Offering an arsenal of practical, evidence-based strategies empowers individuals to live a more balanced, fulfilled life. Anxiety may seem like a formidable foe, but with DBT by their side, many people find the strength to face it head-on and emerge victorious.

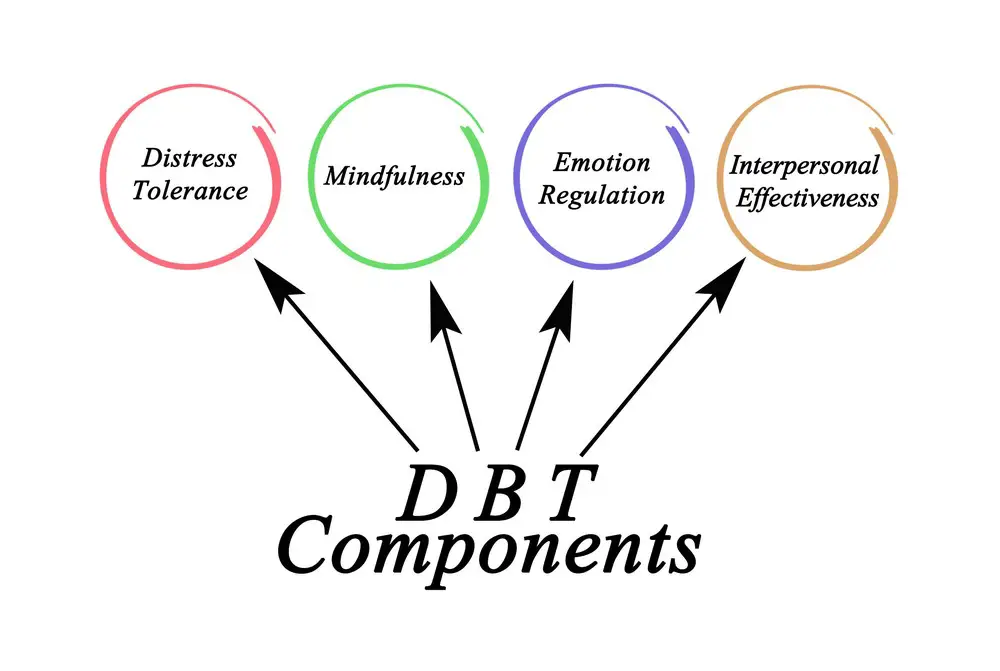
Core Components of DBT
DBT, or Dialectical Behavior Therapy, is an effective and widely recognized approach for helping individuals manage anxiety and other emotional struggles. With its roots in cognitive-behavioral therapy, DBT incorporates several core components for addressing and overcoming anxiety.
Mindfulness
At the heart of DBT lies mindfulness, a skill that teaches individuals to become more aware of their thoughts, emotions, and sensations in the present moment. Through mindfulness skills, such as observing and describing, a person can cultivate a nonjudgmental, curious, and compassionate stance towards themselves and their experiences. This practice fosters self-awareness and helps individuals to identify and challenge unhelpful thought patterns and emotional reactions.
Emotional Regulation
Understanding and managing emotions are key factors in navigating daily life, especially when dealing with anxiety. Emotional regulation skills help individuals recognize and label their emotions, spot triggers, and devise effective coping strategies. By learning various techniques, such as problem-solving, opposite action, and self-soothing, a person can regulate intense emotions and prevent them from causing unnecessary distress.
Distress Tolerance
Life can be unpredictable, and often we face challenging situations that can provoke anxious feelings. Distress tolerance skills in DBT equip individuals to handle crises and emotional upheaval with resilience and grace. Rather than succumbing to negative emotions or engaging in destructive behaviors, clients learn strategies like self-soothing, distraction, and acceptance. Individuals can calmly endure tough situations by developing a toolbox of skills, promoting growth and long-lasting change.
Interpersonal Effectiveness
Anxiety can often lead to difficulties building and maintaining healthy personal and professional relationships. Interpersonal effectiveness skills equip individuals with the tools to communicate their needs assertively, set boundaries, and establish positive connections with others. As the person becomes more proficient in these skills, they’ll experience less interpersonal conflict, enhancing their overall well-being and reducing anxiety in social situations.
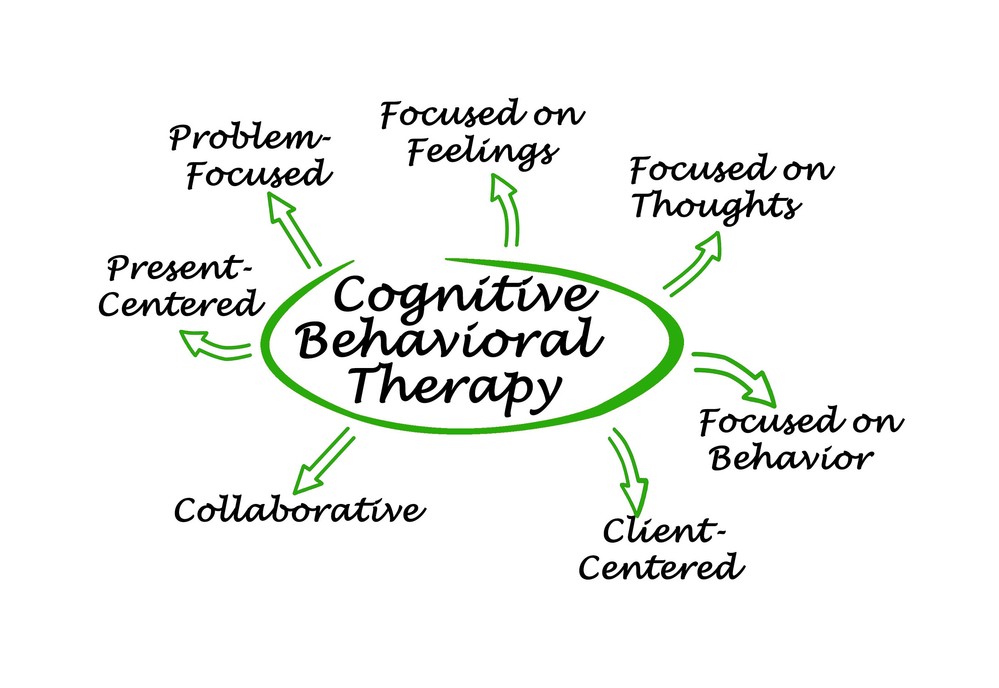
DBT vs CBT
Regarding therapy for anxiety, two approaches often stand out – Dialectical Behavioral Therapy (DBT) and Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT). Both share certain similarities, but each has distinct traits, shedding light on their merits.
DBT, a subset of CBT, was initially developed to treat personality disorders like borderline personality disorder. Over time, however, it has proven beneficial for other mental health issues, including anxiety. By teaching patients how to regulate emotions and tolerate distress, DBT cultivates coping strategies for dealing with anxiety-ridden situations.
On the other hand, CBT primarily focuses on the interplay between thoughts, feelings, and behaviors, helping individuals recognize and reframe negative thought patterns. As a tremendously influential approach, it addresses various mental health concerns, including depression, eating disorders, and anxiety.
In comparing these therapies, one might notice the broader skillset DBT provides. It encompasses mindfulness, emotional regulation, interpersonal effectiveness, and distress tolerance. Through these four components, individuals learn to navigate emotional turmoil more easily.
Contrastingly, CBT zeroes in on the cognitive aspect, challenging irrational beliefs and breaking the cycle of negative thoughts. By doing so, it can effectively alleviate symptoms related to anxiety and other mental health struggles.
In essence, both DBT and CBT bring notable benefits to the table. However, individuals and their therapists must consider personal needs and contexts when selecting the most fitting approach. Ultimately, the right choice varies from person to person, with the end goal being to foster emotional resilience and enhance overall well-being.

The Role of the Therapist
Regarding DBT (Dialectical Behavior Therapy) for anxiety, the therapist is vital in guiding and supporting clients toward emotional stability and improved mental health. These professionals lend their expertise and offer a safe space, enabling individuals to tackle their anxiety head-on.
Therapists typically begin by establishing a strong rapport with their clients, fostering trust and open communication. They then assess the severity of the client’s anxiety, identifying any triggers or disruptive patterns that must be addressed. By doing so, they can tailor the DBT treatment plan to fit the client’s unique needs and goals.
During sessions, therapists introduce clients to key DBT concepts and skills such as mindfulness, emotion regulation, distress tolerance, and interpersonal effectiveness. They demonstrate these techniques and guide the client through practical exercises, helping them gain the necessary tools to manage anxiety more effectively.
Moreover, therapists offer continuous support and constructive feedback as clients navigate the challenges of applying newly learned DBT skills to real-life situations. This crucial guidance ensures clients maintain their motivation and commitment to the transformative process of DBT.
Lastly, a significant part of DBT therapy involves empowering clients to develop self-awareness, self-compassion, and resilience. Therapists help clients embrace the idea of radical acceptance and provide tools to overcome challenges with confidence and grace.
In summary, the therapist’s role in DBT for anxiety is multifaceted: building trust and personalized treatment plans to teaching techniques, offering support and instilling the courage for lasting change. These invaluable professionals are the steady anchor that keeps clients on track toward a healthier, anxiety-free life.
Combination with Medication
Dialectical behavior therapy (DBT) can be incredibly beneficial for individuals struggling with anxiety. But what about the role of medications? You’ll see how combining DBT with anxiety medication can be a match made in heaven.
DBT, in essence, is a comprehensive cognitive-behavioral therapy that has been proven effective in managing various mental health issues, including anxiety. With its focus on helping individuals develop healthy coping strategies and foster emotional regulation, folks often experience significant improvement in their anxiety levels. However, like a flawless dance partnership, sometimes it’s best when paired with medication.
Anxiety medications, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), synergize when combined with DBT. Together, they address both the biological and psychological aspects of anxiety. While DBT improves emotional regulation and interpersonal effectiveness, medication helps balance the brain’s chemistry. This dynamic duo can create an environment where individuals truly thrive in their journey toward overcoming anxiety.
It’s essential to recognize that not all people with anxiety require medication—some find solace in DBT alone. Then again, some might need medications to bring their overwhelming feelings down to a manageable level, thus making it easier for them to work with DBT skills. The collaboration of DBT and medication can not only harness the power of both treatment approaches but also cater to the unique needs of individuals.
To sum it up, the combination of DBT and anxiety medications can enhance the overall effectiveness of treatment. Like yin and yang, DBT and medication complement each other, offering a comprehensive and customizable approach to conquering anxiety. So, if you’re considering treatment options for anxiety, don’t be afraid to explore the potential of this winning partnership.
DBT for Other Disorders
Dialectical behavior therapy (DBT) is well-known for its effectiveness in treating borderline personality disorder, but it doesn’t stop there! This versatile therapy has proven beneficial for individuals struggling with various mental health conditions.
For instance, depression often leaves people feeling as if they’re trapped in a vicious cycle of negative thoughts and emotions. DBT provides skills and techniques that help those experiencing depression to manage their emotions more effectively, ultimately promoting a more balanced mood.
Regarding post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), DBT can be a game changer. Its core principles help individuals face and process traumatic experiences while offering coping strategies for reducing emotional intensity. Mindfulness and distress tolerance tools, in particular, empower sufferers of PTSD to regain control over their lives.
Eating disorders, such as binge eating disorders, can also be addressed through DBT. By incorporating emotion regulation techniques, individuals learn to identify and manage the underlying feelings that may trigger disordered eating patterns. On the other hand, practicing interpersonal effectiveness skills helps create healthier relationships with food and oneself.
Substance use disorders are another area where DBT shines. It’s about quitting and cultivating a sustainable life in recovery. DBT supports individuals struggling with substance abuse by teaching them to resist urges, handle cravings, and deal with triggers more adaptively.
DBT benefits extend far beyond borderline personality disorder. Its multifaceted approach addresses various areas of mental health, contributing to more comprehensive well-being for individuals with mood disorders and other psychiatric conditions. The versatility of DBT makes it an indispensable tool for therapists and patients alike in their journey to improved mental health.
Methods and Techniques
One-Mindfully
One-Mindfully teaches individuals to focus on the present moment without judgment. By doing so, they can change the way they react to anxiety and stressful situations. By practicing one-mindfulness, individuals can develop a sense of acceptance for their thoughts and feelings, allowing them to cope more effectively. They’ll experience a sense of calmness and be more in tune with their body and emotions. This goes hand-in-hand with individual therapy, where clients are encouraged to share their experiences and build upon their skills.
Self-Soothing
Self-soothing is crucial for individuals dealing with anxiety. It involves using the five senses (sight, smell, touch, taste, and hearing) to aid in relaxation and reduce anxiety. Examples of self-soothing techniques include:
- Sight: Looking at calming images or beautiful scenery
- Smell: Aromatherapy or lighting a scented candle
- Touch: Massages or hugging a stuffed animal
- Taste: Savoring a piece of dark chocolate or herbal tea
- Hearing: Listening to soothing music or nature sounds
These techniques promote self-care and show individuals they can manage pain without resorting to self-harm or impulsive behaviors.
Deep Breathing
Deep breathing exercises are indispensable for regulating emotions. Breathing deeply and slowly can help an individual relax, releasing tension and anxiety. When practiced consistently, deep breathing becomes a coping skill for individuals experiencing anxiety or overwhelming emotions.
Visualization
Visualization involves creating a mental image of a calming or happy place, object, or event. For those struggling with anxiety, visualizing a peaceful scene can help distract their focus from negative thoughts, providing a temporary escape. Visualization can be combined with meditation or prayer to enhance relaxation and spiritual well-being. Individuals can practice visualization during talk therapy sessions, guided by their therapist, or as a part of their homework exercises.
Incorporating these methods and techniques into daily life can help individuals manage their anxiety, practice non-judgment, and identify cognitive distortions. Continuing to practice these skills and participate in psychotherapy sessions will ultimately lead to a more balanced, emotionally regulated life experience.
Benefits and Effectiveness
DBT, or Dialectical Behavior Therapy, has proven to be a highly effective treatment for anxiety disorders. It is a well-researched and evidence-based psychotherapy that effectively addresses emotional vulnerability and helps individuals develop skills to manage negative emotions in various emotional situations.
One of the most notable benefits of DBT is its ability to foster positive emotions amidst challenging circumstances. By teaching the patients specific strategies, such as mindfulness and emotional regulation, they gain confidence in their ability to handle emotional turmoil. Consequently, this newfound resilience makes them less prone to be overwhelmed by their negative emotions.
Moreover, DBT supports individuals in cultivating a healthier relationship with their emotions. Instead of trying to avoid or suppress emotional experiences, patients are guided toward embracing them with acceptance and compassion. This approach allows them to understand their emotional patterns and triggers better, leading to a higher degree of self-awareness and emotional intelligence.
Furthermore, DBT has a comprehensive structure that considers various aspects of well-being, such as interpersonal effectiveness and distress tolerance. These modules enhance the patient’s overall quality of life and ability to navigate troubling situations adaptively. As a result, they experience alleviating anxiety symptoms and a more balanced emotional state.
In conclusion, DBT is an incredibly valuable therapy for people suffering from anxiety disorders. It has yielded significant improvements in managing negative emotions, fostering positive emotions, and navigating through emotional situations. DBT has established itself as a trusted and effective intervention, offering hope and relief to countless individuals struggling with anxiety.

Frequently Asked Questions
How does DBT help with anxiety management?
DBT, or Dialectical Behavior Therapy, is a unique approach to managing anxiety. It’s designed to help individuals regulate their emotions, improve interpersonal relationships, and develop healthier coping mechanisms. It teaches mindfulness, emotional regulation, distress tolerance, and interpersonal effectiveness. With these powerful tools, people with anxiety can navigate their daily lives more easily and confidently.
What are some specific DBT skills to cope with social anxiety?
DBT offers various skills to help those with social anxiety. For instance, mindfulness practices like observing, describing, and participating can aid in identifying and managing anxious sensations. Emotional regulation skills, such as opposite action and checking the facts, can assist in assessing and changing one’s emotions. Moreover, interpersonal effectiveness techniques like DEAR-MAN, GIVE, and FAST guide people in communicating assertively and maintaining self-respect while interacting with others.
Can DBT be effective for panic attacks?
Yes, DBT can be effective in managing panic attacks. By incorporating mindfulness and distress tolerance strategies, individuals learn to observe their panic symptoms without judgment and apply grounding techniques, such as paced breathing or 5-4-3-2-1 sensory exercises. This approach helps break the cycle of intense anxiety that often leads to a panic attack, enabling a person to regain control.
How does DBT differ from CBT in treating anxiety?
While DBT and CBT (Cognitive Behavioral Therapy) share certain elements, like teaching coping skills, they differ in focus and methods. CBT emphasizes recognizing and challenging irrational thoughts, whereas DBT prioritizes emotion regulation and interpersonal effectiveness. CBT targets the cognitive aspect of anxiety, while DBT addresses the emotional and relational components crucial in treating anxiety disorders.
Is DBT suitable for treating ADHD and anxiety?
DBT can benefit individuals with ADHD and anxiety by offering versatile techniques that address emotional regulation, impulsivity, and relationship challenges. Though not explicitly designed for ADHD, the mindfulness and interpersonal skills taught in DBT can complement other ADHD treatment options. As always, it’s essential to consult a mental health professional to determine the most appropriate course of action for each individual’s needs.
Are there any limitations in using DBT for anxiety?
Like any therapy, DBT may not be the perfect solution for everyone with anxiety. Some individuals may find that other evidence-based approaches like CBT or exposure therapy better address their needs. Additionally, the intensive nature of DBT, often requiring regular sessions and commitment to practicing skills, may be challenging for some individuals. Nevertheless, the flexibility and adaptability of DBT make it an attractive option for addressing various anxiety-related concerns.
- 7 Ideas to Help You Relax and Unwind on a Family Vacation - April 27, 2025
- How Having Cybersecurity Protection Helps You Relax - April 25, 2025
- 8 Reasons Why Spending Time Outside Calms You Down - April 25, 2025
This site contains affiliate links to products. We will receive a commission for purchases made through these links.