As a BetterHelp affiliate, we receive compensation from BetterHelp if you purchase products or services through the links provided
Pain is a universal experience that affects millions of people worldwide. Whether acute or chronic, pain can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life, limiting their ability to perform daily activities and enjoy the things they love.
While medications can provide temporary relief, they often come with side effects and may not address the underlying cause of the pain.
This is where physical therapy becomes a powerful tool for pain management, offering a comprehensive approach to alleviating discomfort and improving overall well-being.
Understanding Pain
Understanding pain’s nature and causes is essential for effectively managing it. Pain can be classified into two main categories: acute and chronic.
Acute pain is typically short-lived and results from injury, surgery, or illness. On the other hand, chronic pain persists for an extended period, often lasting for months or even years.
Chronic pain can stem from various conditions, such as arthritis, fibromyalgia, or nerve damage. Regardless of the type of pain, it is crucial to seek professional help to develop an appropriate treatment plan.
The Role of Physical Therapy in Pain Management
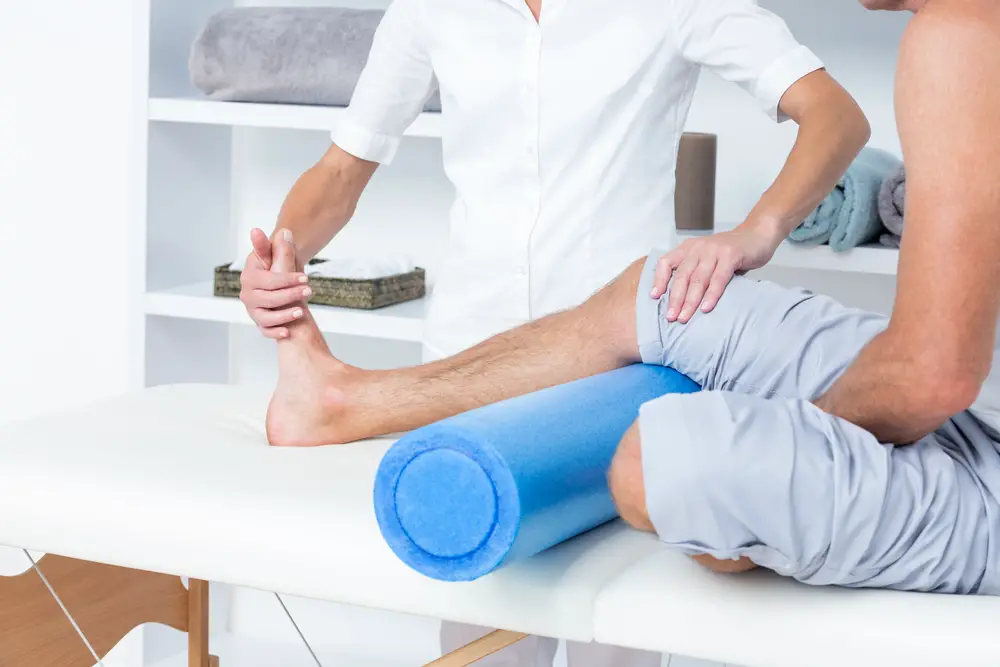
 Physical therapy is a branch of healthcare that focuses on assessing, diagnosing, and treating musculoskeletal and neurological conditions.
Physical therapy is a branch of healthcare that focuses on assessing, diagnosing, and treating musculoskeletal and neurological conditions.
Physical therapists are vital in pain management, helping patients find relief and improve their functional abilities.
Physical therapists combine manual therapy techniques, exercise prescriptions, and patient education to work closely with individuals to develop personalized treatment plans that address their needs and goals.
Manual Therapy Techniques
One of the core components of physical therapy for pain management is manual therapy. This hands-on approach involves specialized techniques to alleviate pain, reduce muscle tension, and improve joint mobility. Some common manual therapy techniques include:
- Soft tissue mobilization: This technique manipulates muscles, tendons, and ligaments to release tension and promote relaxation.
- Joint mobilization: Physical therapists use gentle, controlled movements to improve joint range of motion and reduce pain.
- Trigger point therapy: This technique targets specific muscle points causing pain or referral patterns.
- Myofascial release: This approach focuses on the fascia, the connective tissue surrounding muscles, to release restrictions and improve mobility.
Exercise Prescription
In addition to manual therapy, physical therapists prescribe targeted exercises to help patients manage their pain and improve their overall function. Exercise plays a crucial role in pain management by:
- Strengthening weak muscles: Targeted exercises can help build strength in muscles that contribute to pain or dysfunction.
- Improving flexibility: Stretching exercises can help improve the range of motion in joints, reduce muscle tension, and decrease pain.
- Enhancing cardiovascular fitness: Aerobic exercises, such as walking or swimming, can help improve circulation, reduce inflammation, and boost endorphin production, a natural pain reliever.
- Promoting proper posture and body mechanics: Physical therapists teach patients how to maintain proper alignment and use their bodies efficiently to minimize stress on joints and muscles.
The Benefits of Physical Therapy for Pain Management
Physical therapy offers numerous benefits for individuals dealing with pain. By addressing the underlying causes of pain and providing targeted interventions, physical therapy can:
- Reduce reliance on pain medications: As patients learn to manage their pain through manual therapy, exercise, and self-management strategies, they may be able to reduce or eliminate the need for pain medications, minimizing the risk of side effects or dependency.
- Improve functional abilities: Physical therapy helps patients regain strength, flexibility, and mobility, enabling them to perform daily activities with greater ease and independence.
- Enhance overall quality of life: Physical therapy can help patients enjoy a better quality of life by reducing pain and improving function. This allows them to participate in activities they love and find fulfillment in their daily lives.
- Prevent future injuries: Physical therapists educate patients on proper body mechanics and provide exercises to address muscle imbalances or weaknesses, reducing the risk of future injuries or exacerbations of pain.
Patient Education
Patient education is an integral part of physical therapy for pain management. Physical therapists work closely with patients to help them understand their condition, the factors contributing to their pain, and the steps they can take to manage their symptoms effectively. This may include:
- Teaching proper body mechanics: Physical therapists instruct patients on how to perform daily activities, such as lifting or bending, to minimize stress on the body and reduce the risk of further injury.
- Providing self-management strategies: Patients learn techniques, such as relaxation exercises, deep breathing, or self-massage, that they can use at home to manage their pain and promote relaxation.
- Discussing lifestyle modifications: Physical therapists may recommend changes to diet, sleep habits, or stress management to support overall health and well-being.
Navigating Mental Health: The Hidden Impact of Chronic Pain
 Beyond the physical discomfort, chronic pain holds a profound impact on mental health, a facet of well-being that often goes unaddressed. Millions around the globe find their mental and emotional landscapes deeply affected by the persistent presence of pain, underscoring the importance of integrating mental health care into pain management strategies.
Beyond the physical discomfort, chronic pain holds a profound impact on mental health, a facet of well-being that often goes unaddressed. Millions around the globe find their mental and emotional landscapes deeply affected by the persistent presence of pain, underscoring the importance of integrating mental health care into pain management strategies.
Chronic pain and mental health are intricately linked, with the former being both a physical and emotional burden. The constant struggle with pain can lead to significant psychological distress, including anxiety, depression, and a diminished sense of well-being. Recognizing and addressing these mental health challenges is crucial for individuals seeking to manage their pain effectively and improve their overall quality of life.
The Psychological Effects of Chronic Pain
The experience of chronic pain is not just a physical sensation; it’s an emotional and psychological journey that can take a toll on one’s mental health:
- Depression and Anxiety: The relentless nature of chronic pain can lead to feelings of helplessness and despair, often culminating in depression. Anxiety, too, is a common companion, with worries about pain management and prospects leading to a cycle of stress and discomfort.
- Sleep Disturbances: Pain often interferes with sleep, leading to a cycle of insomnia and fatigue that exacerbates both physical discomfort and mental strain.
- Social Isolation: The limitations imposed by chronic pain can result in withdrawal from social activities, contributing to feelings of isolation and loneliness.
- Reduced Quality of Life: The cumulative impact of physical limitations, emotional distress, and social isolation can significantly diminish one’s quality of life, affecting not just the individual but also their relationships with others.
Integrating Mental Health Care into Pain Management
Addressing the mental health implications of chronic pain is a vital component of comprehensive pain management. This approach includes:
- Psychological Support: Counseling or therapy, particularly cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), can be highly effective in helping individuals cope with the emotional challenges posed by chronic pain.
- Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques: Practices such as meditation, deep breathing, and yoga can reduce stress and improve mental well-being, offering a complementary tool in managing pain and its psychological effects.
- Social Support: Encouraging engagement with support groups or community activities can help alleviate isolation and provide a network of understanding and support.
- Lifestyle Adjustments: Promoting healthy lifestyle choices, including regular exercise, a balanced diet, and adequate sleep, supports overall health and can improve mental health outcomes.
Conclusion
The journey through chronic pain is not solely a physical challenge but a multifaceted experience that impacts every aspect of an individual’s life, including their mental health. By acknowledging the profound connection between physical pain and mental well-being, individuals can seek a more holistic approach to pain management. Incorporating mental health care into the pain management plan not only addresses the physical symptoms but also fosters resilience, offering a path toward a more balanced and fulfilling life despite the challenges of chronic pain. With comprehensive care and support, reclaiming joy and engagement in life becomes a more attainable goal for those navigating the complexities of chronic pain.
This site contains affiliate links to products. We will receive a commission for purchases made through these links.



