As a BetterHelp affiliate, we receive compensation from BetterHelp if you purchase products or services through the links provided
Dialectical behavior therapy (DBT) is a specialized form of cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), designed to help individuals manage intense emotions, relationships, and stressors in their lives. Developed in the late 1980s by Dr. Marsha Linehan, DBT was initially used to treat individuals with borderline personality disorder and chronically suicidal patients. It has expanded to address a wider range of mental health conditions, including anxiety disorders, ADHD, and OCD.
DBT comprises six main points, grounded in the foundational concepts of cognitive behavioral therapy. These points aim to help patients develop new thinking and behavioral skills, fostering personal growth and improved emotional regulation. Acceptance of one’s current circumstances, mindfulness, interpersonal effectiveness, and distress tolerance are key elements of DBT, and trained therapists use these concepts to encourage positive change in their clients’ lives.
Key Takeaways
- Dialectical behavior therapy is a form of cognitive behavioral therapy, designed to help individuals manage intense emotions and improve relationships.
- Originally developed to treat borderline personality disorder, DBT is now used for various mental health conditions such as anxiety disorders, ADHD, and OCD.
- DBT consists of six main points focusing on acceptance, mindfulness, interpersonal effectiveness, and distress tolerance to promote emotional regulation and positive behavioral change.
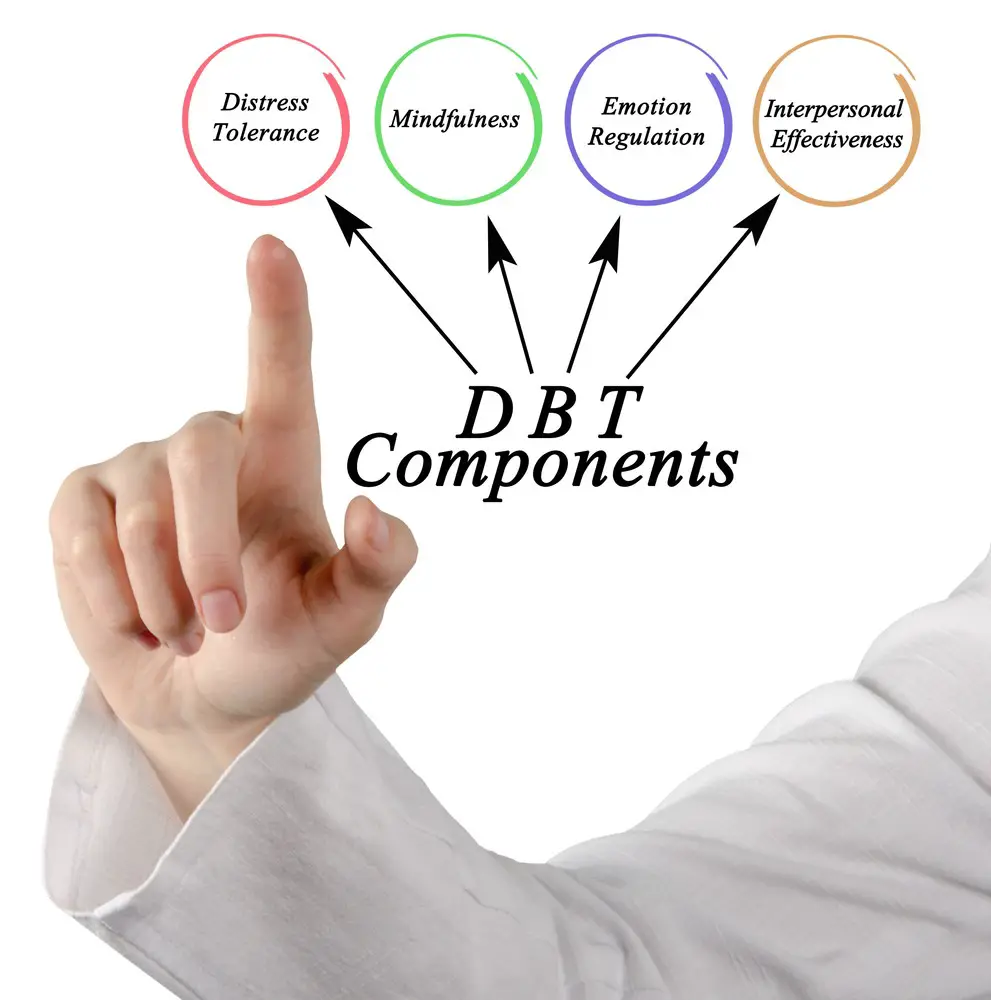
 The Six Main Points of Dialectical Behavior Therapy
The Six Main Points of Dialectical Behavior Therapy
Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT) is a type of cognitive behavioral therapy developed by psychologist Marsha M. Linehan. It focuses on helping you live in the moment, cope with stress, regulate emotions, and improve relationships with others. The six main points of DBT encompass various techniques and strategies, providing a comprehensive approach to addressing several mental health issues. Let’s explore the six key elements of DBT that you need to know.
1. Mindfulness skills: Mindfulness involves being fully present in the moment, without judgment. Practicing mindfulness lets you observe your thoughts, feelings, and sensations without reacting impulsively. This awareness allows you to be more objective in your daily life and helps you to dampen emotional responses when facing challenging situations.
2. Emotion regulation: Developing a better understanding of your emotions and their triggers is a critical aspect of DBT. You’ll learn to discern between appropriate and inappropriate emotional responses, which helps create balance in your daily life. Strategies like opposite action, PLEASE skills, and self-soothing can be employed to manage emotions more effectively.
3. Distress tolerance: DBT teaches you to tolerate distressing emotions without resorting to destructive behaviors like self-harm or substance abuse. By utilizing techniques such as distraction, self-soothing, and radical acceptance, you’ll become better equipped to handle uncomfortable situations and emotional pain in a healthy, constructive way.
4. Interpersonal effectiveness: Healthy relationships are essential for emotional well-being, and DBT focuses on tools for improving communication and maintaining self-respect while interacting with others. Skills like assertiveness, active listening, and setting boundaries are emphasized, helping you build stronger connections and easily navigate difficult social situations.
5. Acceptance and change: DBT balances accepting your current circumstances and initiating the change necessary for personal growth. This concept emphasizes the importance of accepting thoughts, feelings, and experiences while working on strategies to change negative patterns and behaviors.
6. Change: The ultimate goal of DBT is to bring about positive transformation in your life. Applying the above concepts will foster a healthier mindset and greater control in managing your emotions, reactions, and relationships. Developing new thinking and behavioral skills will enable you to adapt and respond to challenges more effectively.
Remember that DBT is a journey aimed at building resilience, fostering personal growth, and enabling you to navigate the complexities of life with greater confidence and stability.
 Core Concepts and Techniques
Core Concepts and Techniques
Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT) focuses on six main points to help you develop new thinking patterns and behavioral skills. These core concepts and techniques work together to enable you to navigate life’s challenges better.
Mindfulness is a cornerstone of DBT, where you’ll learn to live in the present moment without judgment. By practicing mindfulness, you can become more aware of your thoughts, emotions, and surroundings, enabling you to make more conscious decisions and develop healthier ways to cope with stress.
Emotional regulation equips you with tools to effectively manage intense emotions such as anger, anxiety, and sadness. By understanding and accepting your emotions, you can work towards diminishing negative emotional episodes and develop strategies to handle emotional situations in a balanced manner.
Distress tolerance is another crucial aspect of DBT. You’ll acquire skills to tolerate and accept painful situations or emotions without resorting to unhealthy behaviors. Techniques may include distraction, self-soothing, and acceptance, helping you handle stress more adaptively and maintain balance.
Interpersonal effectiveness emphasizes enhancing your communication and relationship-building abilities. This point covers assertiveness, setting boundaries, and dealing with conflict effectively, ultimately fostering deeper connections and better understanding with others.
In DBT, individual therapy assists you in applying these newly learned skills to personal challenges. Your therapist will help you recognize harmful behaviors and thought patterns, replacing them with more adaptive alternatives.
Group therapy, an essential element of DBT, provides a supportive environment where you can practice skills and share your experiences. By engaging with others, you’ll receive feedback, gain insights into other perspectives, and build a sense of camaraderie.
As you apply these core concepts and techniques of DBT, you’re actively working towards regulating your emotions, improving your interpersonal relationships, and finding balance in your life.
 Role of the Therapist
Role of the Therapist
As a DBT therapist, you are crucial in helping patients develop the skills to manage their emotions and behaviors more effectively. One of your key responsibilities involves providing support and understanding, essential in creating a safe and trusting environment for your patients.
In addition to support, you’ll focus on skills training to help individuals learn new ways of coping with difficult situations. As a trained psychologist, it’s crucial for you to not only be knowledgeable in DBT techniques but also to be able to adapt them to suit each individual’s needs.
While engaging in one-on-one therapy sessions, you’ll help your patients identify, modify, and practice new behaviors to replace maladaptive thoughts and actions. You can also employ additional techniques like phone coaching, which provides them access to direct support during crises, bridging the gap between sessions.
Another significant aspect of your role is participating in consultation meetings with fellow therapists. These consultations allow you to discuss your patients’ progress, gain insights, and receive feedback on your performance and strategies. Such collaborations ensure that you remain effective and up-to-date in your practice.
Remember that as a DBT therapist, you play a pivotal role in helping your patients navigate the complexities of their emotions and behaviors. Supporting them, imparting skills training, utilizing consultation meetings, and providing phone coaching are all essential components in offering effective and compassionate care.
Key Takeaway: Your role as a DBT therapist involves support, understanding, skills training, consultation, and phone coaching, all of which contribute to helping patients manage their emotions and behaviors more effectively.
Dialectical Behavior Therapy vs. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy
Regarding addressing mental health concerns, two therapeutic approaches are often compared: Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT) and Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT). Understanding the key distinctions between the two can help you decide which therapy might be more suitable for your needs.
In a nutshell, CBT primarily focuses on identifying and modifying negative thought patterns and behaviors to improve a person’s emotional well-being. Some key aspects of CBT include:
- Challenging negative thought processes
- Promoting relaxation and calming techniques
- Encouraging confrontation of fears
- Teaching healthy coping skills
- Boosting self-confidence and self-esteem
On the other hand, DBT was developed as a specialized form of CBT to primarily address individuals with borderline personality disorder, suicidal tendencies, or self-harming behaviors. However, it has also proven effective for other mental health issues. DBT emphasizes the following six main points:
- Mindfulness skills: Enhancing your present-moment awareness, non-judgment, and focus
- Distress tolerance: Developing techniques to cope with emotional pain and crises
- Emotion regulation: Identifying and managing intense emotions more effectively
- Interpersonal effectiveness: Improving communication, assertiveness, and relationship skills
- Change: Embracing personal growth and behavior modification
- Acceptance: Practicing self-compassion, accepting reality, and reducing self-judgment
The core difference between these two therapies lies in their emphasis: CBT primarily deals with a cognitive and behavioral focus, while DBT incorporates dialectic, meaning it strives to find a balance between acceptance and change. DBT also emphasizes skill-building and group therapy components more than CBT.
Consider your specific needs and goals to determine which therapy is best for you. CBT might be a suitable choice if you primarily struggle with negative thoughts and behaviors. However, if you suffer from more severe emotional dysregulation and interpersonal challenges, DBT could be the better option.
Remember, consulting with a mental health professional to discuss your concerns and get their guidance on the most appropriate treatment for your unique situation is wise.
Targeted Symptoms and Disorders
Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT) targets various mental health conditions, each with its unique set of symptoms. Understanding the disorders that DBT aims to alleviate can give you a deeper understanding of this therapy. Some key mental health conditions treated by DBT include:
- Borderline Personality Disorder (BPD): A mental health disorder characterized by unstable moods, disruptive behaviors, and interpersonal relationships.
- Depression: Intense sadness, hopelessness, and a lack of interest in daily activities.
- Anxiety Disorders: Persistent and excessive worry, fear, and nervousness that interfere with everyday life.
- Eating Disorders: Unhealthy and harmful relationships with food, such as Anorexia Nervosa, Bulimia Nervosa, and Binge Eating Disorder.
- Substance Use Disorders: Addiction to drugs and alcohol, including abuse and dependency issues.
- Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD): Prolonged psychological distress triggered by experiencing or witnessing traumatic events.
- Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD): Difficulty focusing, paying attention, and controlling impulsive behavior, which can negatively impact daily functioning.
- Bipolar Disorder: Extreme mood swings that range from episodes of mania (high energy and irrational behavior) to periods of depression.
DBT techniques are designed to equip you with skills to help you manage these symptoms and improve your overall mental health. For instance, DBT’s mindfulness practices can help you become more aware of your thoughts and emotions. Often, gaining this awareness is the first step towards managing your mental health condition effectively.
Moreover, DBT’s emotion regulation techniques can help you better understand and manage your feelings and emotions so they don’t disrupt your life. For example, the “distract” technique in DBT helps you shift your attention away from negative thoughts and feelings, giving you a break from emotional pain and allowing you to refocus on healthier thought patterns.
Remember that DBT is not a one-size-fits-all approach and may be ineffective for everyone. However, it may benefit those struggling with self-harm, suicidal behavior, and other severe mental health challenges. DBT aims to promote better emotional regulation, interpersonal effectiveness, and mental health management by addressing multiple symptoms and disorders.
Therapy Tools and Techniques
Dialectical behavior therapy (DBT) offers various tools and techniques to help you improve your emotional, mental, and interpersonal well-being. Below are some of these valuable components:
- Diary & Diary Card: DBT often includes keeping a diary or using diary cards to monitor and track your emotions, coping mechanisms, and progress throughout therapy. Recording your experiences can help you identify patterns and work towards effective solutions.
- Homework Assignments: Your therapist may provide assignments designed to help you practice DBT skills and techniques, such as mindfulness or emotional regulation, in your daily life. Completing these tasks can help reinforce your learning and empower you to apply new skills to real-life situations.
- Group Skills Training: DBT often involves group sessions where you learn and practice skills alongside others. This setting fosters interpersonal connections and allows you to receive support from others with similar challenges.
- Mindfulness & Living in the Moment: One key component of DBT is developing mindfulness skills to help you focus on the present moment. Practicing this skill daily can gradually reduce emotional suffering and increase self-awareness.
- Emotional Regulation & Coping Skills: DBT equips you with techniques to recognize, label, and validate your emotions. Through understanding and acceptance, you can develop healthier coping skills and reduce the impact of intense emotions.
- Distress Tolerance & Radical Acceptance: To navigate stressful situations, DBT teaches strategies, such as radical acceptance, which involves accepting reality and adverse circumstances you cannot change. This approach can help you manage crises and lessen emotional distress.
- Interpersonal Effectiveness: DBT helps you build assertiveness and communication skills to enhance relationships and make your needs heard. By cultivating these abilities, you can foster healthy connections and maintain boundaries.
Integrating these tools and techniques into your life takes time and practice. Be patient with yourself and trust the process as you gradually incorporate these valuable skills into your daily routine.
Effectiveness and Outcomes
Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT) has been recognized as an effective treatment for various mental health conditions such as Borderline Personality Disorder, self-harm, suicidal behavior, Post-traumatic Stress Disorder, Substance Use Disorder, eating disorders, depression, and anxiety. This therapy aims to help you improve your quality of life by teaching key skills to manage and regulate your emotions.
Notably, some of the benefits of DBT include:
- Emotional Regulation: DBT helps you better understand and manage your emotions, reducing negative emotions and increasing positive emotions. This can result in an overall improvement in self-esteem and decreased feelings of shame.
- Mindfulness: Learning to live in the moment and focus on the present allows you to develop a healthier relationship with your thoughts and emotions. This skill enhances self-awareness and helps to reduce intense emotional reactions.
- Distress Tolerance: DBT teaches you coping techniques to handle overwhelming situations and distressing emotions effectively. By building your tolerance to distress, you’ll be better equipped to face challenges constructively.
- Interpersonal Effectiveness: This skill focuses on improving your relationships with others by teaching you to communicate effectively, set boundaries, and manage conflict. As a result, your social support network and overall quality of life may improve.
Aside from these benefits, DBT has been associated with reduced urges to engage in harmful behaviors, such as self-harm or substance abuse. By addressing these urges, DBT can contribute to a greater sense of stability and control over your life.
Remember, embarking on your DBT journey can lead to many benefits, ultimately contributing to a more balanced, stable, and fulfilling life. Focus on the skills you’re learning, and be mindful of your progress as you work towards improving your emotional well-being.
Potential Limitations and Drawbacks
While Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT) has been proven as an effective treatment method for various mental health disorders, it is essential to consider its potential limitations and drawbacks. This section will discuss some crucial aspects of DBT that may not work for everyone.
Firstly, one challenge faced in DBT implementation is program development and recruitment of patients. Establishing a comprehensive DBT program requires significant effort and time, which might not be feasible for every mental health professional or organization. Additionally, therapists and clients may face difficulties committing to the substantial time required for DBT. This treatment approach typically involves concurrent individual therapy, group skills training, and telephone coaching, which could be time-consuming and demanding.
Secondly, DBT demands considerable administrative support and organizational investment, which might not always be available. This therapy modality requires extensive training for therapists and ongoing supervision, which can be costly and resource-intensive.
Lastly, DBT may be ineffective for all individuals and mental health conditions. Specific concerns include:
- Self-injury and suicidal attempts: DBT’s primary focus on helping individuals regulate emotions might not be sufficient to address the complexities of self-destructive behaviors. There’s a risk of personal triggers being activated during treatment, potentially leading to self-injurious behaviors.
- Substance use disorders: DBT was initially developed for borderline personality disorder, and its effectiveness for substance use disorders might be limited. While it aims to promote healthy coping strategies, DBT may not address the underlying addiction or compulsive behaviors directly.
- Maladaptive behaviors: DBT focuses on emotional regulation, interpersonal effectiveness, and distress tolerance. However, this treatment approach may not effectively target maladaptive behaviors, such as disordered eating or compulsive behaviors, and additional therapeutic interventions may be needed.
It is essential to be aware of these potential limitations and drawbacks while considering DBT as a treatment option. Remember, individual needs and circumstances vary, and working with a mental health professional to develop a tailored treatment plan that addresses your unique situation is vital.

Who is DBT For? Finding the Right Fit
Let’s cut to the chase: DBT isn’t a one-size-fits-all approach but can be a game-changer for many people.
Who May Benefit from DBT:
- Individuals with Borderline Personality Disorder (BPD): This was the original target group, and DBT is highly effective for them.
- People with Emotional Regulation Issues: If your emotions are often intense and unpredictable, DBT offers tools to manage them more effectively.
- Those Struggling with Relationships: Communication gaps, frequent fights, and fear of abandonment are some of the issues DBT can help address.
- Patients with ADHD, OCD, or Anxiety Disorders: The skills learned in DBT can complement other treatments for these conditions.
Who Might Not Benefit from DBT:
- Those Seeking Quick Fixes: DBT is a commitment and requires you to put in the work.
- People Unwilling to Engage in Group Therapy: DBT often includes a group component, so if you’re uncomfortable with that, this might not be the therapy for you.
Goals of Therapy: What to Expect From Your DBT Journey
Wondering what you’re signing up for? It’s good to have goals, and DBT has a few set out for you.
- Improved Emotional Regulation: Learn to control those rollercoaster emotions without suppressing them.
- Enhanced Interpersonal Effectiveness: Gain the skills to have more fulfilling relationships, whether it’s with family, friends, or significant others.
- Mindfulness: Become more aware of your thoughts, feelings, and actions in the present moment.
- Distress Tolerance: It’s not about avoiding stress but dealing with it more effectively.
Recognizing Progress: How to Know DBT is Working
So, you’ve been attending sessions, doing homework, and practicing mindfulness. But how can you tell if it’s working?
- Emotional Milestones: Are you lashing out less? Are you finding it easier to manage stress and mood swings? That’s progress!
- Improved Relationships: If your relationships are becoming less turbulent and more meaningful, pat yourself.
- Self-awareness: The more mindful you become, the more in tune you are with your needs and wants.
- Coping Skills: Are you better at handling distress without resorting to destructive behaviors? Fantastic! You’re on the right track.
Progress may not happen overnight, but noticing these positive shifts is a sign you’re moving in the right direction. Keep it up, and don’t be afraid to celebrate those wins, no matter how small they seem!
Conclusion and Future Directions
Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT), developed by Dr. Marsha Linehan, has made significant strides in mental health as a powerful talk therapy. The six main points of DBT—mindfulness, distress tolerance, emotion regulation, interpersonal effectiveness, walking the middle path, and validation—have been instrumental in helping individuals cope with intense emotions, enhance their relationships, and improve overall mental well-being.
You can benefit immensely from incorporating DBT’s practices in individual or group sessions. These skills can be applied in various areas of your life, leading to a more balanced and emotionally healthy existence. Remember that DBT remains an evolving form of therapy, and as research continues, it may expand to address other mental health disorders in the future.
Marsha Linehan’s pioneering work in developing DBT has opened doors to further exploration and research in mental health treatments. This progress has set the stage for advancements in adapting DBT’s principles to other therapeutic approaches and ensuring its continued success in group sessions and individual talk therapy.
As the mental health field continues to evolve, it is crucial to stay informed about new findings regarding DBT, its applications, and future developments. You can better leverage DBT’s valuable toolkit in your mental health journey by keeping up-to-date on research and incorporating this knowledge into your understanding. Embrace the benefits of DBT, and remain open to growth and change as you progress towards a healthier, more fulfilling life.
Frequently Asked Questions

What is the difference between DBT and CBT?
Dialectical behavior therapy (DBT) is a modified type of cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT). While both are talk therapies, CBT helps people understand how thoughts affect emotions and behaviors. In contrast, DBT focuses on accepting the reality of their lives and behaviors while learning to change them. DBT places more emphasis on emotional regulation, interpersonal relationships, and mindfulness.
What are the primary goals of DBT?
The primary goals of DBT are to teach people how to:
- Live in the moment,
- Develop healthy ways to cope with stress,
- Regulate their emotions,
- Improve their relationships with others.
These goals are achieved through developing and practicing skills in various areas.
Who is the founder of dialectical behavior therapy?
Psychologist Marsha Linehan originally conceptualized DBT.
What are the core modules of DBT?
DBT focuses on four key elements:
- Mindfulness – improving one’s ability to be present in the moment,
- Distress tolerance – increasing tolerance for negative emotion rather than trying to escape it,
- Emotional regulation – learning how to manage and respond to emotions healthily,
- Interpersonal effectiveness – enhancing communication and relationship skills.
How is DBT applied in therapy sessions?
During DBT sessions, therapists usually:
- Work one-on-one with clients, using individual therapy to address specific issues,
- Conduct group therapy sessions for skill-building where clients can learn and practice new skills,
- Implement phone coaching for real-time support outside therapy sessions,
- Use consultation teams to support therapists in delivering effective DBT treatment.
What key principles guide DBT treatment?
The key principles guiding DBT treatment include:
- A dialectical worldview – recognizing that everything is connected and change is constant,
- Balance – finding a balance between change and acceptance,
- Validation – acknowledging clients’ experiences as real and valid,
- Behaviorism – emphasizing the role of reinforcement in shaping behaviors,
- Skills training – teaching practical skills to achieve better emotional and behavioral control.
About Jacob Maslow
After surviving the traumatizing events of 9/11, I took it upon myself to heal through helping others. I’m the primary caregiver of my children and understand from first-hand experience the lonely paths you have to walk as a partner and parent when leaving an unhealthy relationship.
We’re all echoing in a dark space that doesn’t have to be this empty, and that’s been my mission since finding solace and recovery in therapy: To help comfort others who are still in shock and at the prime of their struggle.
I came across BetterHelp after searching for this type of community. I wanted to belong to a body of proactive therapists and supportive therapy veterans that allowed me to see other sides of the story.
It was unconventional, and that’s what attracted me most. During my most challenging times, when my ex-wife completely cut me off from my children, I found comfort and clarity through BetterHelp.
Instead of being chained to a strict therapist recommendation, I was in charge of who I felt understood my struggle most. That allowed me to find my true peace, as I was reunited with those who read behind my words and had first-hand experience with my trauma.
Recovery is a choice; with BetterHelp, that choice will be a few clicks away. You can join their couples-oriented platform, Regain.us for those stuck with family estrangement and toxic relationship patterns.
- 7 Ideas to Help You Relax and Unwind on a Family Vacation - April 27, 2025

 The Six Main Points of Dialectical Behavior Therapy
The Six Main Points of Dialectical Behavior Therapy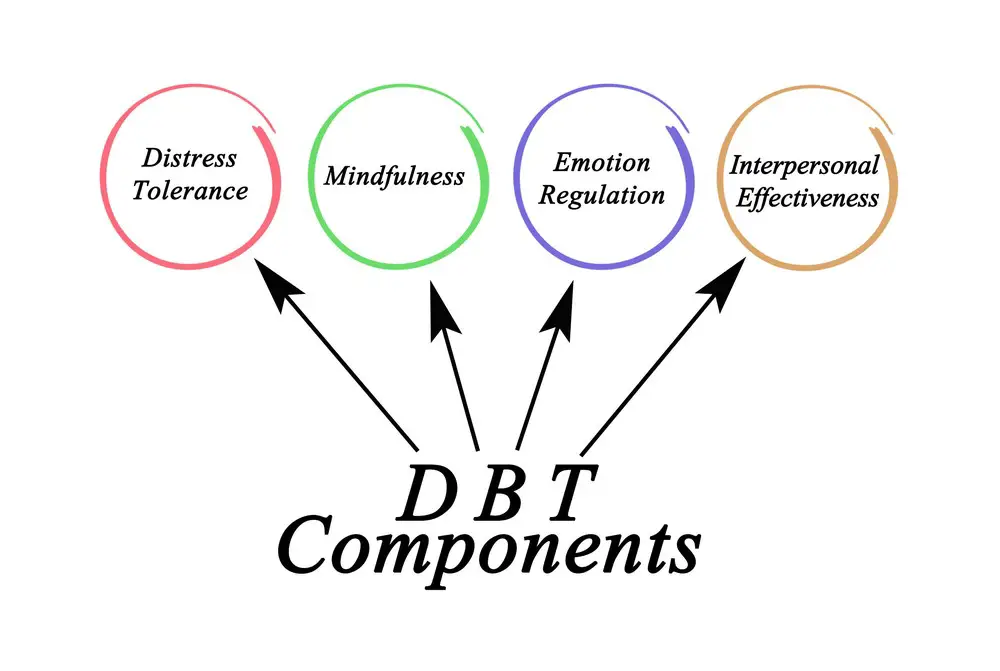 Core Concepts and Techniques
Core Concepts and Techniques Role of the Therapist
Role of the Therapist
