As a BetterHelp affiliate, we receive compensation from BetterHelp if you purchase products or services through the links provided
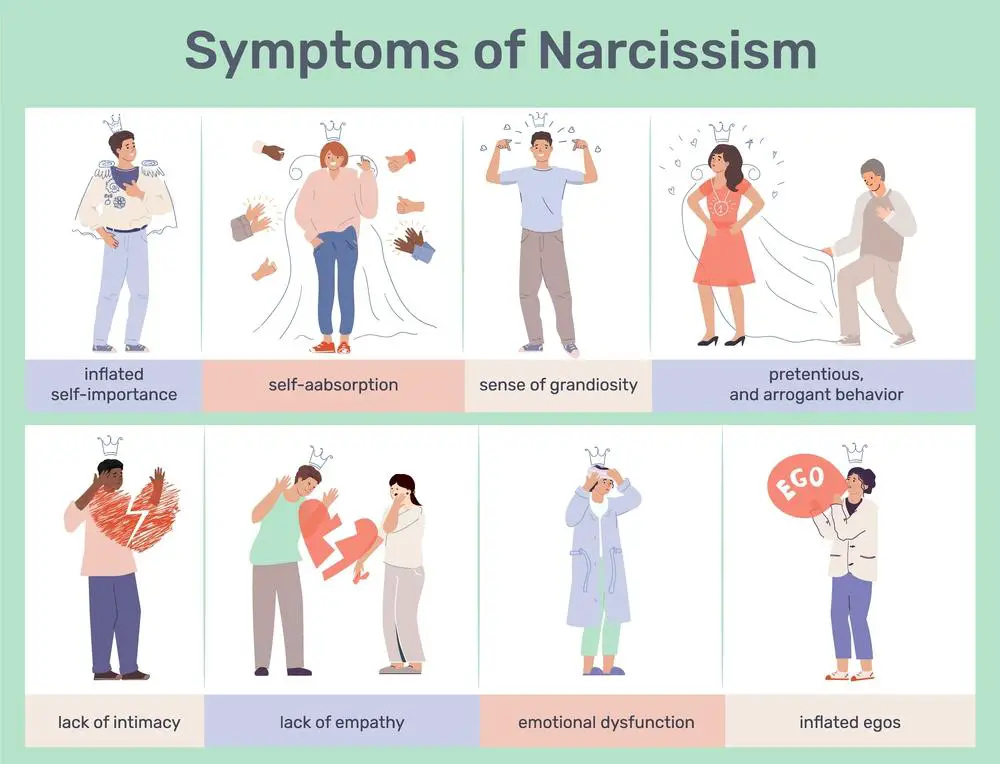
Narcissism is often viewed through overt confidence and self-admiration, but a bedrock of insecurity can lie beneath this facade. Narcissistic Personality Disorder (NPD), characterized by an inflated sense of self-importance and a need for excessive attention, often conceals a fragile self-esteem that is vulnerable to the slightest criticism. The paradox of narcissism lies in the simultaneous demonstration of grandiosity and the internal experience of feeling inadequate.
Understanding the insecure foundation of narcissism requires a look at the defense mechanisms individuals with NPD use. These individuals may respond to perceived threats to their self-image with denial, contempt, or aggression, protecting them from feeling vulnerable. Dive into the emotional struggles of narcissists, one will find that their interactions with others are frequently strained. Relationships become a complex dance of maintaining superiority, often at the cost of genuine connection.
In the digital age, the display of narcissistic traits has found new breeding grounds on social media platforms, where validation comes in the form of likes, comments, and shares. However, the immediate gratification obtained online is often a double-edged sword, as it may reinforce the need for external affirmation while undercutting true self-worth. Therapy and treatment options exist that can help individuals with NPD develop healthier self-esteem and more adaptive coping strategies.
Key Takeaways
- Narcissists may project confidence, but this often masks deep insecurities.
- Narcissistic defense mechanisms guard against feelings of vulnerability.
- Social media can amplify narcissistic behavior and the need for external validation.
Understanding Narcissism
 Narcissism is a multifaceted concept with psychological underpinnings that encompass both expectable personality traits and clinically diagnosed disorders. This section sheds light on the nature of narcissism and distinguishes its everyday presence from its manifestation as a mental health condition.
Narcissism is a multifaceted concept with psychological underpinnings that encompass both expectable personality traits and clinically diagnosed disorders. This section sheds light on the nature of narcissism and distinguishes its everyday presence from its manifestation as a mental health condition.
Defining Narcissism and Its Traits
Narcissism involves thinking, feeling, and behavior patterns that indicate self-centeredness and a craving for admiration. Common traits include:
- Grandiosity: An inflated view of one’s importance or abilities
- Seeking Admiration: A persistent quest for excessive attention and validation
- Lack of Empathy: A deficiency in recognizing or caring for the feelings and needs of others
It’s important to note that these traits can be present in various combinations and intensities.
Personality Trait vs. Disorder
The distinction between narcissism as a personality trait and Narcissistic Personality Disorder (NPD) is critical:
- Personality Trait: Many individuals may display narcissistic traits to some degree. These tendencies do not necessarily impair functioning or constitute a disorder.
- Narcissistic Personality Disorder: NPD is a mental disorder diagnosed by healthcare professionals. It reflects a long-term pattern of behavior that includes an excessive need for admiration and a lack of empathy, which cause problems in many areas of life.
Key takeaway: Understanding the nuances between narcissistic traits and NPD is essential for recognizing when narcissism may become a problematic disorder.
The Insecure Foundation of Narcissism
 Narcissism often stems from deep-rooted insecurities and a fragile sense of self-worth. This paradoxical relationship is crucial to understanding the psyche of a narcissist.
Narcissism often stems from deep-rooted insecurities and a fragile sense of self-worth. This paradoxical relationship is crucial to understanding the psyche of a narcissist.
Core Insecurities in Narcissists
Narcissists typically harbor significant insecurities beneath a veneer of confidence. Despite their outward bravado, they may feel a pervasive sense of inadequacy.
- Feeling of Emptiness: They struggle with an internal emptiness, often trying to fill the void with admiration and attention from others.
- Fear of Failure: Narcissists may fear failure or not living up to their own or others’ expectations, which can lead to avoidance of challenges where they might fail.
- Sensitivity to Criticism: A narcissist’s self-image can be easily threatened by criticism, interpreting it as a personal attack rather than constructive feedback.
Key Takeaway: Insecurities in narcissists can manifest as overcompensation through assertiveness and a need for external validation.
Low Self-Esteem and Its Role
Low self-esteem is a pivotal aspect of a narcissist’s emotional framework. This influences their behaviors and interactions in significant ways.
- Seeking Validation: A continuous quest for validation from others can indicate a narcissist’s underlying low self-esteem.
- Perception of Superiority: To counteract feelings of low self-worth, they may overemphasize their own abilities or accomplishments.
- Relationships: Their relationships are often marred by their need for dominance, stemming from the fear of being seen as weak or flawed.
Key Takeaway: The narcissist’s low self-esteem drives much of their external persona, highlighting the contradiction between their self-aggrandizement and their actual self-view.
Types of Narcissism
 Narcissism manifests in a spectrum of forms, with vulnerable and grandiose narcissism at its poles. These distinct types demonstrate differences in behavior, emotion, and relationships.
Narcissism manifests in a spectrum of forms, with vulnerable and grandiose narcissism at its poles. These distinct types demonstrate differences in behavior, emotion, and relationships.
Vulnerable Narcissism
Vulnerable narcissists often feel defensive and are hypersensitive to criticism. They handle low self-esteem by seeking reassurance from others. In social settings, they may appear:
- Withdrawn: cautious about engaging openly, as they fear rejection.
- Insecure: constantly needing validation to bolster their fragile self-image.
Key Takeaway: Vulnerable narcissists’ actions are driven by an internal sense of insecurity, often leading to a defensive and hesitant approach in their interactions.
Grandiose Narcissism
In contrast, grandiose narcissists exude confidence and self-assuredness. Their characteristics include:
- Boldness: a dominant presence that demands attention.
- Lack of empathy: an underdeveloped capacity to understand others’ feelings.
Grandiose narcissists tend to:
- Pursue their goals aggressively.
- Overestimate their abilities.
Key Takeaway: Grandiose narcissists present themselves with an exaggerated sense of superiority and are often focused on maintaining their self-image through assertive behavior.
 Narcissists in Relationships
Narcissists in Relationships
Narcissists in relationships often grapple with insecurities veiled by a facade of over-confidence. A pursuit of excessive validation and a penchant for controlling dynamics usually marks their interpersonal engagements.
Seeking Validation and Admiration
Often, these individuals engage in relationships to secure constant admiration and affirm their self-perceived superiority. They may:
- Besiege their partners with demands for excessive praise.
- Present their achievements or talents frequently, expecting acknowledgment.
Control and Manipulation Dynamics
In the bid to maintain dominance, narcissists may adopt tactics to manipulate and assert control over their partners. Such behaviors include:
- Decisions: They insist on making unilateral decisions about plans or finances.
- Critique: They might frequently criticize their partner to maintain an upper hand.
- Isolation: Efforts to isolate their partners from friends or family can be a control strategy.
Key Takeaway: A narcissist’s interaction in relationships is often marked by a quest for ceaseless validation while simultaneously striving to retain control through manipulative tactics.
Narcissistic Coping Mechanisms
 Narcissistic individuals often employ specific coping mechanisms to shield their fragile self-esteem from perceived threats. These strategies can both mask and fuel deep-seated insecurities.
Narcissistic individuals often employ specific coping mechanisms to shield their fragile self-esteem from perceived threats. These strategies can both mask and fuel deep-seated insecurities.
Narcissistic Rage and Criticism Avoidance
Narcissists tend to respond with narcissistic rage in the face of criticism, perceiving it as a personal attack. This rage can manifest as intense anger or passive aggression. Their reaction serves to protect a fragile self-image and avoid the discomfort of acknowledging flaws or mistakes.
- Examples of rage reactions:
- Verbal outbursts
- Silent treatment
- Sarcasm
Avoiding criticism is a key strategy for narcissists. They often:
- Surround themselves with people who are unlikely to criticize them
- Discredit the source of the criticism
- Shift the blame to others
Key Takeaway: Narcissists experience criticism as an acute threat, prompting them to react with rage or employ various avoidance tactics to uphold their self-image.
Defensive Grandiosity and Superiority

Narcissists cultivate an aura of superiority as a defensive mechanism. By asserting dominance, they attempt to validate themselves and ward off feelings of insecurity.
- Mechanisms of superiority include:
- Exaggerating achievements
- Belittling others to emphasize their status
- Expressing disdain for anything perceived as threatening their superiority
For fragile narcissists, grandiosity is akin to a suit of armor, deflecting deep-seated vulnerability. Their exaggerated self-importance is a buffer against the painful recognition of their limitations.
- Behaviors demonstrating grandiosity:
- Name-dropping to associate with high-status individuals
- Insisting on having the best of everything
Key Takeaway: grandiosity serves as a shield for narcissists, protecting their delicate self-esteem by projecting an image of unassailable superiority.
Emotional Struggles of Narcissists
Narcissists often deal with internal conflicts that are masked by their outward confidence. These struggles are primarily centered around shame, guilt, anxiety, and depression.
Shame and Guilt
- Shame: Although narcissists may not openly acknowledge it, feeling humiliated about not meeting their or others’ expectations is a common burden they carry.
Key Takeaway: The shame can lead them to react defensively or with arrogance to hide their vulnerabilities.
- Guilt: While not commonly displayed, narcissists can experience guilt, particularly when their actions hurt others and affect their self-image.
Key Takeaway: Guilt may manifest subtly, as narcissists often shift blame to others to protect their ego.
Anxiety and Depression
- Anxiety: They often encounter anxiety, as the need to maintain their perceived superiority can create an underlying tension.
Key Takeaway: The perpetual pressure to uphold an ideal image can be a source of persistent anxiety for narcissists.
- Depression: Failures and perceived threats to their self-esteem can lead to episodes of depression, even if these are not visible to the outside world.
Key Takeaway: Despite a façade of confidence, depression can take hold when a narcissist’s self-worth is challenged.
Social and Interpersonal Dynamics
In exploring the social behavior of narcissists, it is critical to consider the two facets of empathy and the prevalence of certain toxic behaviors within group contexts.
Empathy and Its Lack in Narcissists
Empathy, the ability to understand and share the feelings of another, is often deficient in narcissists, which influences their social interactions. They may struggle to resonate with others’ emotions, making genuine connections rare.
- Understanding Others: Narcissists may find it hard to see things from another person’s perspective.
- Emotional Response: Their reactions can seem cold or uncaring to others’ distress.
Toxic Behaviors in Community Settings
Narcissists can introduce toxic dynamics within communities due to their social habits and desire for dominance.
- Pursuit of Attention: They may attempt to remain the focus, often at the expense of group harmony.
- Manipulative Tactics: Utilizing manipulation to maintain a position of power is shared.
Key Takeaways:
- A lack of empathy results in difficulties in forming deep social bonds.
- Narcissists’ behaviors can lead to unhealthy group dynamics and complicate community interactions.
Therapy and Treatment Options
 Successful therapy for narcissism hinges on recognizing its value and implementing tailored strategies under the guidance of a trained professional.
Successful therapy for narcissism hinges on recognizing its value and implementing tailored strategies under the guidance of a trained professional.
Understanding the Importance of Therapy
Therapy is a cornerstone in the treatment of narcissistic behavior. It offers a safe space where individuals can explore the roots of their narcissism. A therapist’s role is pivotal—they provide a caring and structured environment that encourages self-reflection and growth.
- Key Takeaway: Therapy is vital as it helps understand and address the deep-seated issues contributing to narcissism.
Strategies for Managing Narcissism
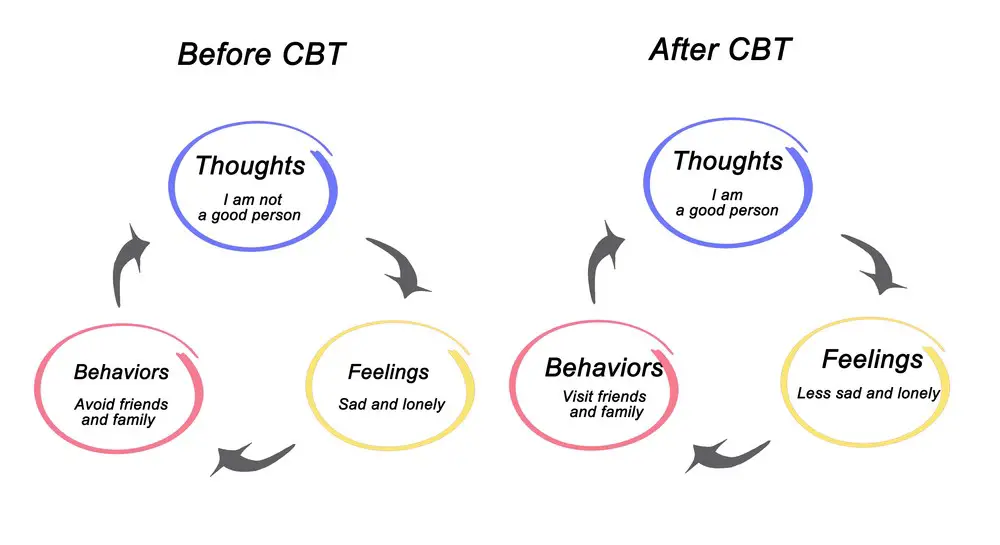 Practical strategies to manage narcissism involve a blend of techniques aimed at fostering empathy, improving relationships, and developing healthy self-esteem. Therapists may use the following approaches:
Practical strategies to manage narcissism involve a blend of techniques aimed at fostering empathy, improving relationships, and developing healthy self-esteem. Therapists may use the following approaches:
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): This focuses on altering negative thought patterns and behaviors.
- Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT): Incorporates mindfulness and distress tolerance skills.
- Group Therapy: Helps nurture empathy by placing individuals among peers.
- Family Therapy: Engages family members to improve dynamics and communication.
- Goal Setting: Therapists work with clients to set realistic and achievable goals to foster personal accountability.
- Consistency: Regular sessions reinforce progress and aid in managing setbacks.
Key Takeaway: A variety of therapy strategies are crucial for managing narcissistic traits and improving overall functioning.
Narcissism in the Digital Age
In the fast-paced digital world, narcissistic tendencies have found a new playground: social media.
Influence of Social Media on Narcissistic Tendencies
Social media platforms are often seen as fertile ground for individuals with narcissistic traits. These digital arenas offer endless opportunities for self-promotion and attention-seeking behavior.
- A key characteristic of narcissistic behavior is the constant need for admiration. Social media facilitates this by allowing users to broadcast their achievements and lifestyle to a broad audience, beckoning likes, comments, and shares.
- Communal narcissism, a form where individuals boast about their self-perceived contributions to a community, thrives on social media. Posts may highlight one’s charitable actions or social awareness to garner approval and admiration.
One significant impact of social media is how it amplifies these tendencies, allowing them to be broadcast to a broad audience. In a digital age where likes and followers can be equated with social standing, it’s easy to see how platforms reinforce and encourage narcissistic behaviors.
Key Takeaway: Social media is a double-edged sword that can amplify narcissistic behaviors by providing a platform for continuous self-promotion and validation.
The Pursuit of Social Validation Online
The quest for online validation spurs an insatiable appetite for social media engagement. This pursuit is intertwined with narcissistic tendencies, as individuals seek to confirm their self-worth through digital recognition.
- For narcissists, online platforms are not just social tools but a metric of their social standing. The number of likes, retweets, or followers can become an index of popularity or importance.
- Social validation online is often pursued through curated self-presentation. Individuals may meticulously manage their online personas to project an idealized image to attract more validation through digital engagement.
Critically, the digital pursuit of social validation can perpetuate a cycle where self-esteem becomes increasingly contingent on online reactions, further entrenching narcissistic behaviors.
Key Takeaway: The relentless pursuit of social validation online can lead to a dependency on digital feedback for self-esteem, reinforcing narcissistic tendencies.
Frequently Asked Questions
Navigating the complexities of narcissism, we often encounter a myriad of questions about how individuals with this condition behave and feel. This section aims to shed light on some common inquiries.
How do narcissists behave in relationships?
In relationships, narcissists may exhibit a need for admiration and a lack of empathy towards their partners. They often strive for control, seeking to maintain a position of power, and may become easily offended by perceived slights.
Key takeaway: Relationships with narcissists can be challenging due to their need for control and lack of empathy.
Can a person with narcissism truly experience happiness?
While individuals with narcissism can feel moments of happiness, their persistent need for admiration and validation might make sustained happiness elusive. They often depend on external validation rather than internal contentment.
Key takeaway: Lasting happiness may be challenging for narcissists as it’s tied to external validation.
Is jealousy a common trait among individuals with narcissism?
Jealousy can be a prominent feature in narcissists, stemming from their need for superiority and fear of being overshadowed. They may perceive others’ success as a threat to their own status.
Key takeaway: Jealousy is often rooted in the narcissist’s fear of not being the best.
What are effective strategies for interacting with an insecure narcissist?
To engage with an insecure narcissist effectively:
- Set clear boundaries.
- Avoid confrontation.
- Use strategic praise to navigate conversations.
Key takeaway: Clear boundaries and strategic communication can aid in smoother interactions with narcissists.
What are some potential risks of being in close contact with a narcissist?
Close contact with a narcissist might expose you to emotional manipulation and inconsistent affection. Such exposure can lead to psychological distress and may harm one’s self-esteem.
Key takeaway: Emotional manipulation is a risk factor in close relationships with narcissists.
Are people with narcissistic tendencies able to form genuine loving connections?
People with narcissistic tendencies might struggle to form genuine connections due to their lack of empathy and self-focused nature. However, some can learn to create more meaningful relationships with self-awareness and therapy.
Key takeaway: Genuine connections are challenging for narcissists but not impossible with effort and self-awareness.
 Jacob Maslow’s Bio
Jacob Maslow’s Bio
Hello! I’m Jacob Maslow. For nearly a decade, I navigated the complexities of co-parenting in a dual household setup after my divorce. However, a year ago, my world shifted dramatically when my ex-wife, exhibiting severe narcissistic behaviors, cut me off from our children. This abrupt change followed a brief period of cooperation with reunification therapy, which ceased as soon as our children agreed to end their alienation from me.
My journey has not been an easy one. To manage my mental health, I take Lexapro and have a long history with therapy, recently joining BetterHelp. I believe in the power of self-care and take long walks daily to clear my head.
My ex-wife’s actions have been challenging to comprehend and cope with. Her pattern of pursuing affairs with community leaders and then engaging in smear campaigns is a hallmark of narcissism. This behavior intensified as she aged, and her refusal to comply with court-ordered shared custody has led to an ongoing legal battle. Her actions have violated court orders and deeply affected our children and me.
Despite these hardships, I’ve channeled my experiences into helping others. Through my writing, I focus on mental health and dealing with narcissistic partners, aiming to support and empower those facing similar challenges. I firmly believe that anyone can overcome their mental health issues.
Additionally, I run a legal site dedicated to assisting individuals dealing with non-compliant spouses, particularly in cases involving the weaponization of children against one parent.
Having shared a close bond with my kids for years, their sudden absence has been a significant blow to my mental well-being. Yet, I remain committed to sharing my insights and experiences, hoping to make a difference in others’ lives.

- 3 Ways Wearing a Hat Can Help Lower Your Stress Levels - April 19, 2025
- Breaking the Silence: Why Men’s Mental Health Matters More Than Ever - April 15, 2025
- How to Transform a Home’s Patio Space into a Relaxing Space - March 23, 2025
This site contains affiliate links to products. We will receive a commission for purchases made through these links.


 Narcissists in Relationships
Narcissists in Relationships Jacob Maslow’s Bio
Jacob Maslow’s Bio
