As a BetterHelp affiliate, we receive compensation from BetterHelp if you purchase products or services through the links provided
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) and Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR) are popular psychotherapy approaches that have gained significant attention over the years. Both therapies aim to alleviate symptoms of various mental health issues, such as anxiety, depression, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). While they share similarities in their objectives, techniques and underlying principles differ.
CBT focuses on identifying and changing negative thought patterns and behaviors associated with emotional distress. The treatment emphasizes collaboration between the therapist and the client, aiming to equip the client with practical coping skills to manage their symptoms. On the other hand, EMDR primarily targets traumatic memories and related symptoms, utilizing bilateral stimulation, such as eye movements or tapping, to help clients process and integrate these memories into their present-day lives.
Although both CBT and EMDR are effective in addressing various mental health challenges, they cater to different aspects of psychological well-being. Choosing between the two, therefore, depends on the specific needs and goals of the individual seeking therapy.
Key Takeaways
- CBT and EMDR are two well-known psychotherapy approaches targeting different aspects of mental health.
- CBT focuses on modifying negative thought patterns, while EMDR emphasizes processing traumatic memories.
- The choice between CBT and EMDR depends on the client’s needs and therapeutic goals.
Understanding EMDR and CBT
Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR) and Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) are two prominent psychotherapy approaches for treating various mental health issues. While they have some similarities, their underlying principles, techniques, and goals differ.
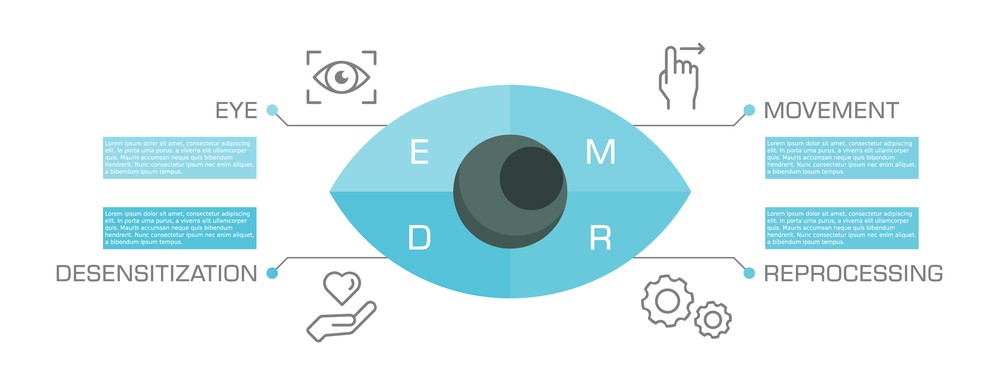
EMDR is a therapy technique developed by Dr. Francine Shapiro in the late 1980s. It focuses on targeting and reprocessing traumatic memories to help individuals overcome the emotional distress caused by such events. EMDR utilizes a combination of eye movements, tapping, or other types of bilateral stimulation to access and reprocess traumatic memories. It is commonly used to treat post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), anxiety, and other trauma-related conditions.
CBT is a broader therapy approach based on the idea that our thoughts, feelings, and behaviors are interconnected and can be modified to improve overall mental well-being. It aims to identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors, promoting healthier coping strategies. CBT is widely used to treat various mental health conditions, including depression, anxiety, obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), and others.
Both EMDR and CBT share a primary focus on helping individuals overcome distressful emotions and thoughts. However, their methodologies differ significantly. EMDR specifically concentrates on reprocessing traumatic memories, while CBT emphasizes altering thought patterns and behaviors. EMDR techniques involve bilateral stimulation, whereas CBT relies on verbal and behavioral exercises, discussion, and goal-setting.
In terms of efficacy, numerous studies have demonstrated the success of both EMDR and CBT in treating mental health concerns. CBT has a long history of research supporting its effectiveness, particularly for depression, anxiety, and OCD. EMDR, though a more recent therapy, has gained substantial validation for treating PTSD and other trauma-related conditions. Choosing between EMDR and CBT largely depends on an individual’s unique needs, mental health concerns, and their preferred therapy approach.
Approaches of EMDR and CBT
 EMDR Approach
EMDR Approach
Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR) is a therapy technique that focuses on treating individuals with post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and other anxiety-related disorders. It helps clients process and resolves past traumatic experiences by stimulating bilateral eye movements while recalling disturbing memories. EMDR consists of eight phases:
- Client history and treatment planning
- Preparation
- Assessment
- Desensitization
- Installation
- Body scan
- Closure
- Reevaluation
The EMDR therapist guides the client through the protocol, helping them identify the target memory, negative cognition, desired positive cognition, emotions, and physical sensations related to the event.
 CBT Approach
CBT Approach
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is a popular psychological treatment that focuses on changing negative thought patterns and behaviors. It is effective for various mental health issues, including depression, anxiety, and phobias. CBT is present-focused and goal-oriented, with an emphasis on the development of coping strategies to manage current issues.
CBT involves four main components:
- Cognitive therapy: Identifying and addressing negative thought patterns
- Behavioral therapy: Implementing strategies to change unhelpful behaviors
- Psychoeducation: Teaching clients about their mental health disorder
- Skills training: Strengthening coping mechanisms and problem-solving abilities
CBT therapists and clients collaborate during sessions to develop treatment plans, set achievable goals, identify barriers, and monitor progress. Clients are often given homework assignments to practice newly acquired skills in real-life situations.
While both EMDR and CBT therapies differ in their approach, they aim to provide individuals with effective solutions to overcome emotional and psychological difficulties related to their past, present, and future experiences.
Techniques in EMDR and CBT
Eye Movements in EMDR
Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR) is a form of psychotherapy that utilizes bilateral stimulation, usually eye movements, to help individuals process traumatic experiences. The technique involves the therapist guiding the client’s eye movements back and forth while they focus on the traumatic memory. This bilateral stimulation, which can also include taps or auditory tones, is believed to facilitate the brain’s processing of the distressing experience, leading to emotional healing.
EMDR consists of eight phases, starting with a comprehensive client history and treatment planning and ending with reassessment and closure. During the core phases of EMDR, the therapist directs clients through eye movements while they recall their traumatic memories. This combination of focusing on the memory and the bilateral stimulation is thought to stimulate the brain’s natural healing process, eventually allowing clients to experience reduced emotional distress related to the memories.
 Thought Patterns in CBT
Thought Patterns in CBT
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is a widely used therapy that focuses on identifying and challenging irrational thought patterns and distorted beliefs contributing to emotional distress and maladaptive behaviors. In CBT, clients work with a therapist to recognize and understand the link between their thoughts, emotions, and behaviors.
One of the key components of CBT is cognitive restructuring, a technique in which clients learn to identify negative thought patterns and replace them with more rational, adaptive alternatives. This process typically involves:
- Identifying the thoughts and beliefs contributing to a problem (e.g., “I’m worthless” or “I will never succeed”)
- Analyzing the thoughts for any cognitive distortions (e.g., all-or-nothing thinking, emotional reasoning)
- Challenging the thoughts using evidence and logic (e.g., instances of success, positive traits)
- Developing alternative thoughts that are more rational and adaptive (e.g., “I have value” or “I can succeed with effort and support”)
While EMDR and CBT approach emotional healing and personal growth from different angles, both therapies effectively treat various mental health concerns, including trauma-related disorders, anxiety, and depression. Ultimately, the choice between EMDR and CBT depends on the individual’s unique needs and preferences and the therapist’s expertise and recommendations.
Applicability of EMDR vs CBT
EMDR in Trauma Therapy
Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR) is particularly well-suited for individuals suffering from the effects of trauma, such as Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD). This therapy involves recalling traumatic events while engaging in bilateral sensory input, such as eye movements or tapping. EMDR aims to reprocess and reduce the distress associated with traumatic memories, resulting in diminished negative emotions and physical sensations.
Research has shown EMDR to be an effective treatment for PTSD, often yielding significant improvement in distress levels and symptom reduction. EMDR has been endorsed by organizations such as the World Health Organization (WHO) and the American Psychological Association (APA) for treating PTSD.
 CBT in Anxiety Disorders
CBT in Anxiety Disorders
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is widely used for various mental health issues, including anxiety disorders such as Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD), Panic Disorder, and Social Anxiety Disorder. CBT encompasses numerous techniques to help individuals identify and change unhelpful thought patterns and behaviors contributing to and maintaining their anxiety.
CBT often incorporates specific techniques such as:
- Psychoeducation: Educating individuals about their anxiety disorder and related symptoms.
- Cognitive restructuring: Identifying and modifying dysfunctional thoughts that contribute to anxiety.
- Exposure therapy: Gradually facing and confronting feared situations to reduce anxiety.
- Relaxation techniques: Incorporating deep breathing and progressive muscle relaxation methods to counter anxiety.
In the context of anxiety disorders, Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT) is a subtype of CBT that emphasizes mindfulness, acceptance, and psychological flexibility to help individuals respond to anxiety more adaptively.
Research has consistently demonstrated the efficacy of CBT in reducing anxiety symptoms, with many individuals experiencing significant improvements in functioning. As a result, CBT is often regarded as a first-line treatment for anxiety disorders by mental health professionals.
Effectiveness and Efficacy
Efficacy of EMDR
Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR) is a psychotherapy treatment designed to alleviate the distress associated with traumatic memories. Many research studies and meta-analyses of randomized controlled trials (RCTs) have explored EMDR’s efficacy in treating various conditions such as anxiety disorders and PTSD. It is important to mention that although EMDR has gained scientific support, not all researchers agree on the extent of its efficacy.
A meta-analysis of RCTs assessing the efficacy of EMDR for treating PTSD found that EMDR significantly reduced PTSD symptoms compared to control groups. Another meta-analysis examining the application of EMDR for anxiety disorders concluded that EMDR effectively reduced anxiety symptoms, with effect sizes similar to or superior to Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) in some cases. However, it must be noted that the quality of evidence in these studies varies.
Regarding other conditions, like chronic pain, research is still limited, and the efficacy of EMDR in this domain requires further investigation.
 Effectiveness of CBT
Effectiveness of CBT
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is a widely-used and well-established form of psychotherapy that aims to address unhealthy thinking and behavior patterns. A substantial body of research supports CBT’s effectiveness in treating a broad range of disorders, especially anxiety disorders, and depression.
For example, a meta-analysis of RCTs investigating the efficacy of CBT for generalized anxiety disorder found that CBT was significantly more effective than control conditions in reducing symptoms. Likewise, several RCTs and meta-analyses demonstrate that CBT is a highly effective treatment option for multiple anxiety disorders, including generalized anxiety disorder, social anxiety disorder, and panic disorder.
CBT has also been found effective in managing pain. In a meta-analysis of RCTs examining CBT for various pain conditions, researchers discovered that CBT significantly improved pain intensity, disability, and emotional distress.
Both EMDR and CBT are effective psychotherapy treatments with a strong evidence base, although the amount of research and the range of conditions treated may differ. Factors such as individual preference, therapist availability, and specific treatment goals should be considered when choosing a therapy.
 Working with Therapists
Working with Therapists
Role of Therapist in EMDR
Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR) therapists are crucial in guiding clients through therapy. They start by helping clients identify specific traumatic memories and associated emotions they would like to target during the sessions. The therapist then works with the individual to address these memories using a structured protocol.
During EMDR therapy sessions, therapists use bilateral stimulation techniques, such as eye movements, tapping, or audio cues, to help clients process disturbing memories and emotions. These therapists may also provide instructions on how clients can use self-calming techniques and grounding exercises to manage potentially overwhelming emotions during and after the session.
EMDR therapists support clients through the various phases of the therapy, including assessment, desensitization, and closure. They ensure clients feel safe and comfortable and pay close attention to their emotional reactions and progress.
Role of Therapist in CBT
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) focuses on helping clients identify and change maladaptive thought patterns and behaviors. They collaborate with individuals to set therapy goals and develop strategies. Typically, CBT therapists lead clients through structured, goal-oriented sessions.
During CBT therapy sessions, the therapist encourages clients to examine their thought patterns, emotions, and behaviors. Various techniques, such as cognitive restructuring and behavioral experiments, help individuals to challenge and modify these patterns, leading to more adaptive ways of responding to situations.
CBT therapists often assign homework tasks for clients to practice and apply the strategies learned in therapy to their daily lives. By regularly reviewing the results and experiences of these tasks in subsequent sessions, the therapist helps clients refine their coping techniques and progress toward their goals.
Application in Different Demographics
EMDR in Children and Adolescents
EMDR (Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing) is effective in treating children and adolescents who have experienced traumatic events. It is a non-invasive therapy that uses bilateral stimulation to help process and integrate traumatic memories. This can help reduce symptoms such as anxiety, depression, and behavioral issues related to the trauma.
In children, the EMDR process may be adapted to ensure their comfort and engagement. This can include using age-appropriate language, incorporating play therapy techniques, and adjusting the pacing of the sessions according to the child’s needs.
Studies have shown the effectiveness of EMDR in treating post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and other trauma-related issues in children and adolescents. EMDR can be particularly useful for this demographic, as younger individuals may struggle to verbalize their experiences and emotions, making other forms of therapy less effective.
CBT in Adults
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is a widely utilized and evidence-based form of psychotherapy that focuses on exploring and modifying thoughts and behaviors contributing to psychological distress. CBT effectively treats various mental health conditions in adults, such as depression, anxiety disorders, obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), and PTSD.
CBT is structured and goal-oriented, often involving homework assignments and collaborative problem-solving between the therapist and the client. By identifying and challenging unhelpful thoughts and behavioral patterns, adults can develop new coping strategies and experience a reduction in symptoms.
Several factors contribute to CBT’s effectiveness in adults, including its focus on the present and building practical skills. Additionally, the collaborative nature of the therapy allows for a supportive environment in which individuals can explore and address their concerns.
Potential Side Effects and Risks
Side Effects of EMDR
Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR) is a therapy that helps individuals cope with traumatic experiences by processing memories of those events. Some potential side effects may arise during or after EMDR sessions:
- Stress: Clients might experience increased stress during the early phases of treatment as they confront their trauma.
- Negative thoughts: Recalling distressing events can lead to temporary negative thoughts or feelings.
- Insomnia: Some individuals report difficulties sleeping due to heightened emotions or restlessness.
Despite these side effects, many clients find EMDR helpful and often experience reduced symptoms over time.
Risks of CBT
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is a widely adopted approach to treating various mental health issues. It focuses on identifying and modifying unhelpful thought patterns and behaviors. CBT is considered a safe therapy, but some risks and side effects exist:
- Discomfort: Some clients may experience discomfort while discussing sensitive issues or childhood memories during sessions.
- Time-consuming: Committing to regular sessions and homework can be challenging and time-consuming for some clients.
- RCT limitations: While Randomized Control Trials (RCTs) have demonstrated the efficacy of CBT, participant variability and limitations in study design may not reflect the experiences of all individuals who undergo treatment.
However, CBT has been proven effective in treating many mental health conditions, and many people experience improved mental well-being.
Deciding the Right Therapy
When choosing between Cognitive Behavior Therapy (CBT) and Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR), it is crucial to consider the individual’s specific needs and circumstances. Both therapies have proven effective in treating various psychological conditions but differ in their approaches and underlying mechanisms.
CBT focuses on the relationship between thoughts, feelings, and behaviors. Its primary goal is identifying and changing negative thought patterns and improving emotions and actions. This therapy is widely used to address anxiety, depression, and other mental health issues. Some variants, like Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT), enhance CBT by incorporating skills training and mindfulness practices.
On the other hand, EMDR addresses the impact of traumatic events on an individual’s mental health. EMDR uses specific eye movements or other forms of bilateral stimulation to help the brain reprocess traumatic memories. This reprocessing enables the individual to experience reduced distress and increase adaptive thoughts and behaviors. EMDR is particularly effective in treating PTSD, anxiety disorders, and trauma-related conditions.
A key difference between CBT and EMDR lies in their methodologies. CBT implements exposure therapy, gradually exposing the individual to anxiety-provoking situations while teaching coping skills. In contrast, EMDR utilizes bilateral stimulation in a structured, eight-phase process for reprocessing traumatic memories.
The procedures involved in each therapy also vary. CBT sessions typically involve homework assignments, goal-setting, and collaboration between the therapist and the individual. EMDR sessions require the individual to focus on specific aspects of a traumatic memory while simultaneously engaging in eye movements or other bilateral stimulation techniques under the therapist’s guidance.
Ultimately, the decision between CBT and EMDR depends on the individual’s unique needs and their issues. Those struggling with thought patterns and emotions related to non-traumatic issues may find CBT more suitable, while EMDR is likely more beneficial for individuals with trauma-related concerns. In some cases, a combination of both therapies may produce the best outcomes. It is essential to consult a mental health professional knowledgeable and experienced in both CBT and EMDR to help guide the decision-making process and determine the most appropriate therapy for each individual.
Cases of Complex Mental Disorders
EMDR in PTSD and Bipolar Disorder
Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR) is a well-known therapy for Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD). It has shown positive results in helping individuals process traumatic events they have experienced. The therapy uses bilateral stimulation, like eye movements or tapping, to help patients process and integrate distressing memories and reduce their emotional impact.
In bipolar disorder, evidence is limited as EMDR was not specifically designed for this condition. However, some studies suggest it may be helpful for patients who have experienced trauma as part of their disorder. By treating the traumatic component, EMDR may contribute to the stabilization of mood symptoms.
CBT in OCD and Schizophrenia
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is an established mental health treatment approach, proven effective for various conditions such as anxiety, depression, and panic attacks.
For Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD), CBT works by helping patients identify and challenge their irrational thoughts and beliefs. It encourages them to face their fears and develop coping strategies to manage their symptoms better. Clients may benefit from exposure and response prevention, a specific CBT technique that involves gradually exposing them to their feared object or situation while refraining from engaging in compulsive behaviors.
For individuals with schizophrenia, CBT aims to reduce symptoms by targeting problematic thoughts and enhancing coping skills. This can include addressing hallucinations, delusions, and negative symptoms through cognitive restructuring, mindfulness techniques, and social skills training. Results show that when combined with medication, CBT for schizophrenia can improve overall functioning and quality of life.
Although each therapy shows promise in treating different mental disorders, it is essential to recognize that every individual’s needs and experiences vary – requiring tailored treatment plans and ongoing research to optimize outcomes.
Final Thoughts
In comparing Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) and Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR), it is evident that both therapies have shown effectiveness in reducing post-traumatic symptoms through randomized clinical trials (RCTs). While CBT focuses on changing thought patterns and reevaluating experiences, EMDR utilizes bilateral stimulation to process traumatic memories and reduce arousal levels.
Both therapies have been effective for various groups, such as individuals suffering from anxiety disorders, PTSD, and depression. Medication can be a supplementary treatment option alongside these therapies, depending on the individual’s needs and circumstances.
Ultimately, the choice between CBT and EMDR depends on the specific needs of the individual and his or her preference for treatment methods. It is essential to consult with a knowledgeable mental health professional who can provide tailored recommendations based on a thorough assessment of the individual’s situation.
Frequently Asked Questions

What is the difference between CBT and EMDR therapy?
CBT (Cognitive Behavioral Therapy) is a form of talk therapy that focuses on identifying and changing negative thought patterns and behaviors. It is based on the principle that thoughts, emotions, and behaviors are interconnected. CBT helps individuals develop new, healthier thought patterns and coping strategies.
EMDR (Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing) is a therapy technique that uses eye movements and other forms of bilateral stimulation to help process traumatic memories and reduce the intensity of negative emotions. It is designed to help individuals deal with unresolved traumas and past experiences.
Is EMDR more effective than CBT for trauma?
The effectiveness of EMDR and CBT for trauma can vary depending on the individual and the specifics of their trauma. Some studies have shown that both therapies can effectively treat trauma-related disorders, such as PTSD. However, EMDR may be particularly helpful for individuals who struggle with vivid, intrusive memories or have difficulty discussing their trauma in a traditional talk therapy setting.
Can CBT and EMDR be used together?
Yes, CBT and EMDR can be used as part of an integrated treatment plan. Some therapists may combine elements of both approaches to tailor treatment to the specific needs of their clients. The combination of therapies may help individuals address both the thought patterns and the emotional components of their trauma more effectively.
Which therapy is better for PTSD, CBT or EMDR?
Both CBT and EMDR are effective in treating PTSD. The choice between the two depends on the individual’s needs, preferences, and the nature of their trauma. Some people may respond better to CBT, while others may find EMDR more helpful. Working with a qualified therapist is essential to determine the best approach for each person.
Is EMDR a form of behavioral therapy?
EMDR is not considered a form of behavioral therapy. Although it shares some similarities with CBT, such as helping individuals process and replace negative thoughts and beliefs, EMDR focuses more on the role of traumatic memories and unresolved emotional experiences. EMDR uses eye movements and other forms of bilateral stimulation to help individuals process these experiences more effectively.
How do CBT and EMDR differ in approach and techniques?
CBT is a talk therapy that identifies and changes negative thought patterns and behaviors. Techniques in CBT may include thought-challenging exercises, exposure therapy, and role-playing. In contrast, EMDR involves eye movements and other forms of bilateral stimulation to help individuals process traumatic memories and reduce the intensity of negative emotions.
About Jacob Maslow
Jacob Maslow is an ardent mental health advocate, sharing his journey with Lexapro and exploring therapeutic avenues like CBT and EMDR. His narrative is tumultuous, marred by a challenging ex-spouse whose narcissistic tendencies led to profound parental alienation, leaving Jacob disconnected from his beloved kids. Amidst court battles and custody disputes that spanned years, the silver lining for Jacob has always been the enduring bond formed over the years with his children.
Finding clarity in nature, Jacob’s long, daily walks are his meditative escape, a ritual to refresh and gather thoughts. His writings, deeply rooted in personal experiences, shed light on mental health issues and the nuances of narcissism, serving as a beacon of hope for others in similar predicaments. Through his legal site, he extends a helping hand to those ensnared in custody conflicts, emphasizing co-parenting’s true essence over its weaponization.
- How to Transform a Home’s Patio Space into a Relaxing Space - March 23, 2025
- 5 Strategies to Use a Cell Phone to Help Manage Your Stress - March 23, 2025
- 4 Ways to Use Measurements to Create a Relaxing Sleep Space - March 23, 2025
This site contains affiliate links to products. We will receive a commission for purchases made through these links.


 EMDR Approach
EMDR Approach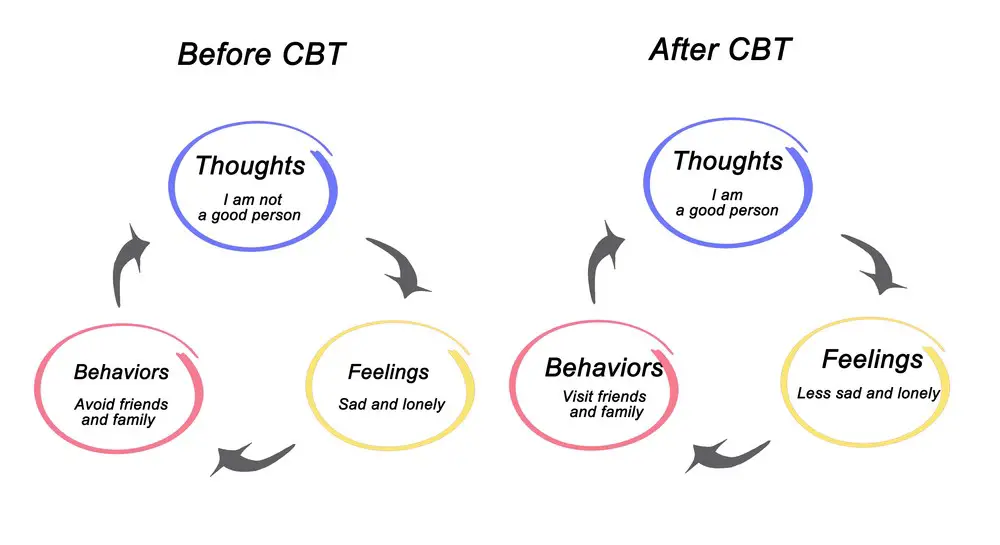 CBT Approach
CBT Approach Thought Patterns in CBT
Thought Patterns in CBT CBT in Anxiety Disorders
CBT in Anxiety Disorders Effectiveness of CBT
Effectiveness of CBT Working with Therapists
Working with Therapists
