As a BetterHelp affiliate, we receive compensation from BetterHelp if you purchase products or services through the links provided
Why is my anxiety worse at night? This question plagues many individuals who experience heightened nighttime anxiety. This blog post will examine the underlying causes of heightened nighttime anxiety and review strategies to help you find restful sleep.
We’ll discuss how your circadian rhythm and various stressors may impact your ability to fall asleep and how diet, exercise, relaxation techniques, stimulants, and technology use exacerbate nocturnal panic attacks. Finally, we’ll touch on when it might be necessary to seek professional help for managing and treating anxiety disorders.
By understanding why your anxiety worsens at night and implementing effective strategies from our discussion points above, you can take control of your mental health and work towards achieving a more peaceful bedtime routine.
Table of Contents:
- Anxiety and Sleep
- The Vicious Cycle of Anxiety and Insomnia
- Sleep Disruptions Caused by Anxiety
- Tips for Improving Sleep Quality Despite Nighttime Anxiety
- Stressors
- Diet & Exercise
- Relaxation Techniques
- Stimulants
- Technology Use
- Professional Help
- Frequently Asked Questions Why is My Anxiety Worse at Night
- Conclusion
Anxiety and Sleep

Anxiety can make it hard to drift off or remain asleep during the night, significantly influencing your sleep quality. The body’s stress response system, activated by anxiety, can lead to physiological changes such as increased heart rate and blood pressure, which interfere with restful sleep. In turn, poor sleep can exacerbate anxiety symptoms during the day.
The Vicious Cycle of Anxiety and Insomnia
When you’re struggling with anxiety at night, it often creates a vicious cycle. The more anxious you feel about falling asleep or staying asleep, the harder it becomes to do so. This leads to increased fatigue during daytime hours, worsening overall anxiety levels.
Sleep Disruptions Caused by Anxiety
- Falling Asleep: Racing thoughts or excessive worry may make it challenging for your mind to settle down enough for you to drift off into slumber.
- Maintaining Sleep: If you manage to fall asleep but wake up frequently due to anxious thoughts or nightmares related to your worries, this disrupts your natural sleep cycles and prevents deep restorative stages of sleep from occurring.
- Nighttime Panic Attacks: For some individuals with severe anxiety disorders like panic disorder or generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), nighttime panic attacks may occur as they try relaxing into sleep mode.
Tips for Improving Sleep Quality Despite Nighttime Anxiety
To break free from this exhausting cycle of nighttime anxiety interfering with healthy sleeping patterns, consider implementing these strategies:
- Form a tranquil pre-sleep habit that conveys to your body and mind that it is time for rest.
- Set a steady bedtime and rising schedule, day after day, even on the days off.
- Make your sleeping environment as comfortable as possible with cozy bedding, blackout curtains, and soothing scents like lavender essential oil diffused in the room.
Incorporating these tips into your daily life can help improve overall sleep quality while reducing nighttime anxiety symptoms. For more comprehensive solutions tailored to your unique needs, consider consulting with a mental health professional or seeking guidance from resources such as the Anxiety & Depression Association of America (ADAA).
Anxiety and sleep are intimately connected, so addressing any factors causing sleeping difficulties can help diminish anxiousness. Let’s look at how they interact better to understand the relationship between stressors and nighttime anxiety.
Stressors
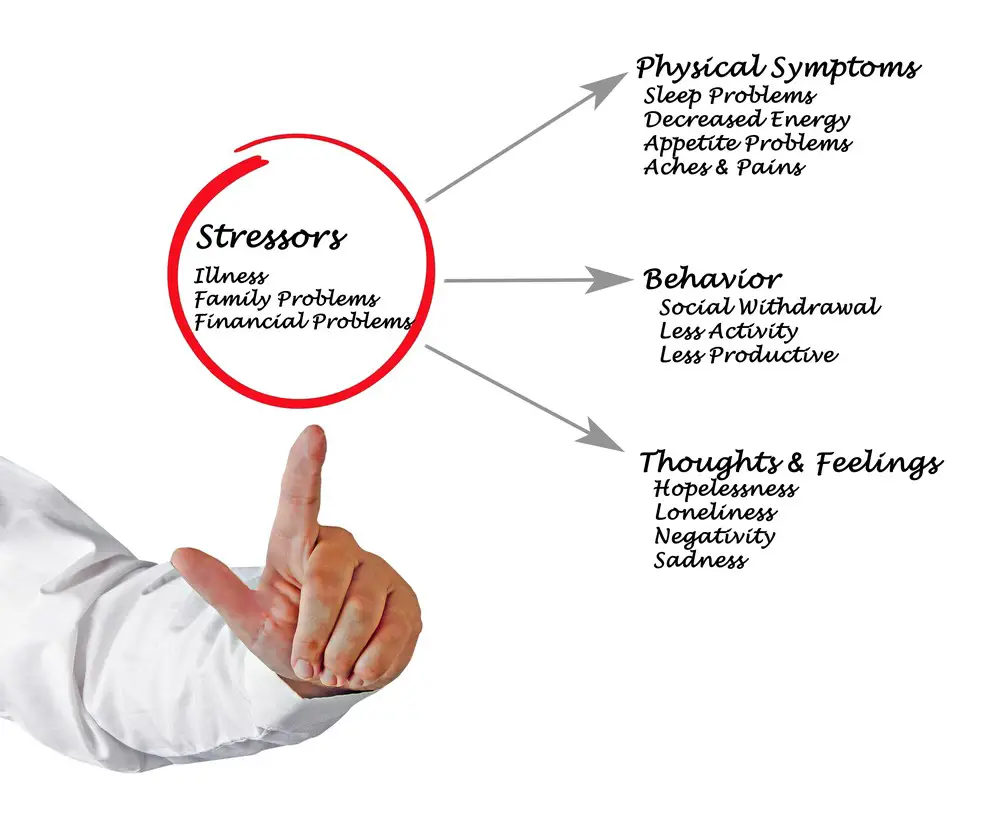
Uncovering the stressors building up during the day is vital to controlling your night-time anxiety. Identifying these stressors is a crucial step in managing your nighttime anxiety.
Work-Related Stress
Work-related stress is among the most common sources of anxiety for many people. Deadlines, demanding bosses, or conflicts with coworkers can increase feelings of tension and worry at night as you replay events from the day in your head.
Family Issues
Your family life may also be contributing to your nighttime anxiety. For example, arguments with loved ones, concerns about children’s well-being, or unresolved issues within relationships can cause emotional turmoil that makes falling asleep more challenging.
Social Anxiety & FOMO (Fear Of Missing Out)
In today’s digital age, where social media plays such an influential role in our lives, social anxiety and Fear Of Missing Out (FOMO) are becoming increasingly prevalent factors causing sleepless nights. In addition, comparing ourselves to others on social platforms or worrying about not being included in certain events can lead to heightened levels of nighttime anxiety.
Tips For Managing Daily Stressors:
- Create boundaries: Establish limits between work and personal life to prevent work-related stress from spilling into your home environment.
- Communicate: Openly discuss any concerns or issues with family members and loved ones to foster a supportive atmosphere at home.
- Digital detox: Limit social media use, especially before bedtime, to avoid the negative impact of FOMO on your mental health. Consider trying a digital detox.
Proactive measures can be taken to combat daily pressures, which may lead to a reduction in nighttime jitters and an enhancement of overall mental health.
Stressors can be a leading factor in causing anxiousness at night, so it’s essential to identify and tackle them for better mental well-being. Maintaining a nutritious diet and regular physical activity are critical for controlling stress levels, as we’ll explore further shortly.
Diet & Exercise

Maintaining a healthy diet and regular exercise are essential to managing anxiety symptoms, especially at night. Both of these factors can significantly impact your overall mental health and well-being.
A Balanced Diet for Anxiety Relief
A diet rich in wholesome foods, fruits, vegetables with lean proteins, and complex carbs may help balance mood swings and anxiety. In addition, consuming foods high in magnesium (e.g., leafy greens), omega-3 fatty acids (e.g., salmon), vitamin B6 (e.g., bananas), and tryptophan (e.g., turkey) may also help reduce anxiety symptoms.
- Magnesium: Leafy greens like spinach or kale
- Omega-3 fatty acids: Fatty fish such as salmon or mackerel
- Vitamin B6: Bananas, chickpeas, or potatoes with skin on
- Tryptophan: Turkey breast meat or pumpkin seeds
Limited Sugar Intake to Avoid Blood Sugar Spikes:
Reducing sugar intake is crucial for managing nighttime anxiety because excessive sugar consumption can lead to blood sugar spikes followed by crashes that exacerbate feelings of stress and unease. Opt for natural sweeteners like honey instead of refined sugars when possible.
Avoid Alcohol Before Bedtime:
While alcohol might seem like an effective way to relax before bed initially, it ultimately disrupts sleep patterns which could worsen nighttime anxiety symptoms. Therefore, it’s best to avoid alcohol consumption in the hours leading up to bedtime.
Exercise for Anxiety Management
Regular physical activity has been proven to help reduce anxiety symptoms, as it releases endorphins, natural mood elevators. Exercise can also improve sleep quality by helping you feel tired and relaxed at night.
- Strive to get in at least thirty minutes of exercise, like a quick jog or swimming, most days of the week.
- Incorporate stress-reducing activities like yoga or tai chi into your routine, which can be particularly helpful in managing nighttime anxiety.
- Avoid intense workouts close to bedtime since they may increase adrenaline levels and make it harder to fall asleep. Instead, opt for gentle stretching or relaxation exercises before bed.
By prioritizing a balanced diet and regular exercise regimen, you’ll be better equipped to manage your nighttime anxiety symptoms effectively while promoting overall mental health and well-being.
To ensure optimum mental well-being, it is essential to maintain a balanced lifestyle that includes both proper nutrition and physical activity. But, moving on, relaxation techniques are also vital in managing anxious feelings – let’s explore how these methods can be used.
Relaxation Techniques

To promote restful sleep, relaxation techniques can be incorporated into the bedtime routine to help alleviate anxious thoughts. By practicing these methods regularly, you can train your mind and body to relax more effectively when it’s time for bed.
Deep Breathing Exercises
Deep breathing exercises are a simple yet effective way to reduce anxiety levels at night. When we’re anxious, our breath tends to become shallow and rapid, increasing feelings of stress. Deep breathing helps counteract this by promoting full oxygen exchange in the lungs and slowing down the heart rate.
- Sit or recline in a relaxed position, placing one hand on your chest and the other on your abdomen.
- Breathe slowly through your nose for four counts, feeling your abdomen rise as you fill up with air.
- Hold that breath for four counts before exhaling slowly through pursed lips over another four counts while focusing on releasing tension from every part of your body.
- Repeat this process multiple times until you experience a sense of tranquility and relaxation.
Progressive Muscle Relaxation (PMR)
Progressive muscle relaxation (PMR) is another helpful technique for reducing nighttime anxiety. PMR involves tensing specific muscle groups throughout the body before consciously relaxing them to release physical tension associated with stress or anxiety:
- First, find a comfortable position, either sitting or lying down.
- Starting with your toes and working through the body, tense each muscle group for five seconds before releasing the tension over ten seconds. Be mindful of how it feels to release that tension from each body part.
- Continue this process until you’ve tensed and relaxed all major muscle groups.
Incorporating these practices into your bedtime routine can foster a sense of serenity and composure, making it easier to drift off despite nighttime worries. Remember, consistency is vital; practicing these methods regularly will make them more effective as you train both mind and body to relax when needed most at night.
Yoga, meditation, and diaphragmatic breathing can reduce stress and augment mental well-being. Stimulants are compounds that can boost wakefulness and vigor in the body.
Stimulants
Nighttime anxiety can be exacerbated by the consumption of stimulants, which directly impact your nervous system and make it difficult for you to relax or fall asleep. Some common stimulants that may contribute to increased nighttime anxiety include:
- Caffeine
- Nicotine
- Sugar
- Certain medications (e.g., decongestants)
Avoiding Caffeine Before Bedtime
Caffeine disrupts sleep patterns, making it harder to fall asleep and stay asleep throughout the night. This disruption in sleep quality can lead to heightened anxiety levels, creating a vicious cycle that’s hard to break.
To reduce nighttime anxiety, limit your caffeine intake during the day and avoid consuming caffeinated beverages at least six hours before bedtime. Give your body a chance to process caffeine so it won’t impede your capacity to unwind before bed.
Reducing Nicotine Consumption
Like caffeine, nicotine is another stimulant that can negatively affect sleep quality and anxiety. In addition, smoking cigarettes or using other tobacco products close to bedtime may cause restlessness and difficulty falling asleep due to its stimulating effects on the brain.
If you’re struggling with nighttime anxiety, consider cutting back on nicotine use altogether or avoiding smoking within two hours of going to bed. You might also want to explore alternative methods like nicotine replacement therapy (NRT) or counseling to help you quit smoking and improve your overall mental health.
Monitoring Sugar Intake
Consuming excessive sugar can lead to spikes in blood sugar levels, which may increase anxiety. Make your evening meals and snacks low in added sugars and high in complex carbohydrates, protein, and healthy fats to support balanced dieting. Choose foods low in added sugars and contain complex carbs, protein, and beneficial fats.
Consuming stimulants with awareness during the day, particularly close to bedtime, can be a critical factor in reducing nighttime stress and improving sleep.
Responsible use of stimulants can be beneficial in managing anxiety, yet the digital realm’s effects on our emotions should also be considered. As a result, technology use has become increasingly popular to address mental health issues and understand how our digital devices may impact us emotionally.
Technology Use

Limiting technology use before bedtime is crucial in managing nighttime anxiety and promoting better sleep quality. For example, the luminosity of monitors can impede the production of melatonin, a hormone that governs sleep-wake patterns, by your organism. This interference can lead to difficulty falling asleep and staying asleep, exacerbating anxiety symptoms.
Avoid Overstimulation
Engaging with electronic devices such as smartphones, tablets, or computers close to bedtime may overstimulate your brain and make it harder for you to relax and fall asleep. Social media platforms and news websites are especially notorious for causing stress and increasing anxiety levels due to their constant stream of information.
Tips for Reducing Screen Time Before Bed:
- Create a tech-free zone: Designate your bedroom as a space free from electronic devices like phones, laptops, or televisions.
- Establish a screen curfew: Set a specific time each night when you will stop using all electronic devices – ideally, at least an hour before bed.
- Incorporate relaxing activities into your evening routine: Replace screen time with calming activities such as reading a physical book, journaling, or practicing mindfulness meditation (learn how here).
- Use blue light-blocking tools: If you must use screens before bed (e.g., due to work commitments), consider using apps that filter out blue light on your device or wearing blue-light-blocking glasses (more info here).
Reducing technology use before bedtime can help create a more relaxing environment that promotes better sleep quality and reduces nighttime anxiety.
Technology use can be an essential tool to help manage anxiety, but it should not replace professional help. Professional help is the best way to address underlying causes of anxiety and find effective treatments for long-term relief.
Professional Help
Click Here To Save 10% On Your First Month
If your nighttime anxiety is too challenging to manage without help, you may want to consider seeking professional assistance. Several mental health professionals can provide guidance and support in managing severe nighttime anxiety symptoms or underlying conditions that may be causing them.
Therapists and Counselors
Licensed therapists and counselors are trained to help individuals cope with various mental health issues, including anxiety disorders. Therapists and counselors can aid you in forming tailored tactics to manage your nocturnal anxiety, such as CBT approaches or exposure treatment.
Psychiatrists
Medication might sometimes be necessary to alleviate severe symptoms of nighttime anxiety. A psychiatrist, a medical doctor specializing in mental health, can evaluate whether medication is appropriate for you and prescribe the correct type of medication based on your specific needs.
Sleep Specialists
Insomnia and other sleep disorders can significantly contribute to heightened anxiety levelsy. Consider consulting a sleep specialist if you suspect a sleep disorder might contribute to your increased nighttime anxiety levels. These experts can assess underlying sleep issues and recommend appropriate treatments or interventions.
Finding the Right Professional Help:
- Referrals: Ask friends, family members, or primary care physicians for recommendations when seeking mental health professionals.
- Insurance: Check with your insurance provider for a list of in-network mental health professionals.
- Online Directories: Utilize online directories, such as the Psychology Today Therapist Directory, to search for therapists and psychiatrists in your area.
No one should have to suffer through sleepless nights filled with anxiety. Seeking professional help can be essential to improving your mental well-being and achieving better quality sleep. Remember, reaching out for support when needed is never too late.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do I stop nighttime anxiety?
To stop nighttime anxiety, establish a consistent sleep routine, practice relaxation techniques like deep breathing or meditation before bed, limit exposure to screens and technology in the evening, maintain a healthy diet, and exercise regularly. Additionally, consider seeking professional help if anxiety persists.
What are three coping strategies for anxiety?
Three effective coping strategies for managing anxiety include practicing mindfulness meditation to stay present-focused, engaging in regular physical activity to release endorphins and reduce stress levels, and challenging negative thoughts through cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) techniques.
What are 5 coping skills for anxiety?
- Mindfulness meditation
- Physical activity
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT)
- Social support from friends or family
- Breathing exercises
Conclusion
By understanding the underlying causes of my anxiety worsening at night, we can begin to make meaningful changes in our lives. Ensuring adequate rest, abating stressors and stimulants, doing physical activity habitually, and employing relaxation tactics are all great methods to lessen your signs. However, seeking a mental health professional for extra help and direction may be beneficial if your anxiety persists despite self-care measures.
By visiting our website, take the first step towards understanding why your anxiety worsens at night. Our expert team can provide valuable advice and resources to help manage your nighttime anxiety.
- 3 Ways Wearing a Hat Can Help Lower Your Stress Levels - April 19, 2025
- Breaking the Silence: Why Men’s Mental Health Matters More Than Ever - April 15, 2025
- How to Transform a Home’s Patio Space into a Relaxing Space - March 23, 2025
This site contains affiliate links to products. We will receive a commission for purchases made through these links.



