As a BetterHelp affiliate, we receive compensation from BetterHelp if you purchase products or services through the links provided
Nighttime depression, a mood disorder, affects many individuals as the sun sets and darkness envelops the surroundings. It presents a unique set of challenges for those who experience it, and understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatments can help alleviate the weight of this debilitating condition. For some, this depressive state can exacerbate existing mental health issues, while others may find it emerging alongside an otherwise stable emotional state.
As one delves into the intricacies of nighttime depression, it becomes apparent that biological, environmental, and lifestyle factors contribute to it. Addressing these components through tailored treatments and interventions can lead to successful management over time. Living with nighttime depression requires patience, support, and appropriate self-care strategies to minimize its impact, assisting affected individuals in leading fulfilling lives.
Key Takeaways
- Nighttime depression is a unique mood disorder that requires understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatments.
- Biological, environmental, and lifestyle factors contribute to the condition, making tailored treatment essential.
- Proper self-care strategies, support, and patience are vital for managing nighttime depression and leading a fulfilling life.
 Understanding Nighttime Depression
Understanding Nighttime Depression
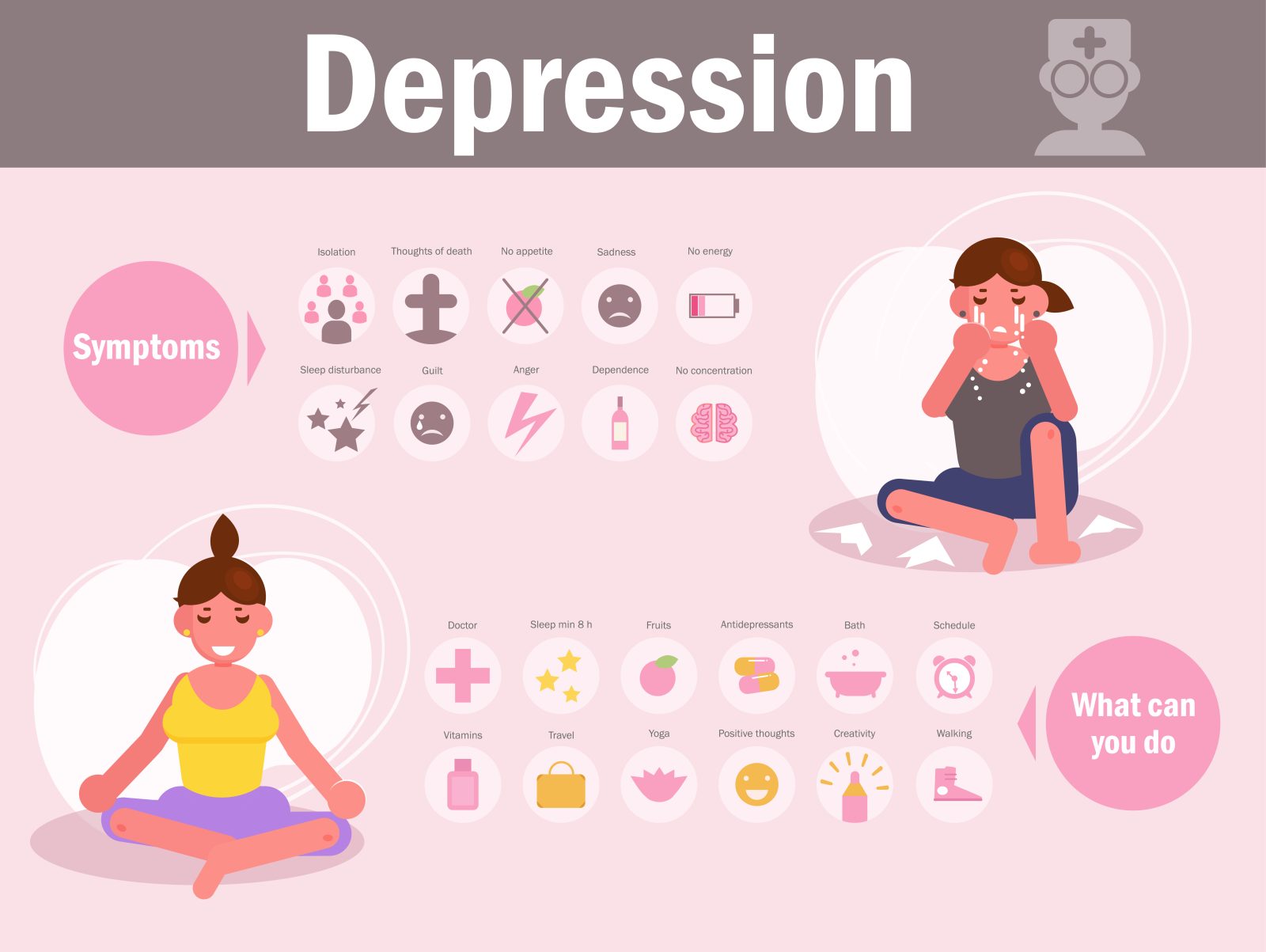
Nighttime depression, also known as nocturnal depression, is a mood disorder that affects individuals during the night hours. It shares many similarities with major depression, but the symptoms primarily occur during the evening and nighttime.
People experiencing nighttime depression may struggle with low mood, irritability, and isolation during the night. These emotions can intensify as the evening progresses, increasing feelings of emptiness and guilt. It is essential to understand that nighttime depression is not a separate disorder but a subset of major depression with a specific time-related symptom pattern.
Some factors might contribute to the worsening of depressive symptoms at night. These may include changes in natural light exposure, disrupted sleep patterns, or reduced social interactions during the evening hours. It is crucial for individuals grappling with nighttime depression to seek professional help, as proper diagnosis and treatment can significantly improve their quality of life.
In conclusion, nighttime depression is a manifestation of major depression that primarily affects individuals during the night hours. The disorder is characterized by low mood, irritability, feelings of isolation, emptiness, and guilt during the evening and nighttime. Understanding nighttime depression is vital for seeking appropriate treatment and support to alleviate its debilitating effects on the individual’s mental health and overall well-being.
 The Science Behind Nighttime Depression
The Science Behind Nighttime Depression
Several factors contribute to the development and persistence of nighttime depression, including biological processes, genetics, and physical health conditions.
One significant factor behind nighttime depression is the disruption of the circadian rhythm. The circadian rhythm is an internal biological clock that regulates the sleep-wake cycle. It is responsible for maintaining a balance between periods of wakefulness and rest, which is crucial for mental and physical well-being. A disrupted circadian rhythm can lead to difficulties falling asleep, staying asleep, or waking up, which might exacerbate depressive symptoms.
The production of melatonin, a hormone that plays a crucial role in regulating the sleep-wake cycle, is another essential aspect of nighttime depression. Melatonin levels naturally rise in the evening, helping the body prepare for sleep. However, exposure to artificial light and irregular sleep patterns might interfere with melatonin production, making it harder for the individual to fall asleep or maintain a stable mood at night.
Genetics may also play a role in the development of nighttime depression. Research suggests that certain genetic variations might predispose some individuals to depression and influence their vulnerability to circadian rhythm disruptions. A family history of depression and sleep disorders may indicate a person’s susceptibility to nighttime depression.
Some physical health conditions have been linked to nighttime depression. For example, chronic pain, sleep apnea, and restless legs syndrome might cause sleep disturbances, contributing to depressive symptoms at night. Individuals with compromised immune systems or hormonal imbalances might also find their mood and mental health adversely affected during nighttime hours.
In conclusion, nighttime depression is a complex condition influenced by circadian rhythm, melatonin production, genetics, and physical health conditions. Understanding the science behind nighttime depression can help develop effective treatment strategies and promote better mental health.

Effects of Nighttime Depression
Nighttime depression can significantly impact an individual’s mental and physical well-being. One of the primary effects of this condition is sleep disturbance. People who experience nighttime depression often suffer from insomnia or poor sleep quality, which can exacerbate their feelings of sadness, anxiety, or irritability.
On the other hand, some individuals with nighttime depression may experience hypersomnia or excessive sleeping. This can lead to persistent fatigue and lack of energy throughout the day, making it difficult for them to engage in regular activities and maintain a healthy lifestyle.
Prolonged nighttime depression can also contribute to physical pain. The combination of poor sleep and increased stress levels can manifest as tension headaches, muscular aches, or even joint pain in some cases. This chronic pain can further impede an individual’s ability to perform daily tasks and maintain a sense of well-being.
Cognitive function is another aspect negatively affected by nighttime depression. Difficulty concentrating and memory issues can arise due to the constant mental strain caused by this condition. The lack of restorative sleep often compromises brain functions like decision-making and critical thinking.
Low self-esteem is a common emotional consequence of nighttime depression. The constant feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and irritability can lead to a negative self-image, further aggravating the depression and creating a cycle of self-doubt and emotional pain.
In severe cases, nighttime depression can lead to suicidal thoughts. The intense feelings of hopelessness and isolation that often accompany this condition can make individuals feel as though they have no other options, and suicide may seem like the only escape from the persistent emotional pain.
Aging can interact with nighttime depression in several ways. Older adults, who may already be experiencing changes in sleep patterns as part of the natural aging process, may find their sleep difficulties exacerbated by nighttime depression. Additionally, the physiological changes associated with aging can amplify the physical pain and cognitive dysfunction experienced by those with nighttime depression.
In summary, the effects of nighttime depression are wide-ranging and can significantly impact an individual’s mental, emotional, and physical well-being. Sleep disturbances, physical pain, cognitive difficulties, and emotional turmoil are all factors that can contribute to the overall burden of nighttime depression.

Lifestyle Factors Influencing Nighttime Depression
Stress and anxiety are prevalent factors that can contribute to nighttime depression. Busy lifestyles, work responsibilities, and personal conflicts can lead to an increase in stress levels, which in turn, exacerbate depressive symptoms at night when the mind has time to ruminate on these issues.
The environment in which an individual spends their evenings can also play a significant role in nighttime depression. Factors such as bright lights or exposure to bright screens on electronic devices before bedtime can interfere with melatonin production, which is crucial for a healthy sleep cycle. It is essential to create a calming and comforting atmosphere in the bedroom to promote relaxation and better sleep quality.
Physical health is another factor that can influence nighttime depression. A lack of regular exercise, poor nutrition, and inadequate sleep can contribute to feelings of depression and low mood. Engaging in regular physical activity, maintaining a balanced diet, and prioritizing sleep can help improve mental health and reduce the risk of nighttime depression.
Substance abuse, particularly the consumption of alcohol and caffeine, can also play a role in nighttime depression. Alcohol may temporarily relieve depressive symptoms but can disrupt sleep patterns and increase depression in the long run. On the other hand, caffeine is a stimulant that can make falling asleep more challenging and may contribute to feelings of anxiety or restlessness.
Lastly, family history should be considered when examining the potential causes of nighttime depression. Individuals with a family history of depression or mood disorders may be more susceptible to experiencing these symptoms at night due to genetic predispositions.
In conclusion, lifestyle factors such as stress, anxiety, environment, physical health, substance abuse, and family history can all contribute to nighttime depression. To minimize the impact of these factors on mental health, individuals should aim to maintain a healthy lifestyle, limit exposure to bright screens and stimulants before bedtime, and seek professional help if needed.
 Screening and Diagnosis of Nighttime Depression
Screening and Diagnosis of Nighttime Depression
When diagnosing nighttime depression, it is essential to identify the symptoms and differentiate them from other mental health conditions. Nighttime depression is characterized by diurnal mood variation, which means the individual’s mood changes based on the time of day. Typically, individuals with nighttime depression experience a significant worsening of symptoms in the evening, improving in the morning.
To make an accurate diagnosis, mental health professionals, specifically psychiatrists, extensively evaluate the symptoms of depression exhibited by the individual. Some common symptoms of depression include:
- Persistent sadness or feelings of hopelessness
- Loss of interest in activities once enjoyed
- Difficulty sleeping or oversleeping
- Changes in appetite or weight
- Fatigue or lack of energy
- Difficulty concentrating or making decisions
- Thoughts of death or suicide
Screening of nighttime depression typically begins with a thorough assessment of the individual’s daily mood fluctuations. Health professionals may ask patients to track their moods or complete questionnaires to provide insight into their emotional state during different times of the day.
When diagnosing this condition, mental health professionals should rule out any potential medical causes of mood fluctuations. In some cases, physical ailments or medications can contribute to developing symptoms mimicking those of nighttime depression.
Once potential medical causes have been ruled out, a psychiatric evaluation can help to confirm the diagnosis of nighttime depression. Psychiatrists might use standardized tests, such as the Hamilton Depression Rating Scale (HDRS), which includes items focusing on diurnal mood variation and sleep disturbances, to determine the severity of nighttime depression and tailor an appropriate treatment plan.
Early identification and intervention are crucial in treating nighttime depression, as it shares many symptoms with other mental health conditions. A correct diagnosis is vital for developing an effective treatment plan tailored to the individual’s unique needs and improving their overall well-being.

Treatments and Interventions
Nighttime depression can be effectively managed through a variety of treatments and interventions. One common approach is the use of medications such as antidepressants. Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs) and Serotonin-Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors (SNRIs) are two types of antidepressants that can help regulate the chemicals in the brain responsible for mood.
In addition to medication, psychological therapies can be beneficial in addressing nighttime depression. For instance, Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is a well-established form of psychotherapy that helps individuals identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors. Through CBT, a person with nighttime depression can learn effective coping strategies for dealing with rumination and other sleep-disruptive thoughts.
Distractions can also be useful in mitigating the effects of nighttime depression. Calming activities such as reading, meditation, or deep breathing exercises before bedtime could help establish a more positive and relaxing bedtime routine.
Moreover, a comprehensive treatment plan that addresses the particular needs of each individual is crucial for effectively managing nighttime depression. This may involve a combination of therapy, medication, and lifestyle changes. Online therapy options have also become increasingly popular and accessible, allowing those affected by nighttime depression to receive support and guidance from the comfort of their own homes.
Ultimately, finding the most appropriate treatment and interventions for nighttime depression is essential for improving overall well-being and sleep quality. A healthcare professional can work with each person to determine the best course of action that aligns with their needs and preferences.
 Self-Care Strategies for Nighttime Depression
Self-Care Strategies for Nighttime Depression
Nighttime depression can make it challenging for individuals to unwind and have a restful night. Incorporating self-care strategies is an essential step in addressing these difficulties. Here are some self-help strategies to improve rest and overall well-being during the night.
Create a nurturing environment: Ensuring one’s bedroom is relaxing, quiet, and cool is crucial. Maintaining a comfortable room temperature and removing distractions can help create an ideal environment conducive to rest and recharge.
Establish a sleep-inducing routine: Adopting a consistent bedtime routine benefits those experiencing nighttime depression. Activities like reading a book, practicing mindfulness meditation, or engaging in gentle yoga stretches can signal the body and mind that it’s time to unwind and prepare for sleep.
Stay active during the day: Incorporating exercise and physical activities can promote better sleep and mood regulation at night. Regular aerobic exercises, such as walking, jogging, or swimming, can positively affect mood and help combat symptoms of depression.
Pay attention to meals and timing: Eating well-balanced meals and being mindful of the timing can impact one’s sleep quality. It’s recommended to avoid heavy meals or stimulants like caffeine or alcohol too close to bedtime. Opt for lighter dinners, and consider establishing a cut-off time for eating to prevent sleep difficulties.
Take short, rejuvenating naps: Naps can be a restorative break during the day, but keeping them brief is crucial. Limit naps to 20-30 minutes in the early afternoon to prevent interference with nighttime sleep patterns.
Monitor sleep hygiene: Those with sleep apnea or other sleep-related disturbances should seek professional help to address these issues. Proper management of sleep disorders is critical for maintaining overall physical and emotional health and alleviating nighttime depression.
These self-help strategies can significantly improve one’s ability to cope with nighttime depression and promote restorative sleep. Prioritizing self-care is essential to managing this mental health concern effectively and achieving overall well-being.

Living With Nighttime Depression
Living with nighttime depression can be challenging and affect daily life. Understanding the factors contributing to this condition and exploring potential coping strategies to promote mental and emotional well-being is vital.
One of the factors that may influence nighttime depression is the disruption of a person’s natural sleep-wake cycle. This can lead to disturbances in mood and may exacerbate feelings of loneliness. By establishing a consistent sleep routine and environment conducive to rest, individuals may be able to mitigate these challenges.
Mental health professionals often recognize that chronic stress can intensify symptoms of nighttime depression. Individuals should be encouraged to identify sources of stress in their daily lives and implement strategies to manage and reduce these stressors effectively. This might include incorporating relaxation techniques such as meditation, engaging in regular physical activity, or seeking professional support from a therapist.
Genetics may play a role in an individual’s susceptibility to nighttime depression and other factors such as heart disease or a history of trauma. Understanding one’s unique risk factors can provide a foundation for a tailored mental health care plan.
Substance abuse is another potential contributing factor to nighttime depression. Individuals who abuse drugs or alcohol may experience an increased vulnerability to depressive symptoms, particularly at night when substance use is often most prevalent. Addressing substance abuse through counseling, support groups, and rehabilitation can lead to an overall improvement in emotional well-being.
A lack of sunlight, especially during Winter, can influence mood and contribute to nighttime depression. Exposure to natural sunlight during the day or utilizing light therapy products can help regulate mood and improve overall mental health.
In summary, living with nighttime depression requires individuals to be aware of various factors that may contribute to their condition. Individuals can work on strategies that promote a healthier emotional state by understanding the role of genetics, addressing substance abuse, and considering their daily routines.
Frequently Asked Questions

What causes evening sadness?
Evening sadness can be caused by multiple factors, including exhaustion from daily activities, hormonal imbalances, or the body’s natural response to darkness. Identifying and addressing the specific triggers for each individual experiencing this issue is important.
How can I cope with nighttime anxiety?
Coping with nighttime anxiety can involve establishing a calming evening routine, practicing relaxation techniques such as deep breathing or meditation, and seeking professional help if necessary. Regular exercise and a healthy diet can also help alleviate anxiety symptoms.
Are there any treatments for nocturnal depression?
Treatments for nocturnal depression may include therapy, medication, and lifestyle changes. Seeking professional help to diagnose and address the underlying causes of this condition is crucial. Implementing a consistent sleep schedule and engaging in activities that promote relaxation can also help.
Why do my emotions worsen during the evening?
Emotions may worsen in the evening due to the body’s natural circadian rhythm, feelings of loneliness, or increased negative thoughts. Identifying the factors contributing to increased emotional strain is the first step in addressing this issue and developing coping strategies.
Is there a connection between sleep and mood?
There is a strong connection between sleep and mood. Poor sleep can contribute to increased irritability, stress, and depression. Conversely, healthy sleep patterns can promote emotional stability and improved overall mental health.
How can I establish a healthy nighttime routine?
Establishing a healthy nighttime routine involves identifying activities that promote relaxation, such as reading or taking a warm bath. Limiting exposure to screens, creating a comfortable sleep environment, and maintaining a consistent sleep schedule can also encourage better rest and emotional well-being.
About the Author: Jacob Maslow
Embarking on a deeply personal journey through mental health, I’ve come to understand the shadows that can envelop our minds, especially when night falls. Relying on Lexapro to navigate the complexities of my emotional well-being, I stand as a testament to the healing power of therapy, having sought its refuge throughout various phases of my life.
My narrative has been further punctuated by a heart-wrenching battle for love and connection with my two children. Facing an ex-partner entrenched in narcissistic behaviors, our once harmonious relationship with our kids is now shadowed by relentless court battles, alienation, and withheld communication, a painful testament to the lengths some will go to weaponize innocent lives.
Each day, I find solace in my long, introspective walks – moments that allow me to breathe, reflect, and reset. Drawing from these experiences, I’ve committed myself to guiding others through the labyrinth of mental health and narcissistic relationships via my writings. It’s my mission to light the way for those feeling lost in the dark, emphasizing that mental health challenges can be conquered with resilience and support.
In addition, my legal platform offers hope and assistance to those struggling with non-compliance with court orders in family matters, providing resources and insights from someone who has walked in those very shoes. I firmly believe we can emerge stronger and more enlightened with knowledge and perseverance through every challenge.
- 3 Ways Wearing a Hat Can Help Lower Your Stress Levels - April 19, 2025
- Breaking the Silence: Why Men’s Mental Health Matters More Than Ever - April 15, 2025
- How to Transform a Home’s Patio Space into a Relaxing Space - March 23, 2025
This site contains affiliate links to products. We will receive a commission for purchases made through these links.


 Understanding Nighttime Depression
Understanding Nighttime Depression The Science Behind Nighttime Depression
The Science Behind Nighttime Depression Screening and Diagnosis of Nighttime Depression
Screening and Diagnosis of Nighttime Depression Self-Care Strategies for Nighttime Depression
Self-Care Strategies for Nighttime Depression
