As a BetterHelp affiliate, we receive compensation from BetterHelp if you purchase products or services through the links provided
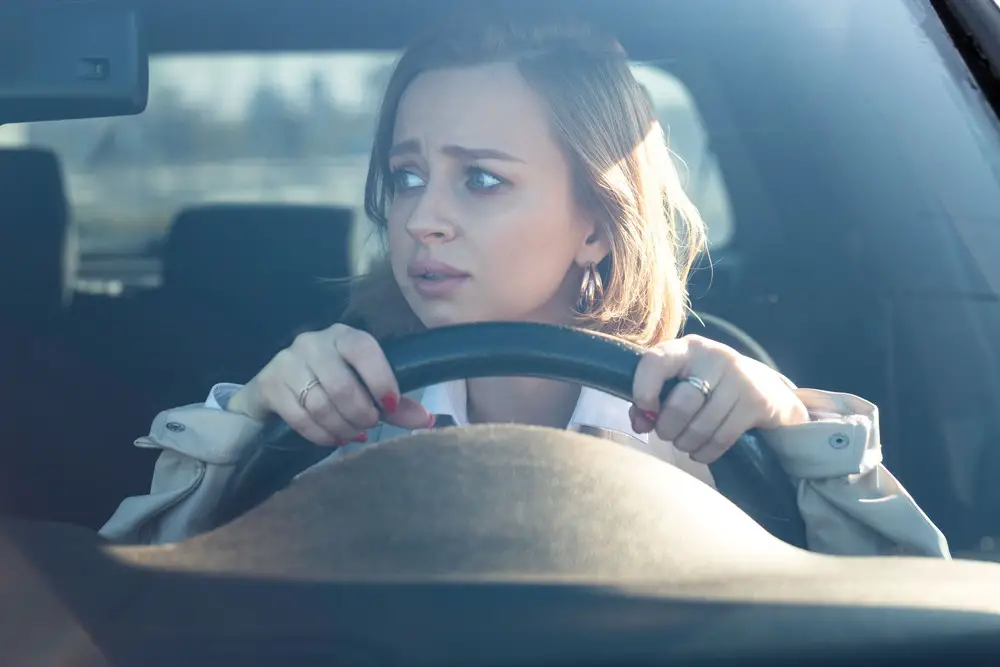
Driving anxiety is a common and debilitating issue that can significantly impact one’s life. It manifests as an overwhelming fear or panic that arises behind the wheel, leading to avoidance or inability to drive and, in extreme cases, severely limiting an individual’s freedom and mobility. By understanding the triggers and effects of driving anxiety, one can begin to take steps toward overcoming this life-altering condition.
For many individuals dealing with driving anxiety, the fear might arise from specific triggers or phobias, such as claustrophobia in traffic or fear of losing control of the vehicle. The consequences of unaddressed driving anxiety can be far-reaching, ranging from stress and decreased quality of life to difficulties in fulfilling work or family obligations. Therefore, it is crucial to recognize and address this issue early on to prevent long-lasting effects.
Key Takeaways
- Driving anxiety can severely impact one’s life, leading to avoidance of driving and decreased mobility.
- Recognizing specific triggers and understanding the effects of driving anxiety is crucial for overcoming the condition.
- Pursuing proven techniques and, if necessary, seeking professional help can assist in managing driving anxiety and preventing relapses

Understanding Driving Anxiety
Driving anxiety is a common issue that affects many people, impacting their daily lives and ability to function on the road. Recognizing the symptoms, understanding the possible causes, and addressing the issue appropriately is crucial.
Recognizing the Symptoms
- Feeling of fear: Those experiencing driving anxiety may feel overwhelming fear or dread when faced with the prospect of driving.
- Panic attacks: Severe cases may result in panic attacks, characterized by shortness of breath, rapid heartbeat, and sweating when thinking about driving or while driving.
- Avoidance behaviors: Individuals with driving anxiety may deliberately avoid driving or engaging in specific situations that trigger their anxiety, such as going on highways or in congested traffic.
- Physical symptoms: Other physical anxiety symptoms may manifest during driving, including shaky hands, dizziness, and chest pain.
Possible Causes
- Past traumatic events: Those who have experienced or witnessed a car accident may develop driving anxiety, associating negative emotions and fear with driving situations.
- General anxiety disorder: People with a pre-existing general anxiety disorder may find their anxiety and fear amplified when facing driving-related situations.
- Lack of experience or confidence: Inexperienced drivers or those lacking confidence in their driving abilities can be prone to driving anxiety.
The severity of driving anxiety varies among individuals, and recognizing the symptoms is a crucial first step to addressing the issue. Understanding the possible causes can also help formulate a personalized plan to manage and overcome driving anxiety.
Common Triggers and Phobias
Amaxophobia and Vehophobia
Amaxophobia and vehophobia are driving phobias that can produce symptoms such as shortness of breath, dizziness, and nausea. These driving phobias concern the fear of participating in or observing vehicular travel. Triggers for these phobias may include:
- High-speed highways
- Busy traffic
- Driving on unfamiliar roads
- Driving in adverse weather conditions
Avoiding driving situations caused by these phobias can lead to isolation and dependence on others for transportation.
Claustrophobia
Claustrophobia is another common trigger associated with driving anxiety. This fear of confined spaces can cause discomfort while driving, especially in tight or closed-in situations. Some examples of triggers for claustrophobic drivers include:
- Being stuck in traffic
- Driving through tunnels
- Sitting in a small or enclosed vehicle
- Wearing a seatbelt tightly
Individuals experiencing claustrophobia while driving may also suffer from shortness of breath, dizziness, and nausea, similar to amaxophobia and vehophobia. Recognizing these triggers and working to address them can help individuals manage their driving anxiety and regain control over their mobility.

Identifying the Effects of Driving Anxiety
Driving anxiety can manifest in various ways and negatively impact a person’s life. One of the primary concerns is the increased risk of a car accident due to heightened stress and fear while driving. A person experiencing driving anxiety may struggle to concentrate on the road, leading to an unsafe environment for drivers and other road users.
Physical symptoms of driving anxiety can include panic attacks, nausea, and lightheadedness. These symptoms may occur before or during driving, making it difficult for the individual to maintain their focus and control over the vehicle. Moreover, some people may experience digestive issues and other health concerns as a direct result of their anxiety, further exacerbating the problem.
The loss of control associated with driving anxiety can lead to avoidance behavior, in which the individual might choose not to drive. This can significantly impact their independence and ability to attend important appointments. Consequently, the individual may become more reliant on others for transportation, negatively influencing their relationships and overall quality of life.
In summary, driving anxiety affects individuals physically, emotionally, and socially. It is essential to recognize these detrimental effects and seek appropriate help to manage and alleviate driving anxiety so that individuals can safely regain their independence on the road.
Proven Techniques to Overcome Driving Anxiety
Relaxation Techniques
One method to overcome driving anxiety is through the use of relaxation techniques. These can help calm the mind and body, making it easier to face challenging driving situations. One common relaxation technique is deep breathing, which involves taking slow, deep breaths and focusing on the sensation of the breath moving through the body. This can help reduce feelings of anxiety and tension. Progressive muscle relaxation is another technique that progressively tense and relaxes various muscle groups, promoting relaxation.
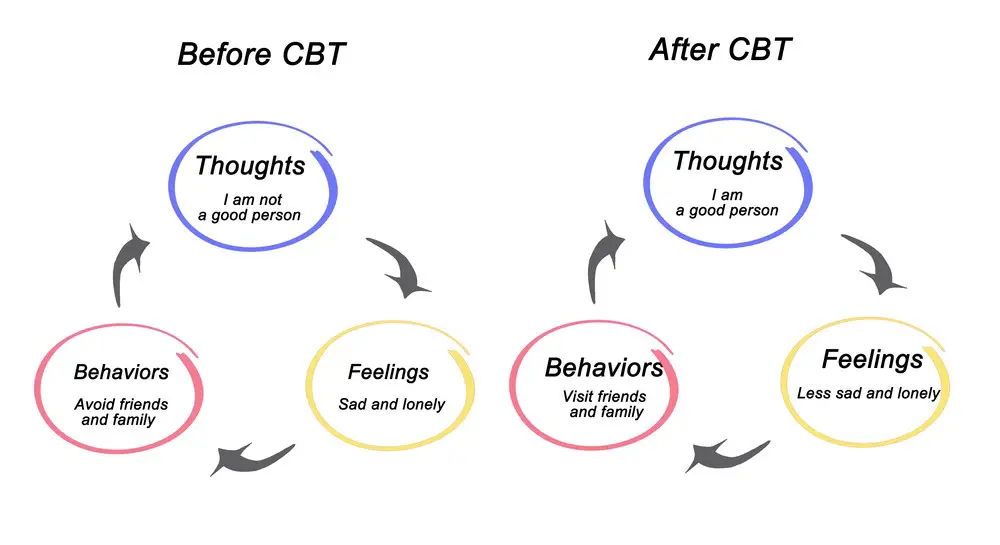
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is a type of psychotherapy that can be highly effective in treating driving anxiety. This therapy focuses on identifying and changing negative thought patterns and behaviors associated with driving. A therapist will work with the individual to explore the root causes of their anxiety and help them develop a more balanced perspective. Through sessions, the person will learn strategies to challenge and reframe their irrational thoughts about driving, ultimately reducing anxiety.
Exposure Therapy
Exposure therapy is based on the idea that the best way to overcome a fear is by gradually facing it controlled and systematically. This method can be beneficial for individuals struggling with driving anxiety. In the context of driving anxiety, the therapist might use a combination of real-world and simulated driving experiences to help the person confront their fears. Individuals will gradually be exposed to more challenging driving situations, allowing them to build confidence and resilience over time. Exposure therapy must be carried out under the guidance of a qualified professional to ensure a safe and effective treatment process.
Seeking Professional Help
Experiencing driving anxiety can hinder daily life, but it is essential to remember that professional help is available. It may be beneficial to consult a mental health professional for those whose anxiety is severely impacting their day-to-day activities.
A mental health professional can assess an individual’s symptoms and severity, potentially diagnosing a generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) if appropriate. According to the National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH), GAD affects approximately 3.1% of the U.S. population. By seeking professional help, one can receive a personalized treatment plan to manage their driving anxiety.
Various organizations, such as the Anxiety and Depression Association of America (ADAA), provide resources and information about mental health professionals and support groups. These supports often allow individuals to learn effective coping strategies, share their experiences, and navigate recovery.
Professionals may often recommend a combination of therapy, medication, and self-help techniques to address driving anxiety. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is a common therapeutic approach to identifying and changing negative thought patterns. Additionally, medications, such as anti-anxiety or antidepressant medications, can help manage symptoms.
In conclusion, seeking professional help for driving anxiety is crucial to improving one’s quality of life. By working with a mental health professional and utilizing available resources, individuals can develop strategies to overcome anxiety and regain control of their driving experiences.
Managing Driving Anxiety in Daily Life
Self-Talk and Mindfulness
Developing strong and consistent self-talk can help people manage their driving anxiety. They should remind themselves of their ability to control the vehicle, navigate traffic using their license, and make necessary choices during the journey. They can practice cultivating positive thoughts while silencing negative ones to regain trust in themselves and their driving skills.
Mindfulness techniques, such as deep breathing and focused attention, can help drivers stay focused on the present moment and reduce anxiety related to getting lost or losing control. Bringing awareness to their bodies, feelings, and the reality of the situation can ground them and help them retain a sense of calm.
Practice Driving and Exposure
Driving lessons and frequent practice are crucial to overcoming driving anxiety. The more they drive, the more comfortable they will become in their abilities. Regularly exposing themselves to traffic situations will desensitize them to the stressors that may lead to anxiety.
In addition to driving lessons, they can gradually increase their exposure to challenging situations, such as driving on highways, in heavy traffic, or unfamiliar areas. This gradual exposure helps them build confidence and reduces anxiety related to fear of public transportation or traffic accidents.
Recovery from driving anxiety is possible if people practice self-talk and mindfulness and expose themselves to their fears through consistent driving experiences. By doing this, they may begin to enjoy the journey and reclaim control over their daily lives.
Preventing Driving Anxiety Relapses
For many individuals, driving anxiety may stem from generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), high-speed situations, or traumatic experiences. However, there is hope for overcoming this fear and preventing anxiety relapses. One can regain control and enjoy driving by implementing specific strategies and coping mechanisms.
Initially, it’s essential to identify triggers that may produce driving anxiety. Common factors include GAD, high-speed roads, or memories of a traumatic event. Acknowledging these triggers will allow a person to manage their anxiety better and minimize its impact.
Adopting relaxation techniques or breathing exercises might be helpful as part of the prevention plan. Before starting the drive, take a few minutes to practice deep breathing, which can help soothe the nervous system and release tension. Developing a mindfulness practice can also encourage a sense of calm and mental clarity.
Another practical suggestion is to expose oneself to driving situations gradually. Start by taking short drives around town or in familiar areas, then gradually increase drive length and venture onto different road types. This incremental exposure will build confidence and reinforce a sense of control.
Physical activity like walking or cycling can reduce stress and improve overall mental well-being. Incorporating regular exercise into one’s routine can keep anxiety at bay and contribute to a more positive outlook on challenging situations.
Finally, having a support system is crucial when dealing with driving anxiety. Open up to friends and family about your concerns and allow them to provide support and encouragement throughout the recovery process. In some cases, seeking professional help from a therapist or counselor may be necessary to address the underlying causes of anxiety and prevent relapses.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are common driving anxiety symptoms?
Driving anxiety can manifest in various ways. Individuals might experience a rapid heartbeat, sweating, trembling, shortness of breath, dizziness, nausea, and panic attacks. Moreover, excessive worry, avoidant behavior, and intrusive thoughts about driving accidents are common psychological symptoms.
How can I manage anxiety while driving on highways?
To manage anxiety while driving on highways, begin by taking deep, slow breaths and focusing on the present moment. Gradually increase the distance driven and practice staying in the right lane to feel safer. Familiarize yourself with the route, and consider driving during less busy hours to build confidence.
How effective is Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for driving anxiety?
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) has proven effective in treating driving anxiety. It focuses on identifying and changing negative thought patterns, beliefs, and behaviors contributing to anxiety. CBT assists individuals in developing coping strategies, gradually exposing them to feared driving scenarios and reinforcing positive behaviors.
What is exposure therapy, and how can it help with driving anxiety?
Exposure therapy is a technique used in CBT designed to help individuals confront and overcome their fears gradually. It involves creating a hierarchy of anxiety-provoking driving situations and slowly exposing individuals to them. Repeated exposure makes the person more comfortable and less anxious in similar scenarios.
Is driving anxiety considered a mental illness?
Driving anxiety is not a standalone mental illness but can be a symptom or part of anxiety disorders such as Generalized Anxiety Disorder, Panic Disorder, or Specific Phobias. In cases where driving anxiety significantly impairs daily functioning, it may be viewed as a mental health concern that requires professional intervention.
What strategies can help overcome the fear of driving alone?
Overcoming the fear of driving alone may involve gradual exposure, starting with short trips and slowly increasing the distance and complexity. Schedule drives during less stressful hours and ensure the car is well-maintained to reduce the risk of breakdowns. Moreover, incorporating relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing and mindfulness, during the drive can also be beneficial.
- Breaking the Silence: Why Men’s Mental Health Matters More Than Ever - April 15, 2025
- How to Transform a Home’s Patio Space into a Relaxing Space - March 23, 2025
- 5 Strategies to Use a Cell Phone to Help Manage Your Stress - March 23, 2025
This site contains affiliate links to products. We will receive a commission for purchases made through these links.



