As a BetterHelp affiliate, we receive compensation from BetterHelp if you purchase products or services through the links provided
Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) therapy has emerged as a promising option for patients with various mental health conditions. As a non-invasive brain stimulation treatment, TMS therapy uses magnetic fields to target specific brain regions linked to mental illnesses such as depression, anxiety, and others. With the rise in its popularity and recommendation by medical professionals, it is essential to analyze the pros and cons associated with its application.
Though TMS therapy has produced remarkable results for many patients, weighing the benefits and disadvantages cautiously is essential. While it proves advantageous over traditional treatments for some, others argue that its effectiveness and safety are yet to be fully explored. This article aims to comprehensively understand TMS therapy’s pros and cons to help individuals make informed decisions about their mental health treatment options.
Key Takeaways
- TMS therapy offers a non-invasive alternative for treating various mental health conditions.
- The procedure’s effectiveness and safety are still scrutinized, with mixed results among patients.
- Comparing TMS therapy to other treatments and considering insurance coverage are crucial factors in making an informed decision.

Understanding TMS Therapy
Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) therapy is a non-invasive technique to treat various mental health disorders, including depression and anxiety. It involves using magnetic fields to stimulate specific brain regions to improve functioning and alleviate symptoms.
TMS therapy is administered by placing a magnetic coil near the patient’s scalp, which generates a magnetic field that penetrates the skull and reaches the targeted brain areas. The magnetic field induces electrical currents in the brain, influencing the activity of neurons and potentially leading to symptom reduction.
One of the key advantages of TMS therapy is its non-invasive nature, which means that no surgery or anesthesia is required. This makes it suitable for patients who cannot tolerate or have not responded to more traditional treatments, such as medication or psychotherapy. Furthermore, TMS therapy has demonstrated a relatively low incidence of side effects, with most patients experiencing only mild discomfort during the procedure.
Despite its potential benefits, TMS therapy may not be suitable for everyone. Some individuals with certain medical conditions or implanted devices, such as pacemakers or deep brain stimulators, may be ineligible for treatment. Additionally, TMS therapy typically requires multiple sessions, which can be time-consuming and expensive.
In conclusion, TMS therapy offers a promising alternative to conventional treatments for certain mental health disorders. While it has its limitations, its non-invasive nature and demonstrated efficacy make it an important option for clinicians and patients to consider.

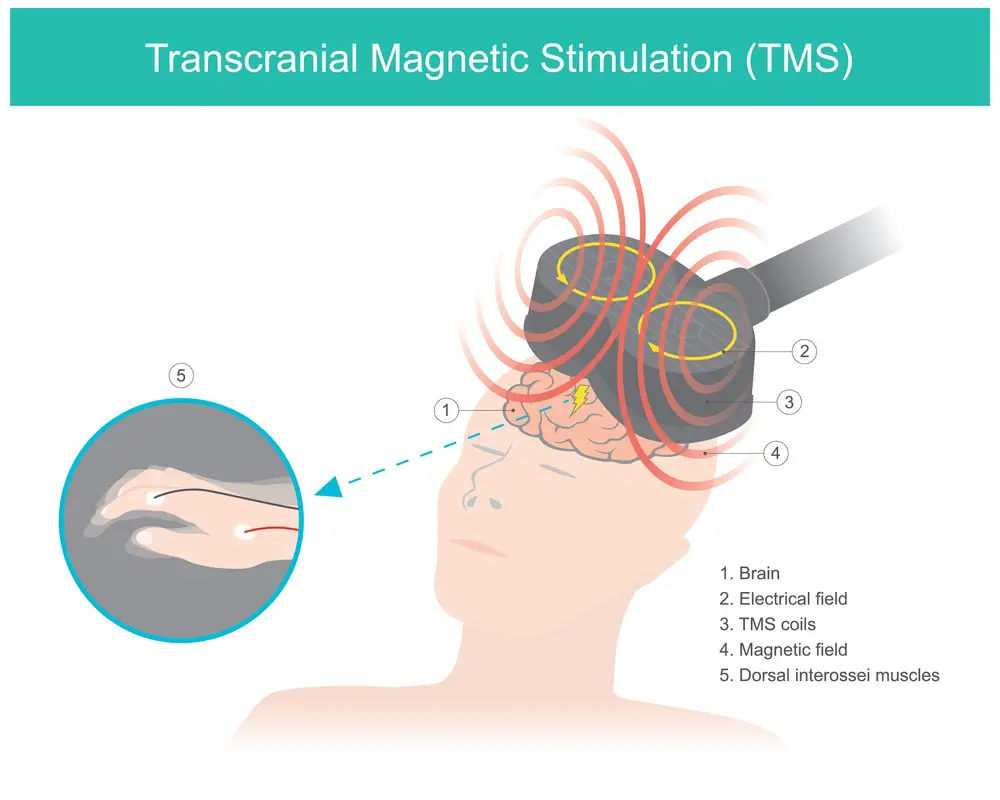
The procedure of TMS Therapy
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) therapy is a non-invasive procedure that uses magnetic fields to stimulate specific brain areas. The treatment begins with a TMS session where the patient is seated comfortably and awake. The scalp is prepared by cleaning the area and applying a conductive gel to facilitate the transmission of magnetic pulses.
During a session, a coil is placed against the scalp, generating magnetic fields that target specific brain regions. These magnetic pulses are painless and penetrate the skull to reach the brain tissues without surgery or radiation. There are various coils, each designed to target different brain areas effectively.
There are two primary TMS stimulation protocols: high-frequency TMS and low-frequency TMS. High-frequency TMS uses rapid pulses to excite brain activity, while low-frequency TMS employs slower pulses to inhibit brain activity. Another advanced protocol, theta burst stimulation (TBS), uses a more rapid stimulation pattern to achieve similar results within a shorter timeframe.
During treatment, the coil produces a series of brief, strong magnetic pulses that last only milliseconds. These magnetic fields induce electrical currents in the targeted brain regions, leading to physiological changes and improvements in symptoms for patients with various neurological and psychiatric conditions.
The number of TMS sessions required varies depending on the patient and the specific condition. Typically, a course of TMS therapy includes multiple sessions spread over several weeks to achieve the desired therapeutic effects. The duration and intensity of the magnetic pulses may also be adjusted throughout the treatment course as needed.
Throughout the TMS therapy process, patients can expect to be closely monitored by a medical professional to ensure the treatment is effective and well-tolerated.
Pros of TMS Therapy
TMS therapy, or transcranial magnetic stimulation, is a non-invasive treatment option for various mental health conditions, with numerous benefits. One of the primary advantages of TMS therapy is its effectiveness in treating treatment-resistant depression. Many patients who have not found relief from traditional antidepressant medications or other therapies have experienced significant improvements with TMS therapy.
The FDA has approved TMS therapy, lending credibility to its safety and efficacy. This approval means the treatment has undergone rigorous testing and research, with proven benefits for specific mental health conditions.
A high success rate is another benefit of TMS therapy. Patients who undergo this treatment often report substantial reductions in their depressive symptoms. Numerous studies have demonstrated the efficacy of TMS therapy for people struggling with depression, anxiety, and other mental health concerns.
Additionally, TMS therapy offers a non-invasive approach without the systemic side effects often associated with medications. Since the treatment targets specific areas in the brain using magnetic pulses, patients can avoid the unwanted side effects of antidepressant medications, such as weight gain, fatigue, or sexual dysfunction.
Overall, TMS therapy presents a promising option for individuals grappling with mental health concerns that have not responded well to traditional treatment methods. Its FDA approval, high success rate, and non-invasive nature make it a valuable alternative to consider in improving mental well-being.
Cons of TMS Therapy
TMS therapy is not without its drawbacks. One of the most common side effects of TMS therapy is the occurrence of headaches. Headaches can range from mild to moderate intensity and often subside as the treatment progresses. However, the headaches can persist for some individuals and be quite bothersome.
Another potential side effect is discomfort in the scalp area where the TMS coil is placed. This discomfort can range from a mild tingling sensation to a more pronounced, painful feeling. Sometimes, the sensation may lead to temporary twitching in the facial muscles or other nearby areas. While these side effects are generally mild and well-tolerated, they may cause some individuals distress or inconvenience during treatment.
Some patients might experience a worsening of their depression while undergoing TMS therapy. Although TMS is specifically designed to alleviate depressive symptoms, in rare instances, the treatment might not yield the desired results, and patients could experience a temporary worsening of their condition.
In conclusion, although TMS therapy has shown promising results in treating depression and other mental health conditions, it’s essential to consider the potential side effects and risks. Headaches, scalp discomfort, twitching, and the possibility of worsening depression might cause some individuals to hesitate in seeking this form of treatment. However, understanding and discussing the risks with a healthcare professional can help patients decide whether TMS therapy is right for them.
TMS Therapy vs. Other Treatments
TMS Therapy, or Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation, is a non-invasive treatment option for various mental health disorders, including depression. TMS Therapy works by using magnetic pulses to stimulate specific regions of the brain responsible for mood regulation.
Compared to other treatments, TMS Therapy has unique advantages and disadvantages. It does not involve any medications, avoiding the potential side effects commonly associated with antidepressants. Likewise, TMS Therapy does not require anesthesia or hospitalization, making it more accessible and less invasive than Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT).
Talk therapy and psychotherapy are non-pharmacological alternatives for treating mental health disorders. While these options may work well for some individuals, they can be time-consuming and require ongoing sessions to maintain effectiveness.
TMS Therapy may produce faster results than talk therapy and psychotherapy, with some patients improving within weeks of treatment. However, the effectiveness of TMS Therapy may vary from person to person, and in some cases, it may not be as effective as other treatment options.
When comparing TMS Therapy to ECT, it is worth noting that ECT has been around longer and is considered an effective treatment for severe depression. However, ECT involves inducing seizures in the patient under anesthesia, which carries risks and side effects. TMS Therapy, on the other hand, does not have these risks, making it a safer alternative for some patients.
In conclusion, TMS Therapy offers a unique treatment option that may be effective for individuals who cannot tolerate or have not succeeded with traditional treatments like antidepressants, talk therapy, or psychotherapy. However, it is important to consider individual factors and consult a healthcare professional to determine each patient’s best action.
Insurance Coverage and Cost
TMS Therapy, or Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation, is a non-invasive treatment for various mental health conditions such as depression and anxiety. It has shown promising results for many patients, but its accessibility can be limited due to insurance coverage and cost factors.
Many insurance companies now acknowledge the potential of TMS therapy as a viable treatment option, particularly for patients who have not responded well to traditional medications. As a result, they may offer coverage for the procedure. However, this coverage can vary greatly depending on the individual insurance plan. Some policies may fully cover TMS therapy, while others may only partially cover the costs or require prior authorization before they agree to cover any portion of the treatment.
The out-of-pocket costs for TMS therapy can be a significant barrier for some patients. The cost of the treatment can range from $6,000 to $12,000 or more, depending on the healthcare provider and the number of sessions required. This financial burden can add to the cons of TMS therapy, especially for those already struggling with the debilitating effects of a mental health condition.
Considering TMS therapy’s long-term benefits and potential savings when weighing the costs is essential. While the treatment can be expensive upfront, patients who respond positively to TMS may experience lasting relief from their symptoms, reducing or eliminating the need for ongoing medication and therapy expenses. Additionally, improved mental health can lead to increased productivity and overall well-being, further outweighing the initial investment in treatment.
In conclusion, insurance coverage and cost are important factors when exploring TMS therapy as a potential treatment option. Prospective patients should research their insurance policy’s specific coverage details, discuss potential financial assistance or payment plans with their healthcare provider, and carefully weigh the long-term benefits against the upfront costs before deciding.
Safety and Effectiveness of TMS Therapy
TMS Therapy, or Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation, is a non-invasive treatment for various mental health conditions. The FDA has approved TMS therapy for depression, obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
The safety of TMS therapy has been well-established in clinical trials. As a non-invasive procedure, it doesn’t require surgery or anesthesia, and patients can typically resume normal activities immediately after treatment. Some potential side effects may include mild headaches, muscle twitching, or lightheadedness. However, these effects tend to be short-lived and minimal. It’s important to note that TMS therapy isn’t safe for everyone, particularly those with implanted metallic devices, such as pacemakers or cochlear implants.
Regarding effectiveness, TMS therapy has shown promising results for many patients who have not responded adequately to other treatments, such as medication or therapy. Most patients experience significant improvement in their symptoms, and some even achieve full remission. However, it’s crucial to understand that not all patients respond to TMS therapy similarly, and some might not experience any improvement at all.
In conclusion, when appropriately administered to eligible patients, TMS therapy is a safe and effective treatment option for certain mental health conditions.
The Future of TMS Therapy
TMS therapy, or Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation, is a non-invasive procedure that has been gaining attention for its potential to treat various mental health disorders, such as depression and anxiety. As the body of research on TMS therapy grows, several pros and potential long-term results are becoming apparent.
One significant advantage of TMS therapy is its non-invasive nature. Unlike other treatments, such as electroconvulsive therapy (ECT), TMS does not require anesthesia or induce a seizure. This reduced invasiveness can lead to a faster recovery time and fewer side effects for patients, making it a desirable alternative for those seeking mental health treatment.
Recent advancements in the field suggest that accelerated TMS could become a game-changer. Accelerated TMS involves administering multiple treatment sessions in a single day, which can lead to a more rapid reduction in symptoms and, ultimately, shorter treatment durations. Researchers continue to study accelerated TMS’s effectiveness and safety, but initial results have been promising.
Despite these advantages, some concerns about the long-term results of TMS therapy remain. Most notably, the effectiveness of TMS therapy may not be as long-lasting as other treatments, with some patients requiring repeated sessions to maintain symptom relief. Future research will determine the ideal duration and frequency of TMS treatments for different patients and disorders.
In conclusion, the future of TMS therapy looks promising, with several pros and a growing body of research supporting its use. While questions about long-term results and accelerated TMS remain, advancements in the field will likely address these concerns as TMS therapy becomes a more widely-adopted mental health treatment option.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common side effects of TMS?
TMS therapy has relatively mild side effects. Patients might experience mild headaches, scalp discomfort, or minor pain at the treatment site. These side effects diminish after the first few sessions as the body adjusts to the treatment.
How effective is TMS for treating depression?
TMS is a proven therapy for treating depression, with numerous studies showing positive results. It has been demonstrated to be effective for patients who have not responded well to other treatments, such as medication or psychotherapy. However, it’s essential to note that individual responses can vary, and not every patient might experience the same level of relief.
Can TMS therapy help with anxiety?
While TMS is FDA-approved for treating depression, research exploring its effectiveness in anxiety treatment is ongoing. Some studies have shown promising results, indicating that it could be a potential treatment option. However, further research and larger-scale trials are needed to confirm these findings.
What are the risks associated with TMS treatment?
TMS therapy is generally considered safe, but like any medical procedure, some risks are involved. Rare side effects might include seizures, hearing loss, or changes in mood or cognition. Discussing the risks with your healthcare provider to make an informed decision is essential.
Who should not undergo TMS therapy?
Certain individuals should avoid TMS therapy, including people with metal implants near the head (e.g., cochlear implants, aneurysm clips), a history of seizures, or other neurologic disorders. Pregnant and nursing individuals should consult their healthcare providers before TMS therapy.
How long do the results of TMS therapy last?
The duration of TMS therapy’s effects can vary from person to person. Some patients experience long-lasting improvements; others might need maintenance sessions to sustain their results. Regular follow-up appointments with a healthcare provider are recommended to monitor progress and discuss the need for additional sessions if necessary.
- 7 Ideas to Help You Relax and Unwind on a Family Vacation - April 27, 2025
- How Having Cybersecurity Protection Helps You Relax - April 25, 2025
- 8 Reasons Why Spending Time Outside Calms You Down - April 25, 2025
This site contains affiliate links to products. We will receive a commission for purchases made through these links.