As a BetterHelp affiliate, we receive compensation from BetterHelp if you purchase products or services through the links provided
Dialectical behavior therapy (DBT) is a widely recognized treatment for individuals struggling with chronic and severe mental health conditions, including depression. Developed by Dr. Marsha Linehan in the 1980s, DBT was initially intended to help those with borderline personality disorder (BPD) manage their overwhelming emotions and self-destructive behaviors. However, due to its effectiveness, it has increasingly been applied to treating other mental health conditions, most notably depression.
Although depression affects millions worldwide, traditional therapies such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) may not be effective for everyone. This is where DBT comes in – it combines the valuable aspects of CBT with newer skills, such as mindfulness and distress tolerance. DBT focuses on helping individuals develop emotional regulation skills, interpersonal effectiveness, and a non-judgmental approach to their thoughts and feelings. By doing so, it provides a powerful framework to help individuals not only manage their depression but also move towards a healthier and more balanced life.
Key Takeaways
- DBT combines CBT with additional skills, such as mindfulness and distress tolerance, to address depression.
- Emotional regulation skills, interpersonal effectiveness, and non-judgmental thinking are key components of DBT.
- DBT has proven to be an effective method for managing chronic mental health conditions beyond its original application for BPD.
Understanding DBT for Depression
Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT) is a form of therapy developed by Marsha Linehan and is a cognitive-behavioral therapy. DBT was created to treat individuals with borderline personality disorder and suicidal thoughts, but research has found it effective in treating depression.
DBT incorporates elements from various therapeutic approaches, like cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), to help individuals better understand their thoughts, emotions, and behaviors. DBT aims to help those struggling with depression develop healthy coping mechanisms, improve their emotional regulation, and build a more satisfying life.
One of the key components of DBT is the concept of dialectics, which emphasizes the need to balance opposites to bring about change. For instance, a person might work on accepting their current emotional state while striving to change it. This balance between acceptance and change allows individuals to develop more effective strategies for managing their depression.
DBT for depression typically involves both individual therapy sessions and skills training group sessions. During individual sessions, therapists work with clients to explore the root causes of their depression and develop personalized strategies for improving their mental health. The skills training group sessions focus on teaching mindfulness, interpersonal effectiveness, emotional regulation, and distress tolerance skills. These skills allow individuals to understand better and manage their emotions, communicate effectively with others, and cope with difficult situations.
In recent years, more mental health professionals have started incorporating DBT as a treatment option for their clients with depression. Research has shown that DBT can significantly improve various aspects of an individual’s life, such as reducing symptoms of depression, decreasing suicidal thoughts, and improving the overall quality of life. As a result, DBT is becoming an increasingly popular and effective therapy option for those struggling with depression.

DBT Key Principles
Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT) is an evidence-based psychotherapy developed by Dr. Marsha Linehan for treating individuals with borderline personality disorder. It is now applied to other mental health conditions, including depression. Its key principles are based on a blend of acceptance and change strategies in a structured, supportive therapeutic environment. This approach aims to help individuals build skills to manage their emotions, enhance their relationships, and improve their overall quality of life.
Mindfulness is at the core of DBT and serves as a foundation for the other principles. It refers to being fully aware and present at the moment without judgment. Mindfulness helps individuals develop an objective and nonreactive perspective on their thoughts and emotions.
Another critical element of DBT is acceptance, which encourages individuals to recognize and accept their thoughts, feelings, and behaviors without judgment. This principle is closely tied to radical acceptance, which involves embracing the reality of a situation and acknowledging that it cannot be changed. By accepting what they cannot control, clients can shift their focus to aspects of their lives where they can make a difference.
Change is the counterpart to acceptance in DBT. While acceptance involves acknowledging the reality of thoughts, feelings, and behaviors, change emphasizes the need for individuals to develop healthier coping strategies and modify harmful behavior patterns. This balance between acceptance and change is essential in DBT, as it helps individuals navigate the complexities of their emotional experiences and work toward personal growth.
Tolerance is another key principle in DBT, specifically distress tolerance. This skill involves managing emotions and coping with challenging situations without engaging in destructive behaviors. Distress tolerance helps individuals build resilience and increase their ability to withstand inevitable emotional stressors.
In conclusion, DBT’s key principles of mindfulness, acceptance, change, and tolerance create a comprehensive and effective approach to addressing emotional dysregulation, improving interpersonal effectiveness, and enhancing overall mental health in individuals with various mental health disorders, including depression. By integrating these principles into their lives, clients can develop the emotional resilience and behavioral flexibility needed to create lasting, meaningful change.
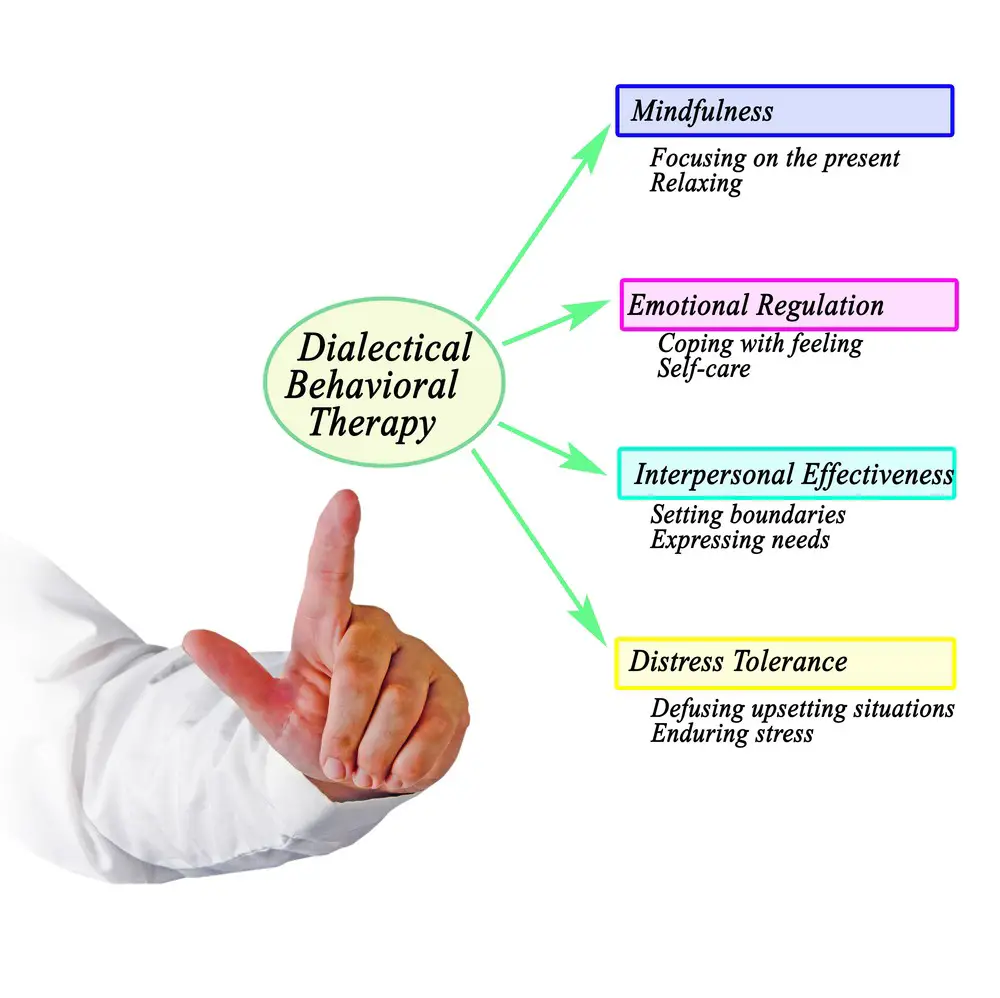
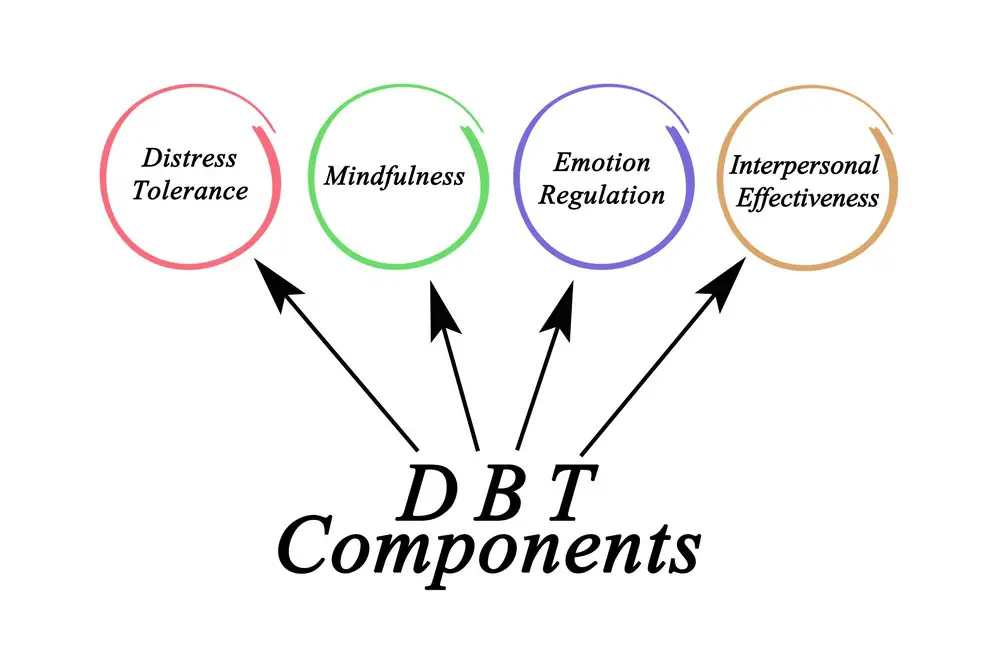
DBT Skills Modules
Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT) is an evidence-based treatment designed to help people suffering from various mental health conditions like depression. DBT incorporates four main skill modules: mindfulness skills, interpersonal effectiveness, emotion regulation, and distress tolerance. These modules teach individuals effective ways of dealing with emotions and life challenges.
Mindfulness skills are the foundation of DBT. These skills entail recognizing one’s thoughts, emotions, and physical sensations without judgment. Practicing mindfulness helps individuals remain present in the moment, enabling them to make better decisions and cope with distressing situations more effectively.
Interpersonal effectiveness focuses on building and maintaining healthy relationships through assertive communication. Developing assertive communication skills empowers an individual to express their feelings, opinions, and needs without guilt or fear of judgment and without violating the rights of others. This module also emphasizes setting boundaries and engaging in conflict resolution strategies.
Emotion regulation teaches individuals how to identify and understand their emotions and develop healthier coping methods. Essential skills in this module include recognizing emotional triggers, implementing self-soothing techniques, and developing effective strategies for problem-solving. Additionally, individuals learn to shift their emotional states through adaptive coping mechanisms, such as engaging in enjoyable activities or relaxation exercises.
Distress tolerance aims to help individuals manage and survive crises without resorting to harmful behaviors or emotional outbursts. This module introduces various techniques for tolerating distress, including distraction, self-soothing, and acceptance of reality. By building resilience and learning to cope with discomfort, individuals can face challenging situations head-on without succumbing to destructive urges or emotional spirals.
In summary, the DBT skills modules (mindfulness skills, interpersonal effectiveness, emotion regulation, and distress tolerance) serve as crucial tools for individuals struggling with depression and other mental health conditions. These modules provide practical methods for enhancing emotional well-being and overall quality of life.
Components of DBT
Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT) is a well-regarded treatment for various mental health conditions, including depression. It involves several components that work together to create a comprehensive, multi-faceted approach to therapy. These components include individual therapy, group therapy, phone coaching, consultation teams, and homework assignments.
Individual therapy is the cornerstone of DBT, focusing on addressing the patient’s specific needs and helping them apply the skills learned in group therapy to their daily lives. Sessions are typically held once a week, with the therapist and patient discussing issues and behavioral patterns that have arisen since the last meeting.
Group therapy is a valuable aspect of DBT for depression. It typically involves multiple participants and is led by a trained therapist. Sessions usually occur once a week and cover specific skills, such as mindfulness, emotion regulation, and interpersonal effectiveness. Patients can share their experiences, receive validation, and support each other’s progress in this setting.
Phone coaching is another essential component, allowing patients to seek support during emotional distress or crisis moments. This service is generally available outside therapy sessions and guides utilizing DBT skills to navigate difficult situations effectively.
The consultation team is a support system for therapists themselves. As DBT can be emotionally taxing for therapists, consultation teams comprise multiple mental health professionals with expertise in DBT. These teams meet regularly to review cases, share resources, and support each other in adhering to the model and maintaining therapeutic effectiveness.
Lastly, homework assignments are an integral part of DBT, allowing patients to apply and practice the skills they have learned during therapy sessions. Assignments can include journaling, self-monitoring, or behavioral experiments designed to test and reinforce the application of DBT techniques.
Together, these components make DBT a comprehensive approach to treating depression, providing various opportunities for patients to develop and practice essential coping skills while receiving support from therapists and peers.
Using DBT for Mental Health Conditions
Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT) is a well-established and effective treatment method for various mental health conditions. Originally developed for individuals with Borderline Personality Disorder (BPD), DBT has since been adapted to address various other mental health challenges, including eating disorders, substance use disorder, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), anxiety, and bipolar disorder.
DBT is grounded in the principles of cognitive behavioral therapy and incorporates mindfulness, emotional regulation, distress tolerance, and interpersonal effectiveness strategies. This unique blend of techniques encourages clients to develop new skills to improve their mental health and overall quality of life.
For individuals with borderline personality disorder (BPD), DBT is particularly effective. Studies have demonstrated that individuals who undergo DBT treatment for BPD experience fewer symptoms, reduced suicidal behaviors, and decreased hospitalizations compared to those receiving treatment as usual.
In eating disorders, DBT is valuable in helping individuals develop healthier coping mechanisms and reducing self-destructive behaviors such as bingeing and purging. This therapeutic approach has also shown promise in treating substance use disorder, as it offers individuals effective tools for managing cravings, developing healthy relationships, and building self-esteem.
Individuals experiencing post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) may also benefit from DBT. This therapy addresses the emotional dysregulation often experienced by those with PTSD and equips individuals with methods for managing flashbacks, intrusive thoughts, and avoidance.
DBT has effectively reduced symptoms and improved overall well-being for those struggling with anxiety. By teaching clients techniques for regulating their emotions, tolerating distress, and navigating interpersonal relationships, DBT can help individuals feel more secure and confident in social situations.
Though DBT was not initially designed to treat bipolar disorder, some individuals experiencing the condition have found the therapy useful in stabilizing their mood, enhancing emotional regulation, and improving interpersonal relationships. However, it is important to note that more research is needed to establish the efficacy of DBT for those with bipolar disorder.
In summary, DBT is a versatile treatment approach for various mental health conditions, including BPD, eating disorders, substance use disorders, PTSD, anxiety, and bipolar disorder. By incorporating a combination of cognitive behavioral therapy principles and mindfulness techniques, this therapy method has the potential to improve mental health outcomes for many individuals significantly.
DBT Benefits and Effectiveness
Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT) has demonstrated significant benefits for individuals with depression. One of the primary advantages of DBT is the ability to help individuals regulate their emotions effectively. This aids in reducing extreme emotional fluctuations, allowing for better control and management of difficult feelings.
Another benefit of DBT is its focus on improving relationships. DBT therapists help clients build and maintain healthier connections by teaching effective communication techniques and fostering empathy. This can lead to improved support systems and a decrease in conflicts.
Additionally, DBT emphasizes developing practical skills that enhance the quality of life. These skills include mindfulness, distress tolerance, and emotion regulation, which equip individuals to handle challenging situations more easily. As a result, those undergoing DBT may experience increased happiness and a more fulfilling life.
In conclusion, DBT offers several benefits for those dealing with depression. By addressing the need for emotional regulation, relationship-building, and life-enhancing skills, DBT can significantly impact an individual’s overall well-being and recovery from depression.

DBT Techniques and Strategies
Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT) is an evidence-based treatment approach for various mental health concerns, including depression. DBT focuses on developing coping skills, managing distressing emotions, and promoting conscious behavior.
One essential aspect of DBT is radical acceptance. This strategy encourages individuals to acknowledge their emotions, thoughts, and experiences without judgment. By accepting the reality of a situation, individuals can begin to make more effective and balanced decisions.
Moreover, DBT teaches various coping skills. These skills, grouped into four categories, include mindfulness, interpersonal effectiveness, emotional regulation, and distress tolerance. Mindfulness practices help individuals stay present, enhancing their ability to concentrate and manage emotions. Interpersonal effectiveness skills involve building assertiveness, setting boundaries, and communicating more effectively. Emotional regulation skills focus on understanding, labeling, and changing emotions when necessary. Distress tolerance skills aim to reduce the intensity of distressing emotions in challenging situations.
Another key strategy in DBT is to improve the moment. This technique guides individuals to use cognitive, behavioral, and environmental interventions to make the situation more tolerable. Examples include visualization, engaging in pleasurable activities, and changing one’s surroundings. These short-term strategies help individuals manage distressing emotions and regain composure in difficult moments.
In summary, DBT offers comprehensive techniques and strategies to foster conscious behavior, enhance coping skills, promote radical acceptance, improve the moment, and manage distressing emotions. These skills and strategies synergistically help individuals with depression navigate life more effectively and work toward recovery.
Challenges and Obstacles in DBT
Individuals undergoing Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT) for depression may face several challenges and obstacles. DBT is specifically designed to help manage negative emotions, but there are some inherent difficulties that patients and therapists may need to address.
One of the primary challenges in DBT is working through the discomfort that often arises when confronting intensely negative emotions. Patients need to learn how to tolerate and cope with them without resorting to self-destructive behaviors. The urge to resort to self-harm, self-injury, or suicidal behavior can be overwhelming at times, making it difficult for patients to fully engage and benefit from the therapy process.
Another obstacle arises from the inherent complexity of DBT as a treatment modality. The therapy consists of four main components: mindfulness, interpersonal effectiveness, emotion regulation, and distress tolerance. Patients may need time and patience to become proficient in each skill, which could challenge both the individual undergoing treatment and their therapist.
The success of DBT often rests on a strong collaborative relationship between the patient and therapist. Establishing trust and openness can be difficult, especially when discussing deeply personal topics and addressing self-destructive behaviors. The process takes time and requires a level of vulnerability from the patient, which can be challenging to achieve and maintain.
Even when patients begin to progress in their therapy sessions, maintaining this progress in their daily lives can be challenging. Integrating new skills and habits in everyday life is crucial for long-term recovery. Still, it can be hard for patients to transition from the controlled environment of therapy sessions to the often chaotic circumstances of daily life. This may include implementing coping mechanisms to avoid self-destructive behaviors and effectively managing negative emotions as they arise.
In conclusion, while DBT is an effective treatment option for individuals struggling with depression, various challenges and obstacles may arise during therapy. Addressing these difficulties is a vital aspect of the therapeutic process, and both patients and therapists must work together to overcome them to achieve a successful recovery.
Adapting DBT for Different Formats
Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT) for depression can be adapted to various formats to accommodate different needs and preferences. One popular adaptation is online therapy, which allows clients to access DBT resources and sessions through video conferencing, chat rooms, or phone calls. This digital approach enables individuals in remote locations or those with limited mobility to receive therapy and engage in their healing journey.
Core mindfulness, a fundamental component of DBT, aims to develop nonjudgmental awareness of the present moment, thoughts, and emotions. In online therapy, clients can practice these skills using guided audio or video recordings or interactive apps. This involvement increases the accessibility of core mindfulness techniques and empowers individuals to practice at their pace and convenience.
For group skills training, clients usually participate in weekly sessions focused on learning specific DBT skills. In adapting to online platforms, groups might convene through video conferences or within dedicated forums. This arrangement ensures the essential support and collaboration between group members remain intact while accommodating varying schedules and locations.
Traditional talk therapy can be incorporated into DBT by offering one-on-one sessions with a therapist, either in person or online. The therapist helps the client address daily life issues, applying DBT skills to real-life situations to improve emotional regulation. Such sessions can be conducted through video conferencing or phone calls, maintaining the effectiveness of talk therapy even in a remote setting.
Lastly, DBT skills training can be adapted to different formats using printed manuals, videos, or audio recordings. Both therapists and clients can access these materials to reinforce DBT principles when they cannot attend traditional face-to-face sessions. This flexibility enhances learning and allows individuals to work on their skills consistently.
Overall, the adaptability and accessibility of DBT for depression across different formats ensure that individuals can efficiently practice these critical skills, irrespective of their circumstances or geographical constraints.
Real-Life Application of DBT Skills
Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT) has proven effective in helping people manage depression symptoms and numerous other mental health challenges. The core concepts of DBT can be easily integrated into day-to-day life to help individuals better cope with stress, improve their emotional regulation skills, and enhance their social skills.
Firstly, emotion regulation skills are critical in maintaining emotional stability and reducing depressive symptoms. DBT emphasizes recognizing, understanding, and accepting one’s feelings. By practicing techniques such as mindfulness meditation, individuals can become more aware of their emotions and better equipped to handle them healthily. People can also implement coping strategies like distraction, self-soothing activities, and problem-solving to handle distressing emotions.
In addition to emotional regulation, DBT highlights the value of effective social skills. Active listening is one vital skill taught in DBT to improve interpersonal relationships. By practicing active listening, individuals can better understand the perspectives of others, avoid miscommunications, and manage conflicting opinions constructively. Moreover, DBT encourages the development of assertiveness, which helps people express their needs and boundaries without harming relationships.
Lastly, DBT offers numerous tools to help individuals cope with stress. Mindfulness, distress tolerance, and self-compassion assist people in dealing with crises and day-to-day stressors. Such skills enable them to recognize and accept challenging moments without becoming overwhelmed, increasing resilience and mental well-being.
Overall, the integration of DBT skills into daily life can lead to significant improvements in one’s ability to manage depression and navigate the challenges of life with greater competence and confidence.
Knowing When to Seek DBT
Dialectical Behavioral Therapy (DBT) can effectively treat individuals struggling with emotional distress and depressive symptoms. Knowing when to seek DBT can significantly impact mental well-being and recovery.
DBT focuses on improving emotional regulation skills, which can benefit individuals experiencing Major Depressive Disorder or Bipolar Disorder. It is crucial to consider DBT as a treatment option when traditional therapies may not have provided satisfactory results or when the emotional challenges seem overwhelming.
Some signs indicating the need for DBT include persistent sadness, hopelessness, or worthlessness and difficulties in managing emotions. These issues may manifest as impulsive behaviors, self-harm tendencies, suicidal thoughts, or difficulty maintaining relationships.
In cases of Bipolar Disorder, DBT can be particularly helpful in addressing rapid mood shifts and extreme emotional states, leading to distressing and disruptive behaviors. Similarly, for Major Depressive Disorder, DBT can provide the much-needed emotional regulation skills to help individuals navigate through prolonged periods of low mood and anhedonia.
Consultation with a mental health professional is essential to determine if DBT is the right treatment choice. They can assess the severity of your depressive symptoms and emotional distress, evaluate your coping strategies, and recommend the most suitable therapeutic approach. Remember to be honest about your needs and concerns, as this information can significantly impact treatment.
In conclusion, recognizing the need for DBT is the first step toward achieving greater emotional stability and overall mental wellness. By targeting emotional regulation skills, DBT has the potential to significantly improve the lives of those struggling with depression and emotional distress.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can DBT be used to treat depression?
Yes, Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT) can treat depression. It is effective in reducing depressive symptoms and improving overall functioning in individuals struggling with depression.
Is DBT evidence-based for depression?
DBT is an evidence-based treatment for many mental health conditions, including depression. Numerous studies have demonstrated the efficacy of DBT in reducing depressive symptoms and improving overall well-being.
When is DBT not appropriate?
DBT may not be appropriate for individuals who are experiencing psychotic symptoms or those with severe cognitive impairments. It is important to consult a mental health professional to discuss personal concerns and determine the most appropriate treatment.
Is CBT or DBT better for depression?
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) and Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT) can be effective treatments for depression. The choice between the two depends on the individual’s needs and symptoms. Some individuals may benefit more from the emphasis on mindfulness and emotion regulation in DBT, while others might find greater success with the problem-solving focus of CBT.
How is DBT different from other therapies?
DBT is unique in its focus on the balance of acceptance and change. It incorporates skills training in four areas: mindfulness, emotion regulation, interpersonal effectiveness, and distress tolerance. This comprehensive approach helps individuals develop the tools to manage their emotions, build healthier relationships, and tolerate distress more effectively.
What are the key components of DBT?
The key components of DBT include individual therapy, group skills training, phone coaching, and therapist consultation. These components work together to provide support and guidance, ensuring individuals have the necessary resources to develop and practice their skills effectively.
- Breaking the Silence: Why Men’s Mental Health Matters More Than Ever - April 15, 2025
- How to Transform a Home’s Patio Space into a Relaxing Space - March 23, 2025
- 5 Strategies to Use a Cell Phone to Help Manage Your Stress - March 23, 2025
This site contains affiliate links to products. We will receive a commission for purchases made through these links.