As a BetterHelp affiliate, we receive compensation from BetterHelp if you purchase products or services through the links provided
Deciding between lorazepam and clonazepam for anxiety treatment can be a challenge, as both medications belong to the benzodiazepine class and are prescribed to help manage anxiety disorders. However, some critical differences between the two drugs can influence their suitability for specific individuals. In this article, we’ll explore the differences in indications for use, dosage and administration, mechanism of action, side effects, and effectiveness so you can make an informed decision.
Lorazepam and clonazepam both offer relief from anxiety and panic attacks, but their specific uses vary slightly. Lorazepam is also prescribed to treat insomnia, panic attacks, and alcohol withdrawal, while clonazepam is used to reduce seizure frequency in certain seizure disorders, in addition to anxiety treatment. Understanding each medication’s indications, effects, and potential side effects can support a conversation with your healthcare provider in choosing the most appropriate medication for your needs.
Key Takeaways
- Lorazepam and clonazepam are both benzodiazepines used to treat anxiety disorders but with some differences in their specific uses.
- Understanding both drugs’ indications, dosage, side effects, and effectiveness can inform your decision-making process.
- Consult your healthcare provider before making any decisions regarding anxiety treatments to ensure the best outcome for your situation.
Understanding Lorazepam and Clonazepam
Lorazepam and Clonazepam are both benzodiazepines, a type of medication commonly used to treat anxiety disorders, panic attacks, seizures, and insomnia. These medications are known by their respective brand names: Ativan (Lorazepam) and Klonopin (Clonazepam).
Lorazepam (Ativan) is primarily used in treating anxiety and as a preoperative medicine. It may also be prescribed for insomnia, panic attacks, and alcohol withdrawal.
Clonazepam (Klonopin), on the other hand, is often used to treat seizure disorders such as akinetic and myoclonic seizures, as well as those resulting from Lennox-Gastaut syndrome. It can also be used short-term for panic disorder and anxiety relief.
Both medications work by increasing the activity of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), a neurotransmitter in the brain that helps regulate mood. This effect makes them efficient in alleviating anxiety and producing sedation.
However, there are some differences between these two anti-anxiety medications that you should be aware of:
- Onset and duration: Lorazepam has a faster onset time than Clonazepam. At the same time, it has a shorter duration of therapeutic effect, which can be beneficial for temporary relief or short-term use.
- Side effects: Common side effects of Lorazepam include drowsiness and dizziness. Similarly, Clonazepam can cause drowsiness as well. However, long-term use of Clonazepam may lead to dependence and other potential issues.
- Clearance: Diazepam (Valium), a related benzodiazepine, has a slow clearance, causing the elimination half-life to vary from 30 to 100 hours. This trait raises concerns about accumulation-related side effects, especially fall risk among the elderly.
Ultimately, your doctor will consider your specific needs, medical history, and the potential risks and benefits of each medication before deciding which benzodiazepine is more appropriate for your situation.
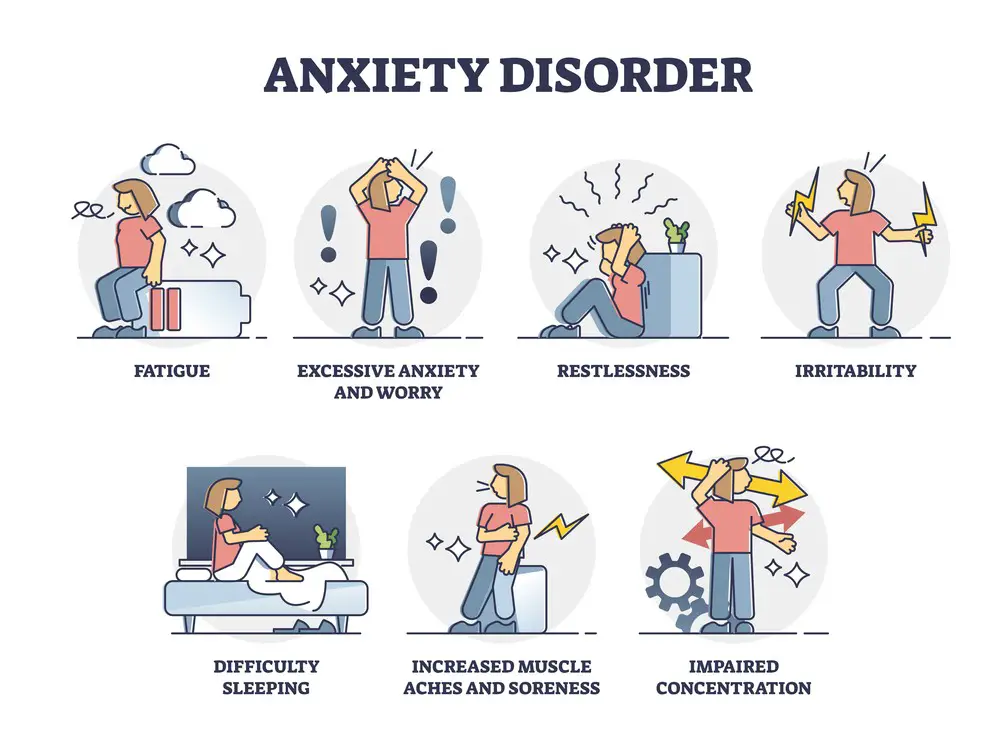
Indications for Use
Anxiety Disorders
Both lorazepam and clonazepam are benzodiazepines, which are commonly prescribed for the management of anxiety disorders. These medications can help with symptoms of anxiety, such as tension and irritability. For panic disorders, they are equally effective, so your doctor may prescribe one based on your specific needs and potential side effects.
Sleep Disorders
Insomnia and other sleep disturbances can be caused by anxiety or other factors. Lorazepam is often prescribed to treat sleep problems due to its soothing properties. On the other hand, a study found that clonazepam and lorazepam can help improve sleep scores, so either medication might be considered for sleep-related issues depending on your doctor’s recommendation.
Seizure Disorders
Clonazepam is widely used for specific seizure disorders, including Lennox-Gastaut syndrome, a rare form of epilepsy. This medication offers a way to reduce seizure frequency and provide relief for those affected. Lorazepam, on its part, is often administered for status epilepticus, a dangerous condition characterized by continuous seizures. Remember, it’s essential to consult with your doctor for the best treatment option based on your circumstances and medical history.
Key takeaway: While both lorazepam and clonazepam can help with anxiety and sleep disturbances, clonazepam is typically chosen for certain seizure disorders. Your doctor will ultimately prescribe the best medication for your condition and needs.
 Dosage and Administration
Dosage and Administration
When it comes to taking Clonazepam or Lorazepam for anxiety, it’s essential to follow the recommended dosage and administration guidelines for each medication.
Clonazepam – This medication is typically administered in an oral tablet form. The initial dose for adults is 0.25 mg, taken twice a day. Your doctor may adjust your dose as needed, but the usual therapeutic dose ranges from 1 to 4 mg daily, taken in divided doses1.
Lorazepam – Lorazepam is available as an oral tablet or as an injection. For adults and children older than 12, the usual dose ranges from 2 to 6 mg per day, taken in divided doses2. Older adults may start with a lower dose of 1 to 2 mg daily, divided into smaller doses2.
Always remember to:
- Follow your doctor’s instructions regarding dosage and administration, as they may adjust your doses based on your needs.
- Take the oral tablets with a full glass of water to help with swallowing and absorption.
- Do not abruptly stop taking either medication, as this can lead to withdrawal symptoms. Your doctor will guide you on taper off the medication safely, if necessary.
- Consult your doctor if you experience any side effects or if the medication does not seem to be effective in managing your anxiety symptoms.
Key takeaway: Dosage and administration guidelines for Clonazepam and Lorazepam differ slightly, and it’s crucial to follow your doctor’s instructions to ensure a safe and effective treatment for your anxiety.
Footnotes
- Clonazepam (Klonopin®): The initial dose is 0.25 mg daily to twice a day; the dose can be increased by 0.125-0.25 mg daily or two times a day every 2-3 days; the usual therapeutic dose is 1-4 mg total/day in divided doses. Benzodiazepines | Johns Hopkins Psychiatry Guide.
- Lorazepam (Oral Route) Proper Use – Mayo Clinic: Adults and children 12 years and older—2 to 6 milligrams (mg) in divided daily doses. Your doctor may adjust your dose as needed. For older adults, 1 to 2 mg in divided doses per day. Your doctor may adjust your dose as needed.
 Mechanism of Action
Mechanism of Action
When it comes to understanding how lorazepam and clonazepam work to help alleviate anxiety, it’s essential to be familiar with their mechanism of action. Both drugs are classified as benzodiazepines, which means they work similarly in the central nervous system (CNS).
One key aspect of their mechanism of action is their impact on GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid). GABA is the main inhibitory neurotransmitter in the CNS, serving to calm down activity within the brain and reduce excitement. When you’re feeling anxious, your brain is in a state of overstimulation and requires something to calm it down. That’s where lorazepam and clonazepam come into play.
- Lorazepam primarily binds to GABA receptors found in high concentrations in the limbic system, a region of the brain involved in emotional responses, as well as the thalamus and hypothalamus. By binding to these GABA receptors, lorazepam enhances the inhibitory effects of GABA neurotransmission, resulting in an increased calming effect on the CNS.
- Clonazepam follows a similar process, impacting GABA receptors within the brain and promoting inhibitory GABA neurotransmission. However, clonazepam is known to have a broader and longer-lasting effect, making it useful for not only anxiety disorders but also certain seizure disorders.
In summary, lorazepam and clonazepam work in your brain by targeting GABA receptors, which are crucial for maintaining a healthy balance between excitation and inhibition. By increasing the inhibitory effects of GABA neurotransmission, these medications help alleviate anxiety by calming down your CNS. Remember that every individual is different, and it’s essential to work closely with a healthcare professional to determine the best medication for your unique needs.
 Side Effects
Side Effects
Common Side Effects
When taking either lorazepam or clonazepam for anxiety, you may experience some common side effects. These side effects are usually mild and go away with continued use, but it’s important to be aware of them. They include:
- Drowsiness
- Dizziness
- Headache
- Blurred vision
- Unsteadiness
- Weakness
- Tiredness
- Nausea
- Vomiting
Monitoring these side effects during your treatment is crucial as well as informing your healthcare provider if they persist or worsen.
 Serious Side Effects
Serious Side Effects
While most people tolerate these medications well, there is a risk of more severe side effects. If you experience any of the following, contact your healthcare provider immediately:
- Depression
- Suicidal thoughts
- Respiratory Depression
- Rage or aggressive behavior
These severe side effects are rare, but it’s essential to be aware of them and report any unusual changes in mood or behavior.
Withdrawal Symptoms
Both lorazepam and clonazepam have the potential for withdrawal symptoms if discontinued abruptly. These medications, like other benzodiazepines, can lead to physical dependence and addiction. To minimize withdrawal symptoms, your healthcare provider will likely reduce your dose gradually. Possible withdrawal symptoms include:
- Sweating
- Increased anxiety
- Irritability
- Insomnia
- Tremors
- Seizures
Remember to consult your healthcare provider before stopping the medication or adjusting. They can guide you through a safe tapering process to minimize withdrawal symptoms.
Warnings and Precautions
When considering the use of Clonazepam or Lorazepam for anxiety, it’s crucial to be aware of the potential risks that come with using these medications. Familiarizing yourself with the appropriate warnings and precautions can help you make an informed decision and ensure you’re using the medications safely.
One critical factor to consider is the potential for dependence. Both Clonazepam and Lorazepam are benzodiazepines, which can lead to physical and psychological dependence when used long-term. To minimize this risk, following your healthcare provider’s recommendations regarding dosage and duration of treatment is important.
If you’re pregnant or breastfeeding, you should talk to your healthcare provider before using these medications. These drugs can potentially have adverse effects on the fetus or be passed to the baby through breast milk, causing potential harm.
The elderly population should exercise particular caution when using Clonazepam and Lorazepam. These medications can cause drowsiness, dizziness, and impaired coordination, increasing the risk of falls and other accidents for older individuals. It’s essential to consult your healthcare provider to discuss the risks and benefits for your specific situation.
Patients with liver or kidney disease also need to be cautious when using these medications, as they are metabolized by the liver and excreted by the kidneys. Individuals with these conditions may require a lower dose or alternative treatments, so discuss this with your healthcare provider.
Finally, it’s crucial to understand the potential for misuse of benzodiazepines like Clonazepam and Lorazepam. Misusing these medications, such as taking them without a prescription or outside the appropriate dosage, can lead to significant harm or even fatal consequences. Stick to your healthcare provider’s guidelines and have an open dialogue about the appropriate use of these medications.
By being conscious of these warnings and precautions, you are taking responsible steps in managing your anxiety with Clonazepam or Lorazepam. Always consult your healthcare provider if you have any questions or concerns about these medications and your health.
Interactions
When talking about anxiety medications like lorazepam and clonazepam, it’s essential to be aware of potential interactions with other substances. These interactions could potentially affect their efficacy or lead to dangerous side effects. To help you better understand some of the possible interactions, here’s a friendly breakdown:
Alcohol
Combining alcohol with either lorazepam or clonazepam can significantly increase the sedative effects, leading to central nervous system (CNS) depression, increased drowsiness, and impaired coordination. It’s best to avoid alcohol when taking these medications for anxiety treatment.
Drug Interactions
Both lorazepam and clonazepam can interact with multiple other substances. A few common drug categories that might cause interactions include:
- Opioids and narcotics: Using benzodiazepines like lorazepam and clonazepam together with opioids or narcotics can lead to increased sedation, respiratory depression, and even potentially fatal outcomes. Be sure to discuss any concurrent opioid use with your healthcare provider.
- Barbiturates and antipsychotics: These medications can also have additive CNS and respiratory depressive effects when taken with lorazepam or clonazepam, leading to an increased risk of adverse reactions.
- Anticonvulsant medications: Since benzodiazepines can act as anticonvulsants themselves, combining them with antiepileptic drugs may alter the effectiveness of both medications.
- Antidepressants: Interactions with selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) or tricyclic antidepressants may lead to increased sedation. Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs), another class of antidepressants, can potentially lead to a dangerous interaction called serotonin syndrome.
- Antihistamines: Combining lorazepam or clonazepam with some antihistamines, especially those with sedative properties, can enhance drowsiness and sedation.
Keep in mind that this list isn’t exhaustive. It’s crucial to consult your healthcare provider or pharmacist for advice on specific drug interactions based on your individual medical history and current medications.
Remember, be open with your healthcare provider about any substances you might be taking, as this allows them to give you the best recommendations based on the latest information. Stay safe and vigilant when taking your anxiety medication.
Off-Label Uses
Regarding off-label uses, both Lorazepam and Clonazepam have some compelling applications that could prove beneficial in certain situations.
Lorazepam, commonly known as Ativan, is often prescribed for treating insomnia and can be effective in managing alcohol withdrawal symptoms. It is quite helpful in easing agitation and controlling seizures during alcohol detoxification. In addition to these uses, your doctor might consider it helpful in treating burning mouth syndrome, as it can relieve the associated sensations.
Clonazepam, on the other hand, is known by its brand name, Klonopin, and has a few off-label uses of its own. It can be beneficial in addressing restless legs syndrome, as it helps in relieving the discomfort and urge to move your legs. Clonazepam also offers support in treating alcohol withdrawal, although it may not be the first choice when compared to Lorazepam.
Here’s a summary of the off-label uses for your convenience:
- Lorazepam: Alcohol withdrawal, insomnia, burning mouth syndrome
- Clonazepam: Restless legs syndrome, alcohol withdrawal
So, as you explore which medication might be better suited for managing anxiety, it’s essential to consider these off-label uses and their relevance to your specific needs. Discussing these options with your doctor can be valuable in making an informed decision about which medication to choose. And remember, it’s always important to follow your doctor’s advice when taking these medications, as doing so will ensure you achieve the best possible results while prioritizing your safety and well-being.
Comparing Effectiveness
When comparing the effectiveness of lorazepam and clonazepam for anxiety treatment, it’s essential to consider their specific uses and benefits. Both medications are benzodiazepines, which help reduce anxiety by enhancing the effect of a neurotransmitter called gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). This results in a calming effect on the brain and body.
Anxiety Relief
Both lorazepam and clonazepam are effective in treating anxiety disorders. A multicenter study revealed no significant differences between the two drugs in terms of improvements in anxiety and sleep scores. However, the specifics of your condition and individual factors may impact which medication is better suited for you.
Insomnia
While clonazepam can help reduce anxiety-related sleep disturbances, lorazepam is also prescribed to treat insomnia directly. Its sedative properties may provide better relief for those struggling with sleep problems in addition to anxiety.
Seizures
Clonazepam is also used to treat seizure disorders, making it a versatile choice for those who experience both anxiety and seizures. However, lorazepam is not typically prescribed for seizure management.
Memory and Coordination
As with other benzodiazepines, both lorazepam and clonazepam can cause temporary memory impairment, impair coordination, and affect attention. The specific impact on cognitive function may vary between individuals, so it is crucial to monitor your reaction to either medication closely.
Mood
Although both medications help manage anxiety, they may affect your mood differently. Talking to your doctor about any mood changes you experience while taking these medications is crucial, as this information can help determine the most appropriate treatment for your individual needs.
In summary, both lorazepam and clonazepam are effective at treating anxiety, but they have different uses and benefits. It is vital to work closely with your doctor to determine the optimal medication for your unique situation, considering factors like insomnia, seizure disorders, cognitive impact, and mood.
Conclusion
In conclusion, both lorazepam and clonazepam are benzodiazepines that can effectively help manage anxiety. They work by increasing the activity of GABA, a neurotransmitter that helps regulate mood. However, there are some differences between the two that may influence your decision:
- Long-term treatment: Clonazepam has been shown to lead to a slightly better Clinical Global Impression of Improvement rating than paroxetine when used as a long-term treatment. This implies that for some individuals, clonazepam may be more effective over time.
- Conditions treated: While both medications can be used for anxiety and panic disorders, only clonazepam is specifically approved for treating seizures like akinetic and myoclonic seizures, as well as those resulting from Lennox-Gastaut syndrome. On the other hand, Ativan (lorazepam) is used for more severe types of seizures like status epilepticus.
Ultimately, your choice between lorazepam and clonazepam for anxiety should be based on your specific needs and in consultation with your healthcare provider. They will consider factors such as your medical history, current medications, and potential side effects before recommending the best option for you. So, remember to always work closely with your healthcare provider when considering these medications for anxiety management.
Frequently Asked Questions
Lorazepam vs Clonazepam: Which has fewer side effects?
Both Lorazepam and Clonazepam are benzodiazepines, so their side effects can be pretty similar. Common side effects for both include drowsiness, dizziness, and impaired coordination. However, the severity and frequency of side effects can vary from person to person. It’s crucial to work with your healthcare professional to determine the best option for you and monitor any side effects that arise.
How do the anxiety relief durations compare between Lorazepam and Clonazepam?
Lorazepam has a shorter half-life than Clonazepam, meaning its effects last for a shorter duration. Lorazepam is typically effective for around 4 to 6 hours, while Clonazepam can last up to 8 to 12 hours. The choice between the two depends on your specific needs and how long you require relief from anxiety symptoms.
Lorazepam vs Clonazepam: Which one is more effective for panic attacks?
Lorazepam and Clonazepam are both effective in treating panic attacks. Lorazepam may be preferred due to its rapid onset of action, which can provide relief within 20 to 30 minutes. In contrast, Clonazepam has a slower onset but provides longer-lasting effects. Your healthcare provider will consider your specific needs and medical history when prescribing the most appropriate medication for you.
Can you switch between Lorazepam and Clonazepam safely?
Switching between Lorazepam and Clonazepam should be done under the guidance and supervision of a healthcare professional. They will consider factors such as your medical history, current medications, and the reason for switching. The process might involve gradually tapering off one medication while introducing the other to ensure a smooth and safe transition.
What are the main differences between Lorazepam and Clonazepam?
- Duration of action: Lorazepam has a shorter duration of action (4-6 hours) than Clonazepam (8-12 hours).
- Onset of effects: Lorazepam offers faster anxiety relief (within 20-30 minutes), while Clonazepam takes longer to take effect.
- Primary uses: Lorazepam is typically used for acute anxiety and panic attacks, while Clonazepam is often prescribed for long-term anxiety management and seizure disorders.
Which medication is better for long-term anxiety management: Lorazepam or Clonazepam?
Clonazepam is usually a preferred choice for long-term anxiety management due to its longer duration of action. However, it’s essential to keep in mind that long-term use of benzodiazepines can lead to dependence and potential withdrawal symptoms. Your healthcare professional will closely monitor and reevaluate your medication regimen to ensure it remains effective and safe.
Key Takeaway: Both Lorazepam and Clonazepam are effective for treating anxiety, but they differ in their duration of action, onset of effects, and primary uses. It’s crucial to work with your healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate medication for your specific needs and to monitor for side effects and potential dependence.
- How to Transform a Home’s Patio Space into a Relaxing Space - March 23, 2025
- 5 Strategies to Use a Cell Phone to Help Manage Your Stress - March 23, 2025
- 4 Ways to Use Measurements to Create a Relaxing Sleep Space - March 23, 2025
This site contains affiliate links to products. We will receive a commission for purchases made through these links.

 Dosage and Administration
Dosage and Administration Mechanism of Action
Mechanism of Action Side Effects
Side Effects Serious Side Effects
Serious Side Effects
