As a BetterHelp affiliate, we receive compensation from BetterHelp if you purchase products or services through the links provided
Depression is a common but serious mental health condition affecting millions worldwide. It can manifest in various ways, including persistent sadness, hopelessness, and a lack of interest in daily activities. Seeking treatment is essential for those with depression, as it can significantly improve their quality of life and overall well-being. Outpatient depression treatment is one such option, offering flexibility and tailored support for individuals as they navigate their mental health journey.
Outpatient treatment for depression allows individuals to receive therapy, medication management, and other services while living at home and maintaining their daily routines. This type of care provides a less restrictive environment than inpatient programs, making it a suitable choice for many individuals with mild to moderate depression who may not require round-the-clock care. Outpatient care also benefits those stepping down from inpatient programs or supplementing their ongoing treatment plan with additional support.
Key Takeaways
- Outpatient depression treatment offers flexible support for individuals with mild to moderate depression, allowing them to receive care while maintaining daily routines.
- In outpatient settings, various therapeutic approaches are available, including medication management and non-conventional therapies.
- Factors to consider when seeking outpatient depression treatment include insurance coverage, treatment locations, and the mental health professionals involved.

Understanding Outpatient Depression Treatment
Outpatient depression treatment offers a convenient and effective approach to managing mental health concerns. Patients can continue living at home while attending scheduled therapy sessions, allowing them to maintain regular life activities. This treatment program caters to individuals with moderate depression or those who have completed inpatient care and require ongoing support.
Types of Outpatient Treatment
Several types of outpatient treatment options are available to address patients’ diverse needs. Key therapies include:
- Individual Therapy: This one-on-one therapy addresses personal challenges and develops coping strategies. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is a popular choice for individual therapy, as it teaches patients to recognize and reframe negative thought patterns, improving mood and behavior.
- Group Therapy: This approach involves individuals working together in a therapeutic setting, sharing experiences and providing mutual support. Group therapy can enhance individual therapy by offering a sense of connection and normalizing the struggles associated with depression.
- Psychoeducation: This treatment option equips patients with the knowledge and tools to understand their mental health condition better. Psychoeducation can empower individuals to take control of their recovery through self-help techniques and resources.
- Mindfulness-Based Cognitive Therapy (MBCT): By combining aspects of both mindfulness and cognitive therapies, MBCT helps patients develop skills to combat negative thought patterns related to depression. This therapy is particularly helpful in preventing relapses in those with treatment-resistant depression.
When choosing an outpatient treatment program, it’s essential to consider each patient’s unique needs and preferences. The right combination of therapy modalities can lead to effective management of depression symptoms, ultimately improving overall mental health and well-being.
 Depression Diagnosis
Depression Diagnosis
Depression diagnosis begins with a thorough assessment by a mental health professional, such as a psychiatrist or psychologist, with the expertise to identify and treat mood disorders accurately. The evaluation typically includes exploring the individual’s thoughts, feelings, and behaviors to determine if they meet the criteria for a depressive disorder.
A psychiatrist may diagnose an individual with persistent depressive disorder if they experience symptoms continuously for at least two years. Additionally, severe depression may warrant a more urgent intervention, especially if the person has suicidal thoughts or tendencies.
When evaluating a patient for depression, mental health professionals assess several factors, such as sleep disturbances, appetite changes, and cognitive shifts. They also explore feelings of hopelessness, irritability, and difficulties in concentration.
In some cases, younger patients may benefit from a specialized approach. For example, a pediatric mood clinic can offer targeted support for children and adolescents experiencing depressive symptoms. By examining a comprehensive range of factors, mental health experts can ensure that patients receive the most appropriate diagnosis and treatment plan.
See our article, Understanding the Clinical Definition of Depression, for more in-depth information about diagnosing this condition.
 Therapeutic Approaches in Outpatient Settings
Therapeutic Approaches in Outpatient Settings
Outpatient depression treatment involves a range of therapeutic approaches that aim to address the patient’s needs and support mental health improvement. One can find behavioral therapy, cognitive therapy, and various talk therapy options among the most common outpatient treatments.
Behavioral therapy modifies negative behaviors and teaches new coping mechanisms to manage depression symptoms. It is an effective treatment option because it helps patients understand the relationship between their feelings, thoughts, and actions.
Cognitive therapy, on the other hand, addresses negative thought patterns that may contribute to the development and persistence of depression. By challenging these thoughts, patients can develop healthier and more adaptive thinking patterns, ultimately improving their mood.
Talk therapy approaches, such as individual, group, and family therapy, allow patients to express their feelings and thoughts in a supportive and non-judgmental environment. Sharing experiences with others in similar situations can offer valuable insights and encouragement.
Many outpatient treatment programs also include prescription antidepressants, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs). These medications work by increasing neurotransmitters in the brain, which can help alleviate symptoms of depression. Following the prescribed treatment and consult with the healthcare provider before changing the medication regimen is essential.
In addition to the approaches, as mentioned earlier, alternative and creative therapy options may be effective for some individuals. For instance, art therapy allows patients to explore and express their emotions through various artistic mediums, contributing to emotional healing. Equine therapy involves engaging with horses in a therapeutic setting and can improve patients’ emotional well-being, communication skills, and self-awareness. Finally, dance therapy uses movement to encourage emotional expression, enhance self-esteem, and promote social interaction which, in turn, can help alleviate depressive symptoms.
Each therapeutic approach in outpatient settings is tailored to the unique needs of the patient, offering a comprehensive yet flexible, treatment plan. By combining various therapies and interventions, patients can work towards improved mental health and a better quality of life.
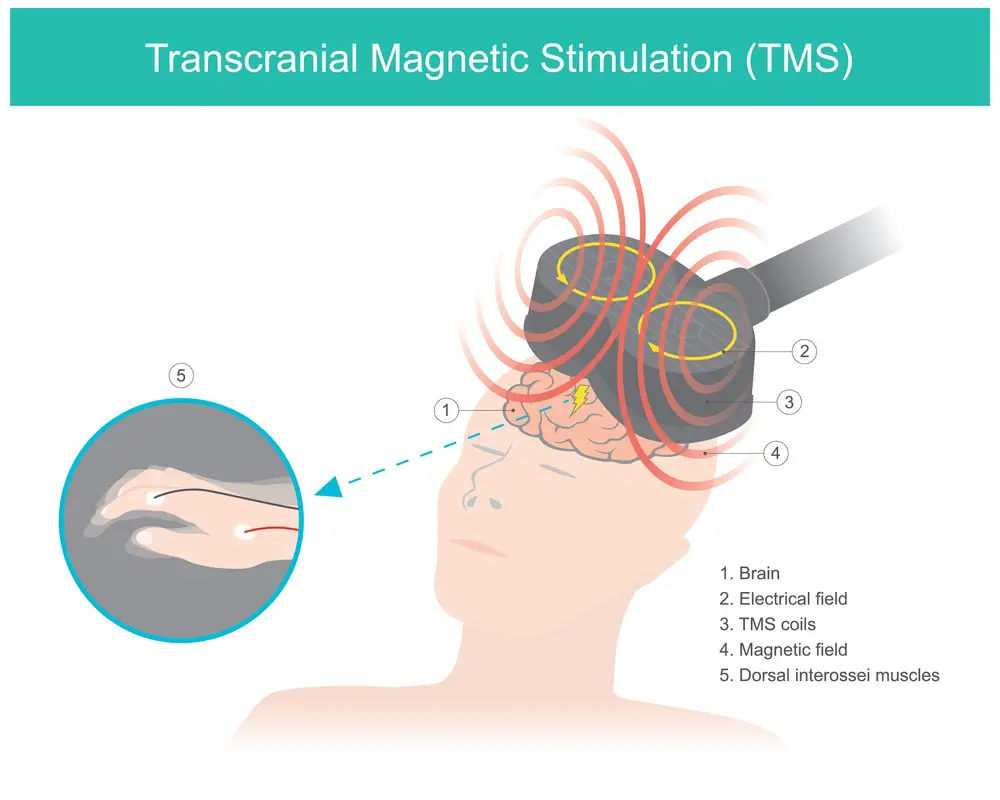
Non-Conventional Therapies
Outpatient depression treatment often incorporates a variety of non-conventional therapies, which may be used as adjuncts to traditional psychotherapy or pharmacological interventions. These alternative approaches include transcranial magnetic stimulation, mindfulness, meditation, yoga, and behavioral activation.
Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) is a promising non-invasive brain stimulation treatment that uses magnetic fields to stimulate specific brain areas. TMS is effective when conventional treatments are not successful or suitable. The treatment typically involves several sessions for weeks, with few side effects reported.
One of the most widely-recognized alternative approaches is mindfulness, which emphasizes being present and fully aware of thoughts, feelings, and bodily sensations, without judgment. This practice has been shown to reduce depressive symptoms, stress, and anxiety in some individuals. Various forms of meditation, such as mindfulness-based stress reduction (MBSR) and mindfulness-based cognitive therapy (MBCT), have been developed to incorporate mindfulness principles into structured programs.
Yoga is another non-conventional therapy that has been found to benefit individuals with depression. This ancient practice combines physical postures, breathing techniques, and meditation to promote relaxation and mental well-being. Yoga practitioners often report improvements in mood, stress levels, and overall quality of life.
Behavioral activation is a therapeutic approach that focuses on helping individuals with depression increase engagement in rewarding activities. The premise of behavioral activation is that by increasing the frequency and range of positive experiences, individuals can counteract the negative thoughts and behaviors contributing to depressive symptoms. This therapy is typically provided in a structured format with specific goals and objectives.
In summary, non-conventional therapies can play an important role in the outpatient treatment of depression. These approaches offer alternative or complementary options to traditional interventions and may help individuals experiencing varying depressive symptoms. While the effectiveness of these therapies may vary depending on the individual, incorporating a combination of treatments tailored to the person’s unique needs can often lead to improved mental health outcomes.
Inpatient vs Outpatient Treatment
Inpatient treatment and outpatient treatment are two common approaches to addressing depression. Inpatient depression treatment typically occurs in a hospital or residential program and requires patients to stay on-site for a specified duration. This type of care would involve more intensive therapy, including individual and group counseling, and may be necessary for those struggling with severe depression.
Outpatient treatment, on the other hand, allows patients to maintain their daily routines while receiving therapy at a clinic or day program. This approach usually involves regular therapy sessions, with the patient returning home daily. One notable outpatient treatment option is partial hospitalization, which provides more intensive therapy than a standard outpatient program but does not require an overnight stay.
The main differences between inpatient and outpatient treatment lie in the intensity of care and the level of disruption to the patient’s daily life. Inpatient treatment generally provides more comprehensive and structured support, while outpatient options offer greater flexibility and independence.
When considering the best course of action for individuals facing depression, it’s crucial to evaluate the severity of their symptoms and the level of support they require. Healthcare professionals can guide in choosing the most appropriate treatment plan based on each patient’s unique needs and circumstances.
 Mental Health Professionals Involved
Mental Health Professionals Involved
In outpatient depression treatment, patients can access a diverse team of mental health professionals. This multidisciplinary approach aims to provide comprehensive care and support tailored to each individual’s needs.
Therapists play a significant role in the treatment of depression. They are licensed professionals trained to provide various forms of therapy, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), interpersonal therapy (IPT), and dialectical behavior therapy (DBT). Therapists help patients identify and change negative thought patterns, develop coping strategies, and improve communication skills.
Psychiatrists are medical doctors specializing in psychiatry, the branch of medicine focused on diagnosing, treating, and preventing mental illnesses. They are responsible for evaluating and diagnosing depression and may prescribe medication to help manage symptoms. Psychiatrists work closely with other mental health professionals, such as therapists and psychologists, to ensure a patient receives comprehensive care.
Psychologists also play a critical role in treating depression. They have a doctorate in psychology and are trained to provide various forms of therapy. As experts in human behavior, psychologists can help patients with depression by assessing their mental health, providing treatment recommendations, and coordinating with other mental health professionals on the patient’s care team.
Nurses are essential members of the mental health care team, particularly those with specialized training in psychiatric nursing. They may help administer medications, monitor side effects, and provide support and education to patients and families about depression and its treatment.
The Department of Psychiatry and Psychology typically oversees outpatient depression treatment programs. This department includes professionals from diverse healthcare fields, working together to implement evidence-based therapies and support services to promote patients’ well-being.
In conclusion, outpatient depression treatment involves a dedicated team of mental health professionals, each playing a distinct role in providing comprehensive and individualized care. These professionals work together to address the various aspects of depression, ensuring patients receive the best possible support on their path to recovery.
 Considering Insurance and Costs
Considering Insurance and Costs
When exploring outpatient depression treatment options, it’s important to consider the role of insurance and the associated costs. Insurance companies often offer coverage for mental health services, including therapy and medication management. Understanding the extent of your insurance coverage is crucial in determining which outpatient services are accessible.
Review your specific insurance policy to determine what mental health services are covered. These include individual or group therapy, psychiatry appointments, and medication management. Also, consider any requirements your insurance provider might have, such as obtaining prior authorization or utilizing in-network providers. This information can often be found in your insurance policy details or by contacting your provider directly.
Once you understand your coverage, you must know the costs of outpatient depression treatment. Some factors to consider include:
- Copays: Many insurance plans require copayments for services such as therapy or psychiatry appointments. These out-of-pocket charges can vary depending on your specific insurance plan.
- Deductibles: Depending on your plan, you may need to meet a certain deductible before your insurance begins to cover mental health services. This is the amount you must pay before being reimbursed by your insurance.
- Out-of-Pocket Maximums: Insurance plans may also have out-of-pocket maximums, representing the most you’ll have to pay for covered services in a calendar year. Once you reach your out-of-pocket maximum, your insurance may cover all additional expenses after that point.
- Out-of-Network Providers: If you choose to see a mental health professional who is not in your insurance network, you may still be covered but at a lower rate. This can result in higher out-of-pocket costs for you.
- Sliding-Scale Fees: Some outpatient depression treatment providers offer sliding-scale fees, which can help reduce the cost of care for those without insurance or with limited financial resources. This can be an important factor to explore if your insurance coverage is limited or you’re concerned about the financial aspects of ongoing treatment.
Remember that each individual’s situation will differ, so gathering all relevant information and weighing your options carefully is important. By being well-informed about your insurance and the costs associated with outpatient depression treatment, you can make the best decision for your mental health and financial situation.
 Potential Complications
Potential Complications
Outpatient depression treatment can be an effective course of action; however, it is important to acknowledge potential complications that may arise during the process. Individuals with co-occurring disorders or additional mental health challenges may face unique hurdles while undergoing outpatient treatment.
Substance use can significantly impact the effectiveness of depression treatment. Patients with depression and a co-occurring substance use disorder may require specialized, integrated care to address both issues simultaneously. Integrating substance abuse treatment into depression therapy can enhance the likelihood of successful outcomes, but those with severe addiction may require inpatient care first.
Patients undergoing outpatient treatment should be educated on relapse prevention strategies for both depression and any other potential disorders they may be managing. Relapse rates can be high for people with mood disorders, and a comprehensive understanding of triggers, warning signs, and coping skills is crucial to maintaining progress.
Outpatient depression treatment should also be mindful of patients with co-occurring diagnoses such as schizophrenia or obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD). In these cases, therapy and medications should be tailored to address the unique requirements of each individual and manage the complexities of treating two or more disorders simultaneously.
Cyclothymic disorder is another unique challenge in outpatient depression treatments. This milder form of bipolar disorder requires careful monitoring, and treatment often includes mood stabilizers alongside depression medications and therapy. Outpatient care providers must be attentive to mood fluctuations and potential triggers indicating a shift to manic or depressive states.
Additionally, outpatient depression treatment should consider the presence of eating disorders in individuals seeking support. Eating disorders and depression have complex relationships, and concurrent treatment demands the consideration of therapists experienced in both areas.
Lastly, individuals with a history of trauma may have unique needs during outpatient depression treatment. Therapists must balance addressing the depressive symptoms and triggers stemming from the traumatic events with appropriate sensitivity and techniques, such as trauma-focused cognitive behavioral therapy (TF-CBT), to avoid retraumatization.
Overall, outpatient depression treatment providers must navigate the complexities and potential complications when working with individuals with co-occurring disorders or additional mental health challenges. By carefully considering these factors, patients can benefit from effective outpatient therapy while minimizing potential risks.
Available Treatment Locations
There are several locations where patients can receive outpatient depression treatment. Notable treatment centers exist across various states in the United States.
The Mayo Clinic has multiple campuses providing outpatient depression treatment services. With locations in Arizona, Florida, and Minnesota, the Mayo Clinic is well-equipped to offer comprehensive and tailored treatment plans for patients suffering from depression. Their renowned expertise and dedication to research make them a reliable choice for those seeking outpatient treatment.
The Mayo Clinic Depression Center is a nationally recognized treatment center specializing in diagnosing and treating depression and mood disorders. This facility primarily focuses on providing patients with evidence-based depression treatments designed to be effective and safe. They employ skilled multidisciplinary teams, including psychiatrists, psychologists, and other mental health professionals, to ensure each patient receives optimized care.
In addition to the Mayo Clinic facilities, numerous other treatment centers are scattered around the country, providing inpatient and outpatient services. These centers may offer a variety of therapy approaches, medication management, support groups, and other resources for patients and their families. Patients must thoroughly research the available locations and choose one that meets their needs.
Access to outpatient depression treatment may vary depending on the location. Some areas may have more limited options than others, making it essential for patients to explore their region’s available services and resources. By doing so, they can find a suitable and accessible facility to support their recovery journey.
Frequently Asked Questions
 What is the most effective intervention for depression?
What is the most effective intervention for depression?
The most effective intervention for depression varies from person to person. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), Interpersonal Therapy (IPT), and medication management can be effective interventions. A mental health professional will match the intervention to the individual’s needs.
What type of treatment is used for depression?
Depression treatment typically involves a combination of psychotherapy and medication. The specific treatment plan depends on the severity and type of depression and the individual’s needs and preferences.
How does an IOP work for depression?
An Intensive Outpatient Program (IOP) for depression provides structured, evidence-based therapy in a group setting. IOP clients attend therapy sessions multiple times per week while still being able to maintain work or school commitments. This type of treatment is ideal for those needing more support than traditional outpatient therapy.
Which therapy options are available for outpatient depression treatment?
Outpatient depression treatment may include individual psychotherapy, group therapy, and family therapy. Evidence-based approaches, such as Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT), and Interpersonal Therapy (IPT) are commonly used in outpatient settings.
Are medication and psychotherapy combined for outpatient treatment?
Yes, medication and psychotherapy can be combined for outpatient depression treatment. This combination is often more effective than either treatment alone. A psychiatrist prescribes and monitors medication, while a psychologist or therapist provides psychotherapy.
How long does outpatient treatment typically last for depression?
The duration of outpatient treatment for depression varies depending on the individual’s needs and progress. Some people may require only a few months of therapy, while others may need ongoing treatment for a year or longer. Regular assessments by the treatment team help determine the appropriate duration of care.
Jacob Maslow: Navigating Mental Health Through Experience and Advocacy
Jacob Maslow is a beacon for those journeying through the complex corridors of mental health. An advocate of Lexapro for its restorative effects on his well-being, Jacob’s credentials aren’t just academic; they are sculpted from the clay of personal experience. As a seasoned therapy participant, he possesses a unique perspective on the intricacies of depression and the shadowy realm of narcissism—much of this knowledge originating from a heart-wrenching legal confrontation with an ex-partner. This battle, characterized by a sorrowful detachment from his children and unceasing breaches of court-ordered custody, paints a vivid backdrop for his writings.
Outside the tumults of the legal realm, Jacob seeks refuge and clarity in his daily ritualistic long walks. These introspective journeys act as a cathartic release and a muse for his insightful articles. Through his work, he aims to illuminate the paths for those struggling with mental health and narcissistic relationships, underscoring the belief in the human spirit’s resilience.
Complementing his mental health advocacy, Jacob also runs a dedicated legal platform. Here, he lends a hand to those ensnared in the legal quagmire due to defiant spouses, emphasizing the essence of co-parenting, mental well-being, and the right to shared guardianship.
- 7 Ideas to Help You Relax and Unwind on a Family Vacation - April 27, 2025
- How Having Cybersecurity Protection Helps You Relax - April 25, 2025
- 8 Reasons Why Spending Time Outside Calms You Down - April 25, 2025
This site contains affiliate links to products. We will receive a commission for purchases made through these links.


 Depression Diagnosis
Depression Diagnosis Therapeutic Approaches in Outpatient Settings
Therapeutic Approaches in Outpatient Settings Mental Health Professionals Involved
Mental Health Professionals Involved Considering Insurance and Costs
Considering Insurance and Costs Potential Complications
Potential Complications What is the most effective intervention for depression?
What is the most effective intervention for depression?
