As a BetterHelp affiliate, we receive compensation from BetterHelp if you purchase products or services through the links provided
Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) is a mental health condition characterized by intrusive thoughts, urges, or images, and compulsive behaviors performed to alleviate anxiety caused by these obsessions. Many factors can contribute to the severity of OCD, including environmental triggers, lifestyle choices, and comorbid conditions. Understanding these factors can help you better manage this complex and challenging disorder.
For individuals with OCD, encountering specific triggers can worsen symptoms and lead to increased distress. These triggers may arise in various aspects of life, such as relationships, physical health, and work situations. Additionally, certain behaviors and lifestyle choices may exacerbate OCD, including stress, lack of proper sleep, and substance use. By being aware of these possible catalysts, you can adopt strategies to minimize their impact and maintain better control over your OCD.
Key Takeaways
- Trigger awareness is crucial in effectively managing OCD
- Lifestyle choices, such as stress management, play a significant role
- Comorbid conditions can complicate OCD, making treatment essential
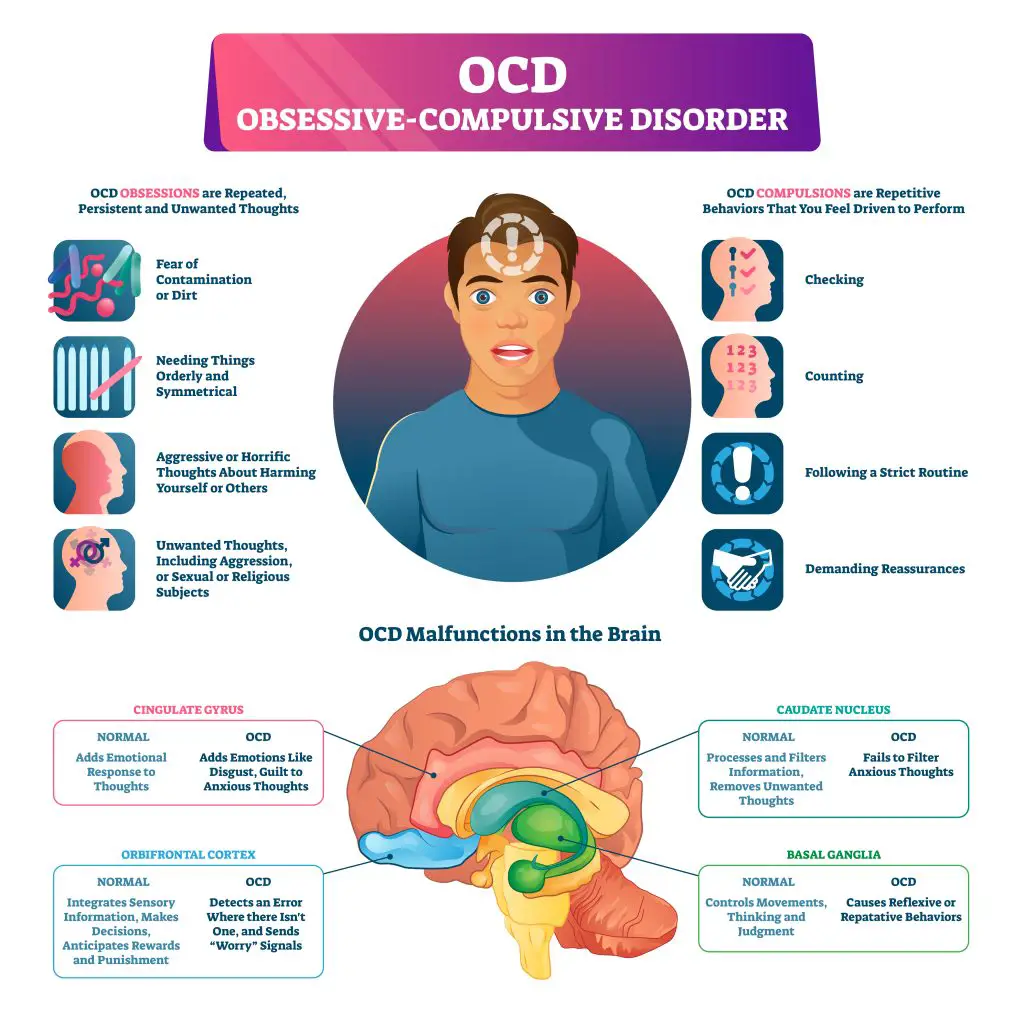
Understanding OCD
If you or someone close to you is struggling with Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD), it’s essential to have an understanding of the condition. OCD is a mental health disorder characterized by a combination of obsessions and compulsions. These two components can significantly interfere with everyday life and can make it challenging to manage daily activities.
Obsessions are unwanted, intrusive thoughts that cause anxiety, distress, or discomfort. They can take various forms, such as excessive fears about germs, constant doubt about one’s actions, or even disturbing thoughts about harm to oneself or others. No matter how hard you try, you can’t seem to shake off these thoughts, and they persistently invade your mind.
Compulsions, on the other hand, are repetitive, time-consuming behaviors or mental rituals you perform in response to the obsessive thoughts. Some common examples include excessive hand-washing, checking tasks multiple times, or arranging objects in a particular manner. These compulsive behaviors momentarily quell the anxiety and discomfort caused by the obsessions, but they don’t provide long-term relief.
Recognizing the symptoms of OCD is the first step in finding ways to manage and possibly alleviate them. Here are some key aspects of OCD to be aware of:
- Persistent and intrusive thoughts: OCD causes obsessive thoughts that are difficult to control and often lead to increased anxiety.
- Compulsive behaviors: Due to the obsessive thoughts, you may engage in repetitive actions or mental rituals.
- Time-consuming: Both obsessions and compulsions can consume a significant amount of time, affecting your daily routine and quality of life.
- Interference: OCD can interfere with your ability to function at work, school, or in social situations.
As you explore OCD further, it’s essential to remember that the disorder can manifest differently for every individual. Identifying the unique aspects of your experience will enable you to understand better how OCD affects you, paving the way for more personalized strategies to manage the condition.

Triggers that Worsen OCD
You may have noticed that your OCD symptoms seem to get worse in certain situations. Recognizing and understanding these triggers can help manage your OCD. Here are some common factors that can worsen OCD symptoms:
Stress and stressful life events: It’s no surprise that stress can exacerbate your OCD. Whether it’s work-related, relationship-based, or stemming from other life changes, stress can make it harder to resist compulsions and increase obsessive thoughts.
Trauma and abuse: Past traumatic experiences or abuse can contribute to the development of OCD and may also trigger worsening symptoms. It’s essential to address any unresolved trauma to manage your OCD better.
Anxiety and anxiety disorders: Fear and anxiety can feed obsessive thoughts and compulsive behaviors, making it even more challenging to break the cycle. If you’re dealing with other anxiety disorders in addition to OCD, addressing them can help reduce overall anxiety and improve your ability to cope with OCD.
- Key takeaway: Identifying and addressing stress, trauma, and anxiety can play a critical role in managing OCD.
Stressful times: When you’re going through a particularly stressful period of your life, you might notice your OCD symptoms getting worse. Be mindful of these challenging times and practice self-care to reduce their impact on your OCD.
Fears: Specific fears, such as a fear of germs or a fear of harm coming to a loved one, can drive your OCD compulsions and obsessions. Recognizing these fears and working through them can help lessen their influence on your OCD symptoms.
To cope with these triggers, try the following tips:
- Make time for relaxation and self-care, like exercise, meditation, and hobbies.
- Reach out for support from a therapist, family, or friends.
- Address any underlying anxiety or trauma with professional help.
- Develop healthy coping strategies for dealing with stress.
- Key takeaway: Taking care of yourself and addressing your triggers can make a significant difference in managing your OCD symptoms.
Remember, you’re not alone. By understanding and addressing these triggers, you’re taking the first steps in taking control of your OCD. Empower yourself with knowledge and support, and you can make a positive difference in your life.
 Impact of Lifestyle and Behavior
Impact of Lifestyle and Behavior
Your lifestyle and behavior can significantly influence the severity of your OCD symptoms, as well as the overall quality of your life. It’s essential to recognize the aspects of your everyday routine that may trigger or worsen the condition.
Exercise and Physical Health: Regularly exercising and maintaining a healthy lifestyle can help manage your OCD symptoms. Exercise has been proven to reduce stress, improve mood, and boost self-esteem, which can all have a positive impact on the severity of your OCD.
Establishing a Routine: Having a set routine can provide you with a sense of order and control, reducing the need for rituals and repetitive behaviors. Be sure to include time for self-care, relaxation, and social interaction to foster overall well-being.
Avoidance and Doubts: Trying to avoid situations that trigger your OCD can lead to isolation and a decline in the quality of your relationships. Instead, confront your triggers and face your doubts head-on. This approach can help reduce the power that your OCD has over you.
Coping Strategies: Developing healthy coping strategies is crucial for managing your OCD. These strategies might include mindfulness techniques, deep breathing exercises, and cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT). Experiment with different strategies to find the ones that work best for you.
- Maintaining Social Connections: It’s crucial to maintain your relationships and avoid isolation when dealing with OCD. Social interaction can provide support, encouragement, and a healthy distraction from obsessive thoughts and rituals.
Remember, a balanced lifestyle with a proactive approach to managing OCD can significantly improve your well-being and reduce the impact of your condition on your quality of life.
 Comorbidities and Complications
Comorbidities and Complications
When it comes to OCD, it’s essential to be aware of comorbidities and complications that can make the condition worse. Understanding these factors helps you take actionable steps for self-improvement.
Depression is a common comorbidity, often coexisting with OCD. The combination of both can amplify negative emotions and feelings of hopelessness. Addressing and treating depression may lessen your OCD symptoms as well.
Social anxiety disorder is another comorbidity that may accompany OCD. Feeling judged or scrutinized by others will hinder your progress and your ability to manage your condition effectively. Seek professional help to manage your anxiety, such as therapy or support groups.
Tic disorders, including Tourette syndrome, may be linked to OCD. Coping with these tics can be challenging; however, you can learn to manage them better through professional guidance and various coping strategies.
Sadly, substance abuse disorders often accompany OCD due to attempts to self-medicate. It’s crucial to recognize this and seek treatment to prevent further complications and worsening symptoms.
Exhaustion from the constant cycle of obsessive thoughts and compulsions can make OCD even harder to cope with. Make sure you take time for yourself to rest and practice self-care. Proper sleep, healthy eating, and regular exercise are all great ways to combat exhaustion.
These comorbidities and complications impact your progress and compromise your ability to manage your OCD effectively. Remember, it’s okay to ask for help, and with the proper treatment and support, you can work towards a healthier YOU.
 Role of Fear and Uncertainty
Role of Fear and Uncertainty
Dealing with OCD can be particularly challenging when fear and uncertainty come into play. These emotions are closely related to the core of OCD, as they can fuel the cycle of obsessive thoughts and compulsive behaviors. Let’s take a look at why these factors have such an impact on OCD.
First, fear and anxiety often trigger obsessive thoughts. When feeling threatened or anxious, it’s natural to want to gain control over your emotions. Unfortunately, with OCD, this desire can manifest in unhelpful and unhealthy ways. For example, you might start obsessing over your worries or performing rituals to alleviate the fear.
Uncertainty and doubt can also make OCD worse because they feed into your worries. When uncertain about a situation, it’s hard to shake off the feeling that something isn’t quite right. In the case of OCD, your brain might latch onto these doubts and amplify them, leading you down a spiral of worry and compulsive behaviors.
Now, how can you cope with fear, anxiety, uncertainty, and doubt in the context of OCD? Here are some strategies:
- Acknowledge your feelings: Recognize that fear and uncertainty are normal emotions and try to accept them without judgment.
- Develop healthy coping mechanisms: Ground yourself in the present moment through mindfulness exercises, deep breathing, or any activity that helps you relax and focus.
- Challenge your thoughts: Use cognitive-behavioral techniques, such as examining the evidence or considering alternative explanations for your worries, to create a balanced perspective.
By understanding the role of fear and uncertainty in exacerbating OCD symptoms, you can take steps to manage these emotions and, in turn, better manage your OCD. Remember that it’s okay to experience fear and anxiety, but learning how to handle them healthily can make a world of difference in your battle against OCD.
Effects of Aging and OCD
As you grow older, you might notice that your experience with Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD) can change. Aging can have various effects on your OCD symptoms and even introduce new risk factors that may impact how you manage the condition. Let’s dive into the key aspects of aging and its potential consequences on OCD.
First, it’s important to remember that everyone experiences aging differently. Some men may find that as they age, their OCD symptoms improve, while others might see an increase in symptom severity. It’s crucial to pay attention to your journey and any patterns that may emerge.
In some cases, aging can lead to cognitive decline and memory issues. This might make it harder for you to perform exposure and response prevention therapy effectively. However, don’t let this discourage you—continue working with your therapist and implement strategies that work best for you.
As you age, your risk of developing other health issues increases. These additional concerns may interact with OCD in various ways:
- Stress: Managing health problems or experiencing life changes common in older age can exacerbate stress. High-stress levels can worsen OCD symptoms.
- Sleep disruptions: Aging may impact your sleep quality, and insufficient rest can make it harder to manage OCD symptoms properly.
- Medications: The medications used to manage age-related health problems might interfere with your OCD treatment. It’s essential to discuss this with your doctor and find the best balance for you.
Considering these factors, here are some tips for managing your OCD as you age:
- Stay physically active: Regular exercise can benefit your mental health and help keep stress levels in check.
- Implement relaxation techniques: Meditation, deep breathing exercises, or yoga can support your mental well-being.
- Address sleep issues: Prioritize good sleep hygiene and discuss any sleep disturbances with your doctor.
- Communicate with your healthcare team: Keep your doctor and therapist informed about any new health conditions, medications, or changes in your OCD symptoms.
In conclusion, while aging might present new challenges for individuals living with OCD, paying attention to patterns and adopting helpful strategies can support you in managing your symptoms throughout your life journey.
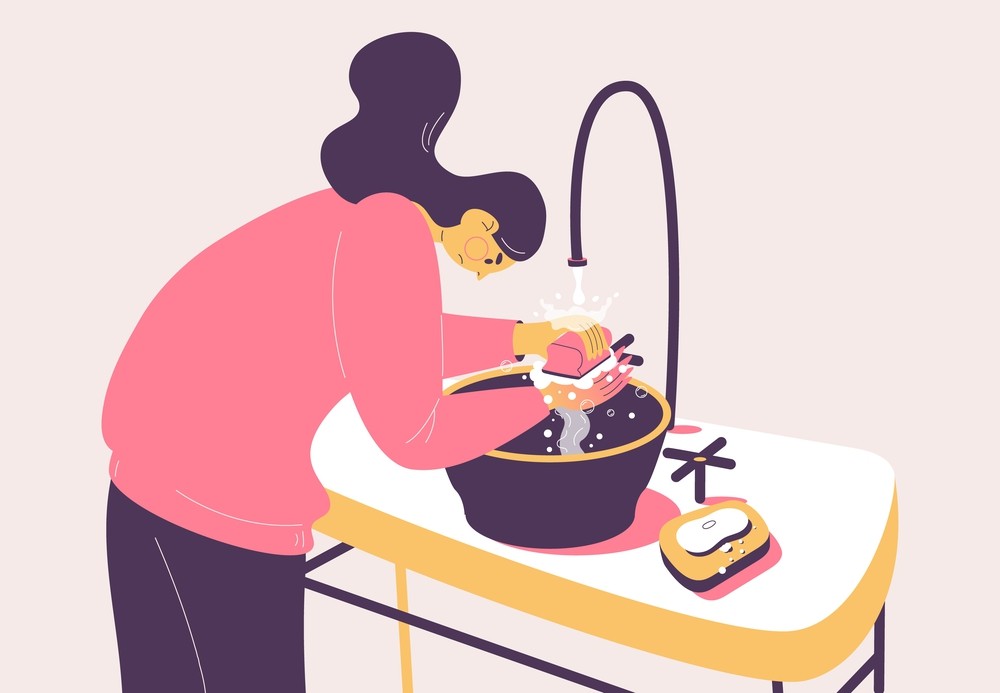

OCD and Relationship with Germs
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD) can significantly impact your life, especially when it comes to germs and contamination. People with OCD often feel uneasy around dirt and may engage in repetitive behaviors, such as hand washing or counting, to alleviate their anxiety.
Germs: The hidden menace
You might be worried about germs more than most people, as the idea of contamination can be overwhelming. It’s normal for you to feel a strong urge to clean your hands, objects, or spaces to prevent the spread of germs. This meticulous behavior can provide temporary relief from anxiety but often requires an excessive amount of time and energy.
The impact of contamination fears
Feeling uncomfortable around dirt can lead to an array of issues in your everyday life:
- Avoiding public spaces
- Experiencing distress when touching objects that others have touched
- Constantly seeking reassurance from others regarding cleanliness
Counting and rituals: A temporary solution
To ease your stress, you might develop counting rituals or specific behavior patterns when dealing with germs and contamination. These behaviors can involve:
- Counting hand washes or time spent washing
- Tapping objects for reassurance
- Engaging in mental rituals to suppress distressing thoughts
While these strategies might provide temporary relief, they often reinforce the cycle of OCD and result in long-term challenges.
Tips for managing OCD and germ-related fears
Here are a few strategies to help you cope with your germ-related worries:
- Gradual exposure: Start exposing yourself to mildly contaminated objects and gradually increase the level of dirtiness. This can help reduce anxiety over time.
- Mindfulness: Practice mindfulness and focus on the present moment to help reduce rumination on germs and contamination.
- Seek professional help: A mental health professional can guide you through evidence-based treatments, such as Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT), to help manage your OCD symptoms.
Incorporating these techniques into your life can help counteract germ-related OCD symptoms, allowing you to regain control over your daily activities.
 Influence of Medication
Influence of Medication
Managing OCD can be challenging, and finding the proper treatment options is crucial. It’s essential to be aware of how certain medications may influence your symptoms. Let’s break down some essential information about medications for OCD.
Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs), like Prozac (Fluoxetine), are standard treatment options for OCD. These medications help regulate serotonin in the brain. While they may work well for some people, it’s essential to be aware of potential side effects.
- Side effects: SSRIs can sometimes have unwanted side effects. You may experience headaches, insomnia, or nausea when starting the medication. These side effects usually decrease after a while, but it’s essential to monitor how you feel and communicate with your healthcare provider.
- Fluoxetine (Prozac): Prozac is one of the more well-known SSRIs and is often prescribed for OCD. It’s generally well-tolerated, but like other SSRIs, side effects can occur. Make sure you follow your doctor’s instructions carefully when using Prozac as a treatment.
Medications play a crucial role in treating OCD, but it’s essential to be cautious of their influence. Consider the following tips when starting any new medication:
- Keep a side effects diary: tracking how you feel about the medication can help you and your doctor better understand its impact and make any necessary adjustments.
- Be patient: finding the proper treatment can take some trial and error, so stick with it and don’t hesitate to ask questions or raise concerns with your doctor.
- Research additional treatments: medications are just one part of the equation. Consider exploring other therapies like cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) to help you manage your OCD symptoms.
Incorporating medication into your treatment plan can lead to significant improvements, but finding the right balance may take time. Remember, you have control over your treatment; always communicate with your healthcare provider to ensure the best possible outcome.

Role of Therapy in Managing OCD
Dealing with OCD can sometimes feel overwhelming, but fortunately, various therapies can help you manage your symptoms. One critical approach is Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), which involves identifying your thought patterns and learning how to change them.
Behavior therapy, a subtype of CBT, focuses explicitly on modifying unwanted behaviors. A trained therapist can help you identify triggers that exacerbate your OCD and work with you to replace negative patterns with healthier ones.
Exposure and Response Prevention (ERP) is a highly effective form of behavior therapy for OCD. In this approach, you’ll gradually confront your obsessions and resist engaging in the compulsions that usually follow. With practice, your anxiety will decrease, and you’ll find it easier to manage your OCD.
In addition to working with a therapist, there are other self-help strategies you can explore to manage your OCD:
- Meditation: Practicing mindfulness and relaxation techniques can help ease anxiety and stress, making it easier to resist compulsions.
- Support Groups: Connecting with others who have OCD can provide valuable insights, encouragement, and practical tips for managing your symptoms.
- Learning: Educating yourself about OCD and its treatment options can empower you to take charge of your mental health.
Remember, finding the right combination of therapies and self-help strategies may take trial and error, so don’t be too hard on yourself. Be patient and trust the process. With dedication and effort, you can learn to manage your OCD and live a more fulfilling life.
Further down in this article, we will discuss signs you need therapy.
Strategies for Prevention and Coping with OCD
It’s essential to find ways to prevent OCD from worsening and cope with it effectively. By developing prevention and coping strategies, you can improve your quality of life and minimize the impact of OCD on your daily life. Here are some tips that may prove beneficial for you:
- Seek professional help: If you haven’t already, consider seeing a mental health professional with experience in treating OCD. A therapist can teach you valuable coping skills that will empower you to manage your symptoms better.
- Establish a daily routine: Creating a structured routine can help you feel more in control and reduce anxiety. Aim to incorporate healthy habits such as regular exercise, balanced meals, and adequate sleep into your daily schedule.
- Face your fears: Engaging in gradual exposure to your feared situations or thoughts (a technique called Exposure and Response Prevention) might help reduce compulsions and obsessions over time.
- Limit reassurance-seeking: While it’s natural to want reassurance for your worries, excessive reassurance-seeking can perpetuate OCD. Try to resist the urge to repeatedly seek reassurance from friends, family, or online sources.
- Develop coping mechanisms: When distressing thoughts or urges arise, have a few coping strategies. This could include practicing mindfulness, deep breathing exercises, or grounding techniques that bring your focus back to the present moment.
- Stay connected: It’s essential to maintain a sound support system, so don’t isolate yourself—contact friends, family, or support groups to share your feelings and experiences.
In addition to these tips, remember that educating yourself about OCD can give you a better understanding of your condition and empower you to take control of your healing journey. By putting these strategies into practice and seeking help when necessary, you’ll be better equipped to handle the challenges of OCD and maintain a high quality of life.
Heeding the Signal: Indicators Therapy Might Be Your Next Step
Engaging with a therapist or counselor can be a transformative step for someone dealing with Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD). Sometimes, it’s clear that professional help is needed, while other times, the signs might be more subtle. Here are some indicators that it might be time to seek therapy:
• Increased Interference: If OCD symptoms are increasingly interfering with your day-to-day life—whether that’s at work, in relationships, or in your time—it’s a vital sign that you could benefit from professional support.
• Escalation in Symptoms: Sometimes, symptoms of OCD can escalate or evolve. If you notice that your compulsions or obsessions are becoming more severe or are manifesting in new ways, therapy can be a crucial step.
• Avoidance Behavior: Are you avoiding certain places, people, or situations due to your OCD? Avoidance can be a coping mechanism, but it’s not a solution. Therapy can help you work through these avoidance behaviors and find better coping strategies.
• Increased Stress and Anxiety: It’s natural to feel stressed or anxious occasionally, but if you’re feeling overwhelmed more often than not, therapy can provide relief.
• Self-Harm or Suicidal Thoughts: These are severe signs that you should seek professional help immediately. Therapy can provide support and coping mechanisms to work through these challenging thoughts and behaviors.
• Seeking Reassurance: If you find yourself constantly seeking reassurance from others to mitigate your OCD fears or concerns, this can be a sign that therapy could be beneficial.
• Impact on Physical Health: OCD and the associated stress can take a toll on your physical health. If you’re experiencing sleep problems, weight fluctuations, or other health issues, it might be time to consider therapy.
• Exhaustion: Battling with OCD can be mentally and emotionally exhausting. If you’re feeling fatigued and impacting your quality of life, therapy may provide the support and strategies you need.
A good starting point is consulting with a healthcare professional who can diagnose accurately and suggest a treatment plan. Therapy can provide the tools to manage OCD symptoms and improve your quality of life. Moreover, engaging in a supportive community, online or in person, can provide invaluable understanding and encouragement. Remember, it’s never too late to seek help and start on the path toward healing and self-discovery.
 Charting Your Course: Setting Goals in Therapy
Charting Your Course: Setting Goals in Therapy
Embarking on a therapeutic journey requires a clear map. Setting goals can be your compass to guide you through the healing process. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you set meaningful goals:
• Self-Reflection:
- Begin with self-reflection to understand your current challenges and what changes you desire.
- List down your fears, triggers, and how OCD interferes with your life.
• SMART Goals:
- Formulate your goals using the SMART criteria—Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound.
- Example: “I aim to reduce the time spent on my compulsive behaviors by half within the next three months.”
• Collaboration with Therapist:
- Share your goals with your therapist, who can help refine them and suggest a realistic timeline.
- Your therapist can also provide professional insight into setting achievable milestones.
• Flexibility:
- Be open to adjusting your goals as you progress or as circumstances change.
- Celebrate small victories along the way, stepping stones towards your larger goal.
• Documentation:
- Keep a therapy journal to document your goals, progress, and any insights or challenges you encounter.
- Reflecting on your documented journey can provide motivation and clarity.
Measuring Milestones: Recognizing Progress in Therapy
Recognition of progress, no matter how small, is fuel for your therapeutic journey. Here’s how you can recognize and celebrate your strides:
• Reduced Anxiety and Distress:
- Notice if you experience a decrease in anxiety or distress surrounding your obsessions and compulsions.
• Improved Functioning:
- Are you finding it eaiser to engage in daily activities, work, or relationships? That’s progress!
• Achievement of Set Goals:
- Revisiting and achieving the goals set at the outset of therapy is a clear indicator of progress.
• Increased Awareness:
- Recognizing your triggers and having a better understanding of your responses is a major step forward.
• Positive Feedback:
- Seek feedback from your therapist and loved ones who understand your journey.
• Reduced Avoidance Behaviors:
- Engaging in situations you previously avoided showcases growth.
• Maintenance of a Progress Journal:
- Document your feelings, challenges, and victories. Over time, reviewing this journal can highlight your progress.
• Self-Compassion:
- Progress may vary, and it’s vital to practice self-compassion. Every step, no matter how small, is a step in the right direction.
Remember, therapy is a unique journey for each individual. The pace and nature of progress will differ. Celebrate your journey because every step forward is a triumph over OCD.
Frequently Asked Questions

Why is my OCD worsening with age?
As you age, hormonal changes and life stressors can affect your OCD. It’s not uncommon for OCD symptoms to worsen with age. Keep in mind, though, that OCD is highly treatable, and seeking help from a mental health professional can lead to effective management of your symptoms.
What triggers OCD episodes?
Various factors can trigger OCD episodes, such as:
- Stressful life events
- Changes in routines or environment
- Illness or other physical health issues
- Hormonal shifts
Remember that triggers can differ from person to person, so it’s essential to identify and understand your triggers to manage your OCD better.
Does discussing OCD make it worse?
Talking about OCD isn’t harmful, and it can be helpful. Discussing your struggles with a trusted person or a mental health professional can provide crucial support and guidance. The key takeaway here is to open up and connect with someone who understands and can provide helpful advice.
What foods can exacerbate OCD?
Some research suggests that certain foods may worsen OCD symptoms. These include:
- Caffeine
- Added sugars
- Processed foods
- Alcohol
A well-balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains can positively impact your mental health and contribute to better management of OCD symptoms.
What is an OCD flare-up?
An OCD flare-up refers to a temporary increase in the intensity or frequency of your symptoms. Flare-ups can be caused by stress, an event that triggers anxiety, or changes in your life. Recognizing and addressing these factors can help you reduce the severity of flare-ups.
What are effective coping strategies for OCD?
You can use the following strategies to help manage your OCD:
- Engage in regular physical activity
- Practice relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing and meditation
- Use cognitive-behavioral therapy techniques
- Talk to a mental health professional if you’re struggling
- Develop a support system
- Maintain a consistent sleep schedule
Implementing these tips can contribute to overcoming your challenges and improving your quality of life in dealing with OCD.
About Jacob Maslow
After surviving the traumatizing events of 9/11, I took it upon myself to heal through helping others. I’m the primary caregiver of my children and understand from first-hand experience the lonely paths you have to walk as a partner and parent when leaving an unhealthy relationship.
We’re all echoing in a dark space that doesn’t have to be this empty, and that’s been my mission since finding solace and recovery in therapy: To help comfort others who are still in shock and at the prime of their struggle.
I came across BetterHelp after searching for this type of community. I wanted to belong to a body of proactive therapists and supportive therapy veterans that allowed me to see other sides of the story.
It was unconventional, and that’s what attracted me most. During my most challenging times, when my ex-wife completely cut me off from my children, I found comfort and clarity through BetterHelp.
Instead of being chained to a strict therapist recommendation, I was in charge of who I felt understood my struggle most. That allowed me to find my true peace, as I was reunited with those who read behind my words and had first-hand experience with my trauma.
Recovery is a choice; with BetterHelp, that choice will be a few clicks away. You can join their couples-oriented platform, Regain.us, for those stuck with family estrangement and toxic relationship patterns.
- 7 Ideas to Help You Relax and Unwind on a Family Vacation - April 27, 2025
- How Having Cybersecurity Protection Helps You Relax - April 25, 2025
- 8 Reasons Why Spending Time Outside Calms You Down - April 25, 2025
This site contains affiliate links to products. We will receive a commission for purchases made through these links.


 Impact of Lifestyle and Behavior
Impact of Lifestyle and Behavior Comorbidities and Complications
Comorbidities and Complications Role of Fear and Uncertainty
Role of Fear and Uncertainty Influence of Medication
Influence of Medication Charting Your Course: Setting Goals in Therapy
Charting Your Course: Setting Goals in Therapy
