As a BetterHelp affiliate, we receive compensation from BetterHelp if you purchase products or services through the links provided
Depression and low testosterone are two conditions that can greatly impact a person’s mental and physical well-being. Although they may appear as separate issues, recent research suggests that there may be a connection between the two. This article aims to examine the link between depression and low testosterone, discuss the effects of low testosterone levels on the mind and body, and explore the available treatment options.
Testosterone is a hormone that plays a crucial role in regulating various physiological processes. It is predominantly produced in men by the testes, and its deficiency can lead to various health issues. As depression and low testosterone share certain symptoms, such as fatigue, irritability, and decreased libido, it is essential to understand how these conditions may be interconnected.
It is crucial to properly diagnose and treat both depression and low testosterone, as their impact on an individual’s overall well-being and quality of life cannot be understated. A comprehensive approach to managing these conditions will ultimately ensure better outcomes for those affected.
Key Takeaways
- Depression and low testosterone may be connected, impacting mental and physical well-being.
- Testosterone plays a vital role in men’s health, and its deficiency can cause various issues.
- Proper diagnosis and treatment of depression and low testosterone are essential for improving the quality of life.
 The Link Between Depression and Low Testosterone
The Link Between Depression and Low Testosterone
Physiological Effects of Depression
Depression can contribute to various physical and emotional changes in an individual. One of the possible physiological effects of depression is its impact on hormone levels, particularly testosterone. Testosterone is known to influence libido, energy, motivation, and self-confidence.
Low testosterone levels have been linked to various symptoms, such as fatigue, irritability, anxiety, sleep disturbances, and reduced concentration ability. These symptoms can be similar to depression, which may create a complex relationship between the two conditions.
The stress that often accompanies depression can further disrupt hormonal balance. Elevated levels of stress hormones like cortisol can contribute to the suppression of testosterone production. Moreover, poor sleep quality, a common symptom of depression, can contribute to a decrease in testosterone levels, making it even harder for individuals to overcome the negative emotional effects of depression.
In some cases, depression and low testosterone can occur simultaneously, presenting a challenge in determining which condition is the primary cause of the other. As both conditions share overlapping symptoms and can exacerbate one another, it is crucial for individuals experiencing these symptoms to consult with a medical professional for appropriate evaluation and treatment.
Understanding Testosterone
The Role of Testosterone
Testosterone is a vital male hormone primarily produced in the testicles and to a lesser extent, the adrenal glands. It plays a crucial role in developing male reproductive tissues, such as the testes and prostate. It promotes secondary sexual characteristics like body hair growth and muscle mass. Classified as an androgen, testosterone belongs to a group of hormones responsible for controlling the appearance of masculine traits.
In addition to its reproductive functions, testosterone influences mood, energy, and overall health. Testosterone production is regulated by luteinizing hormone (LH) – a hormone synthesized and secreted by the pituitary gland that stimulates the testes to produce testosterone when levels decline.
 Testosterone and Aging
Testosterone and Aging
As men age, their testosterone levels typically decrease. By the time an individual reaches their 40s, testosterone levels can drop at a rate of about 1 to 2 percent per year. Testosterone levels are typically measured in nanograms per deciliter (ng/dL), with the normal range varying by age and laboratory standards. Generally, a normal range for adult males is between 300 and 1,000 ng/dL.
It is important to note that various factors can influence testosterone levels, including age, time of day, and individual health conditions or medications. Furthermore, low testosterone levels can manifest as fatigue, low sex drive, muscle weakness, and depression. This association has sparked interest in understanding the relationship between depression and testosterone. However, one must be cautious not to draw conclusions solely based on reduced testosterone levels since many other factors can contribute to an individual’s mental health.
Physical Effects of Low Testosterone
Low testosterone, also known as hypogonadism, can cause several physical symptoms that affect a person’s daily life. The most common symptoms are decreased muscle mass, increased body fat, and diminished bone density. These changes in an individual’s body composition can lead to fatigue, reduced energy, and muscle weakness.
A major effect of low testosterone on the body is the reduced ability to maintain muscle mass. This can result in decreased muscle strength and an overall decline in physical performance. At the same time, a person may experience increased body fat, particularly in the abdominal area. Weight gain can further contribute to fatigue and decreased energy levels.
Another significant impact of low testosterone is on bone density and bone mass. With a decline in testosterone levels, there might be an increased risk of developing osteoporosis, resulting in weaker and more brittle bones. This increases the likelihood of fractures and poses serious health risks, particularly for older adults.
Erectile dysfunction, a common problem in men with low testosterone, is another physical effect that can severely impact an individual’s quality of life. Difficulty in achieving or maintaining erections can be distressing for both the individual and their partner. Moreover, low testosterone levels can lead to reduced libido and sexual desire, further complicating matters.
In some cases, individuals with low testosterone might experience changes in sleep patterns, such as sleep apnea. Sleep apnea is a condition where breathing is repeatedly interrupted during sleep, which can cause daytime fatigue and other health-related issues.
Gynecomastia, or the enlargement of breast tissue in men, can also be a side effect of low testosterone. This condition might lead to feelings of self-consciousness or embarrassment, affecting an individual’s overall well-being.
Additionally, low testosterone can cause a decrease in body and facial hair, as testosterone plays a significant role in the growth and maintenance of hair. This change in appearance can also impact a person’s sense of self and confidence.
Lastly, low testosterone can affect red blood cell production, contributing to anemia and its associated symptoms, such as fatigue, shortness of breath, and pallor. This adds to the overall impact of low testosterone on a person’s energy levels and general health.
 Psychological Implications of Low Testosterone
Psychological Implications of Low Testosterone
Low testosterone can have a significant impact on an individual’s mental well-being. One of the most common consequences of reduced testosterone levels is depression. Numerous studies have found a strong correlation between low testosterone and depressive symptoms, suggesting hormonal imbalances may contribute to mood disorders.
Irritability and anxiety are also commonly associated with low testosterone levels. Individuals experiencing hormonal imbalances may have difficulty managing their emotions and maintaining a balanced mood. This can lead to increased feelings of stress, making it challenging for them to navigate daily life situations and interpersonal relationships.
Another psychological implication of low testosterone is reduced motivation. Individuals with decreased testosterone levels often report a lack of drive and enthusiasm, hindering work performance, personal growth, and overall life satisfaction.
Self-confidence can also be affected by low testosterone. People with lower testosterone levels may experience insecurity and doubt, hurting their decision-making and interpersonal relationships.
Memory and concentration are other areas that low testosterone levels may impact. Research suggests that individuals with hormonal imbalances may struggle with cognitive functioning, leading to issues with memory retention and an inability to focus on tasks for extended periods.
In summary, the psychological implications of low testosterone are wide-ranging and include depression, irritability, anxiety, reduced motivation, feelings of stress, mood changes, decreased self-confidence, and issues with memory and concentration. This highlights the importance of having balanced hormonal levels for overall mental well-being.
Diagnosis of Low Testosterone
To diagnose low testosterone (often referred to as Low T), doctors primarily rely on the presence of symptoms and the measurements of testosterone levels through blood tests. Combining these factors is usually necessary to determine if an individual is experiencing low testosterone.
For most men, testosterone levels naturally decline with age. However, it is vital to consult a healthcare professional if an individual suspects they are suffering from Low T, as symptoms can vary greatly and sometimes mimic those of other conditions. Common symptoms of low testosterone include fatigue, reduced sex drive, and difficulty concentrating.
When diagnosing low testosterone, doctors typically begin by thoroughly examining a patient’s medical history and performing a physical exam. They may also request a series of blood tests to measure testosterone levels accurately. Various factors can affect testosterone levels, so multiple blood samples may be needed to provide accurate measurements.
Blood tests are generally taken early in the morning when testosterone levels are at their highest. Healthcare professionals consider testosterone levels below 300 ng/dL as low. It is important to note that the proper diagnosis of Low T should be made based on multiple blood tests and not just a single measurement, as results can sometimes be influenced by other factors such as stress or illness.
To support the diagnosis of low testosterone, doctors often evaluate the presence of other symptoms. These symptoms can include changes in mood, difficulty sleeping, erectile dysfunction, and a decrease in overall muscle mass. Although these symptoms can indicate Low T, they may also be caused by other health-related conditions.
In conclusion, diagnosing low testosterone combines assessing symptoms, evaluating a patient’s medical history, and conducting blood tests. It is crucial to consult a healthcare professional if one suspects they may have Low T to ensure proper diagnosis and treatment.
Causes of Low Testosterone
A variety of factors, both physiological and environmental, can cause low testosterone. One common cause of low testosterone is aging. As men age, their testosterone levels naturally decrease, with a more significant decline typically occurring after age 30. This decrease in testosterone can lead to various symptoms, such as fatigue, low sex drive, irritability, and decreased bone density.
Hypogonadism, a condition in which the body does not produce enough testosterone, is another cause of low testosterone levels. Hypogonadism can be classified into two types: primary and secondary. Issues with the testicles cause primary hypogonadism, while secondary hypogonadism is related to problems with the pituitary gland. Factors that may contribute to hypogonadism include Klinefelter syndrome, undescended testicles, and chemotherapy.
Medications can also influence testosterone levels. Some drugs, such as opioids and corticosteroids, are known to decrease testosterone production. In addition, chemotherapy and radiation treatments for cancer can negatively affect the testicles and lead to low testosterone levels.
Obesity also affects low testosterone, as excess body fat can affect hormone production. Increased body fat often leads to higher levels of estrogen, which can then decrease testosterone levels. Maintaining healthy testosterone levels is essential to maintain a healthy weight.
Another potential contributor to low testosterone levels is alcohol use. Excessive consumption of alcohol can hurt the reproductive system and lead to decreased testosterone production. It is crucial to limit alcohol intake to avoid potential complications.
Certain medical conditions can also lead to low testosterone levels. Diabetes, HIV, and infections in the testicles may all affect testosterone production. Furthermore, prostate issues, including prostate cancer and prostatitis, can negatively impact hormone levels.
Testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) may be recommended for men with low testosterone levels due to the abovementioned factors. However, TRT has potential risks and side effects, such as worsening sleep apnea symptoms, increasing the risk of blood clots, and stimulating the growth of prostate cancer cells. Therefore, the risks and benefits of TRT should be carefully considered before initiating treatment.
It is essential to be aware of the signs and symptoms of low testosterone to seek prompt medical intervention when necessary. Symptoms may include decreased libido, fatigue, hot flashes, reduced sperm production, and infertility. Early detection and treatment can help alleviate these symptoms and improve overall quality of life.
 Treatment Options for Low Testosterone
Treatment Options for Low Testosterone
A variety of treatment options are available for men experiencing low testosterone. These treatments aim to improve energy, sleep, libido, and mood changes associated with low testosterone levels. It is essential to consult a doctor to discuss the most suitable options before initiating treatment.
Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT) is a common treatment for low testosterone. This therapy provides the body with additional testosterone through various methods such as injections, patches, and gels. The aim is to restore testosterone levels to a normal range and alleviate the symptoms experienced by men with low testosterone.
Injections are one of the most popular forms of TRT, as they allow for precise dosage adjustments and are cost-effective. Testosterone injections are typically administered every one to two weeks, depending on the patient’s needs. Patches, however, are applied daily and provide a steady dose of the male hormone throughout the day.
It’s essential to note that testosterone therapy is not without potential side effects. Some of these include acne, fluid retention, and increased risk of blood clots. Therefore, careful monitoring by a healthcare professional is necessary during treatment.
Another treatment option for low testosterone is hormone replacement therapy (HRT), often recommended for men with symptoms that don’t improve with TRT or who have been diagnosed with hypogonadism. HRT can help to balance hormone levels and improve overall well-being.
In addition to direct testosterone treatments, individuals can consider making lifestyle changes to support healthy testosterone levels. A well-balanced diet with adequate protein, healthy fats, and essential vitamins and minerals can improve hormonal balance. Engaging in regular physical activity, maintaining healthy body weight, and getting adequate sleep can help support testosterone production.
In conclusion, many treatment options exist for men experiencing low testosterone. A personalized approach that includes consultations with a doctor and carefully considering potential side effects is crucial in determining the most suitable treatment for each individual.
Frequently Asked Questions
Does low mood impact testosterone levels?
Yes, low mood can impact testosterone levels. Studies have shown that depression and low mood can cause a decrease in testosterone production in the body. This can lead to a further decline in mood and overall well-being.
Can emotional stress lead to reduced testosterone?
Emotional stress can indeed lead to reduced testosterone levels. When the body experiences stress, it produces cortisol, which can hurt testosterone production. Prolonged stress may cause a significant decrease in testosterone levels.
Are there links between mental health and hormone levels?
There is a strong link between mental health and hormone levels. Hormonal imbalances can contribute to various mental health issues, including depression and anxiety. Conversely, mental health issues can also impact hormone levels, potentially causing an imbalance.
What are common symptoms of both depression and low testosterone?
Some common symptoms of depression and low testosterone include fatigue, loss of energy, decreased libido, difficulty concentrating, and changes in sleep patterns. These overlapping symptoms can sometimes make distinguishing between the two conditions difficult.
Does treating depression help increase testosterone levels?
Treating depression can potentially help increase testosterone levels. As depression improves, an individual’s mood and overall well-being may stabilize, allowing the body to produce testosterone more efficiently. However, it’s essential to note that treating depression alone may not always lead to a significant increase in testosterone levels.
Can low testosterone treatment help in alleviating depression?
Low testosterone treatment, such as testosterone replacement therapy, may help alleviate depression in some cases. Studies have shown that individuals with low testosterone levels who undergo treatment often experience improvements in their mood and depressive symptoms. However, consulting with a healthcare professional before pursuing any hormonal treatment is crucial, as it’s not suitable for everyone.
Jacob Maslow: Delving Deep into Mental Health Through Personal Odyssey and Expertise
Jacob Maslow, the voice behind “Can Depression Cause Low Testosterone? Exploring the Link and Implications,” is not just a writer but a passionate advocate for understanding the multifaceted world of mental health. Drawing from his journey—relying on Lexapro as a beacon in managing his mental health and his immersive experience as a therapy participant—Jacob’s insights resonate with authenticity.
The depths from which Jacob draws his understanding are profound. An ongoing, tumultuous legal battle with an ex-partner, who stands as an embodiment of extreme narcissism, has thrust him into a maelstrom of challenges, the most heartrending being the alienation from his children. The persistent breaches of court-ordered shared custody only emphasize the painful disconnection that once was a closely-knit bond.
Beyond the confines of written words and courtrooms, Jacob seeks solace in his daily extended walks—a ritual that offers both clarity and mental rejuvenation. Through these experiences, he crafts articles aiming to assist and guide those grappling with the shadows of mental health issues and the suffocating grasp of narcissistic relationships. His writings radiate hope: that triumph over mental health challenges is attainable.
Furthering his dedication, Jacob also curates a specialized legal platform, supporting those in legal battles with defiant spouses. His focus is clear: championing the importance of shared parenting, mental equilibrium, and adherence to judicial mandates.
- 3 Ways Wearing a Hat Can Help Lower Your Stress Levels - April 19, 2025
- Breaking the Silence: Why Men’s Mental Health Matters More Than Ever - April 15, 2025
- How to Transform a Home’s Patio Space into a Relaxing Space - March 23, 2025
This site contains affiliate links to products. We will receive a commission for purchases made through these links.


 The Link Between Depression and Low Testosterone
The Link Between Depression and Low Testosterone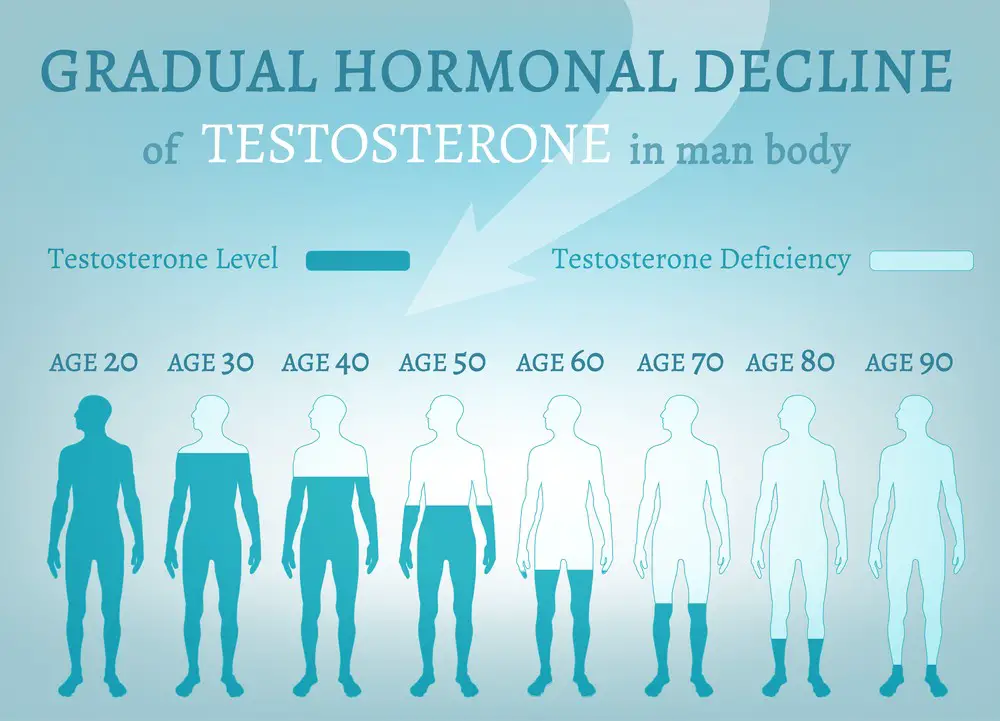 Testosterone and Aging
Testosterone and Aging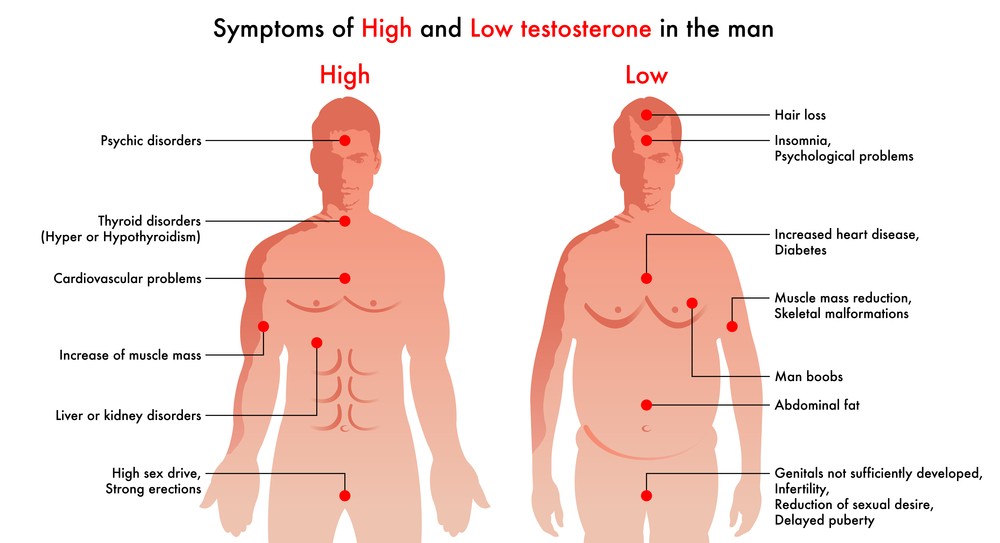 Psychological Implications of Low Testosterone
Psychological Implications of Low Testosterone Treatment Options for Low Testosterone
Treatment Options for Low Testosterone
