As a BetterHelp affiliate, we receive compensation from BetterHelp if you purchase products or services through the links provided
Narcissistic personality disorder (NPD) is a condition marked by an inflated sense of self-importance and a deep need for attention and admiration. Characteristics often include a lack of empathy and a preoccupation with fantasies of success, power, and attractiveness. On the other hand, hypochondria, or health anxiety, is characterized by excessive worry about having or acquiring a serious illness, often based on standard body sensations or minor signs. Individuals might misinterpret these signs as proof of a severe disease.
These two conditions come together in a unique and complex way in narcissistic hypochondria, where the narcissist’s preoccupation with their self-image extends into the domain of their health. They may display behaviors that call for reassurance or attention by expressing health concerns, which might not be based on factual or medical evidence. The role of healthcare providers becomes crucial as they navigate providing care while managing the psychological and behavioral patterns presented by those dealing with narcissistic hypochondria.
Key Takeaways
- Narcissistic personality disorder and hypochondria are distinct conditions with unique behaviors and psychological impacts.
- When combined, these conditions create particular challenges in individuals’ lives and for those providing their care.
- Healthcare providers must balance validating concerns with providing accurate medical advice to those experiencing narcissistic hypochondria.
 Understanding Narcissism
Understanding Narcissism
Narcissism involves many characteristics, notably a broad sense of self-importance and an acute need for admiration. Your grasp of this topic can provide insights into the behavior of narcissistic individuals.
Defining Narcissistic Personalities
Narcissistic Personality Disorder (NPD) is a mental condition characterized by a long-term pattern of abnormal behavior that includes grandiosity, an intense need for admiration, and a lack of empathy for others. Here’s a snapshot of typical traits:
- Self-Centeredness: The person’s world revolves around themselves.
- Grandiosity: Feelings of being unique or superior, often without commensurate achievements.
Key Takeaway: Recognize that at the core of narcissistic personalities lies a fragile self-esteem that’s vulnerable to the slightest criticism.
Narcissism and Self-Perception
Narcissists see themselves through a lens of grandeur and entitlement. They often display:
- An exaggerated sense of ability and achievement.
- A belief that they are unique and should associate with high-status people or institutions.
However, these self-images are typically fragile and vulnerable to deflation.
Key Takeaway: Your understanding of the mismatch between a narcissist’s self-perception and reality can inform your interactions with them.
 Object Relations and Narcissism
Object Relations and Narcissism
Object relations theory suggests that people relate to others through their internal images from early relationships, particularly with caregivers. For narcissists, these relationships may be marked by:
- A deep need for affirmation from others.
- Difficulty with empathy and true intimacy due to their sense of grandiosity.
Key Takeaway: Recognizing the impact of early relational patterns can shed light on a narcissist’s interpersonal difficulties.
Remember, these features of narcissism provide a framework to fathom better the motivations and behaviors of individuals with narcissistic traits.
 Exploring Hypochondria
Exploring Hypochondria
Hypochondria is a condition characterized by excessive worry about having a serious illness. Understanding its nuances is essential for recognizing those with hypochondria’s experiences.
Hypochondria Symptoms
- Persistent doubts about your health: Even when medical tests come back clear, you might fear being ill.
- Regularly checking your body for signs of illness: Lumps, pain, or changes in your skin could indicate you’re experiencing hypochondria symptoms.
Key Takeaway: The main symptoms of hypochondria involve a constant preoccupation with health concerns and seeking reassurance from health-related information.
Hypochondria and Anxiety
- Hypochondria often overlaps with anxiety disorders. The persistent worry about health can cause significant distress and disrupt your daily life.
- Coping strategies like mindfulness, exercise, and therapy can help manage the anxiety linked to hypochondria.
Key Takeaway: If you’re grappling with hypochondria, it’s likely anxiety is a companion in your journey. Recognizing this connection may pave the way for effective management.
Morbid Fears and Hypochondria
- With hypochondria, common health concerns can escalate into fears of severe diseases or death.
- This can lead to behaviors aimed at avoiding the feared diseases, even though there is no evidence of serious illness.
Key Takeaway: Morbid fears of death can be a heavy aspect of hypochondria, but with support, you can learn strategies to ease these fears and improve your quality of life.
 Intersection of Narcissism and Hypochondria
Intersection of Narcissism and Hypochondria
When exploring the complex behaviors of individuals, you might notice that the lines between certain psychological conditions can blur. Understanding the overlap of narcissism and hypochondria sheds light on how individuals can exhibit both sets of traits, impacting their perspective and interactions.
Narcissistic Hypochondriac Traits
Narcissism represents a pattern where individuals have an inflated sense of importance and a deep need for attention and admiration.
Psychological Impact
When facing the intertwining traits of narcissism and hypochondria, your psychological well-being can be severely affected. This segment zeroes in on the inherent challenges to your sense of self and the emotional turmoil that often accompanies them.

Impact on Sense of Self
Your sense of self is at the core of who you are, shaping how you perceive the world and interact with others. A narcissistic hypochondriac may experience a tenuous sense of self, which wavers between grandiosity and vulnerability. Here’s how this plays out:
- Fragile self-esteem: You may find your self-esteem precariously balanced, with a persistent need for validation from others.
- Shame and guilt: It’s common to feel shame when your self-image is threatened or guilt when you perceive that you’ve fallen short of your standards.
These shifts in self-perception can leave you feeling unstable and unsure of your worth, especially when your health concerns are dismissed or downplayed by others.
Emotional Consequences
Your emotional landscape can take a hit as well. The interplay between narcissism and hypochondria often leads to complex emotional responses, including:
- Lack of empathy: You might find it difficult to understand or share the feelings of others, mainly when preoccupied with your health concerns.
- Struggle with remorse: Recognizing and expressing genuine remorse may be challenging if you’re overwhelmed by your issues and needs.
These emotional struggles can further isolate you from support systems and impede your ability to form and maintain meaningful relationships.
Key Takeaway: Your emotional well-being hinges on a stable sense of self, which can be disrupted by narcissistic hypochondriac traits, leading to significant emotional challenges.
Behavioral Patterns
In exploring the behavioral patterns of a narcissistic hypochondriac, you’ll notice two key tendencies: a quest for attention and special treatment, as well as manipulative tactics. These behavioral traits often emerge due to a deep need for validation and fear of being ignored or undervalued.
Seeking Attention and Special Treatment
Narcissistic hypochondriacs frequently exhibit an intense desire for attention. You may observe the:
- Regularly share detailed accounts of their health issues at social gatherings or online forums.
- Expecting others to prioritize their needs, often without regard for others’ boundaries.
They aim to secure special treatment through:
- Exaggerating symptoms to trigger a reaction.
- Insisting on unwarranted medical care or accommodations.
Key Takeaway: Your awareness of these attention-seeking behaviors can help you respond with compassion while setting healthy boundaries.
Manipulative Behaviors
Manipulation is a tool often utilized by narcissistic hypochondriacs to maintain control and take advantage of others. Look for:
- Guilt-tripping: Implying that refusal to help would worsen their condition.
- Playing the Victim: Portraying themselves as perpetually suffering to sidestep accountability for transgressions.
They may manipulate situations to:
- Shift blame when their actions or words are called into question.
- Coerce you into providing them with undivided attention and support, often at your expense.
Key Takeaway: Recognize these manipulative strategies to protect yourself from being unfairly exploited while offering appropriate support.
The Role of the Doctor
Navigating the complexities of treating a narcissistic hypochondriac demands a nuanced understanding of the doctor-patient relationship and the unique challenges it presents.
Doctor-Patient Dynamics
When you’re a doctor working with a patient who displays narcissistic hypochondriac tendencies, the dynamic is delicate. Remember, your role is pivotal in guiding them through their concerns without feeding into their attention-seeking behavior.
- Empathy and Authority: You must communicate with empathy to be seen as a caring witness to their suffering and establish your authority so they trust your expertise.
- Boundaries: Setting clear boundaries helps maintain a professional relationship and manage expectations.
Key Takeaway: Balance empathy with authority and maintain clear boundaries for a healthy doctor-patient dynamic.
Challenges in Treatment
Treating such patients can often feel like navigating a maze. Every corner may present a new challenge, but with the right strategies, you can find your way through.
- Validation: Patients seek validation for their ailments, so they acknowledge their distress but remain firm in realistic assessments.
- Education: Provide accurate information, dispelling misconceptions that could exacerbate their condition.
- Consistency: Offer consistent messages from appointment to appointment to avoid confusion and build trust.
Key Takeaway: Stay consistent in your approach, educate with care, and validate feelings to manage treatment challenges effectively.
 Physical and Psychological Health
Physical and Psychological Health
When it comes to the intersection of narcissism and hypochondria, you’ll find that the concerns about physical wellness often intertwine with psychological health needs.
Perceived Physical Fragility
You may notice that individuals with these traits have a heightened focus on their body’s condition, worrying excessively about the potential for illness or injury. They may express these concerns as frequently:
- Visits to healthcare providers
- Requests for medical tests
- Discussions about physical symptoms despite a lack of medical evidence
Although often not medically substantiated, the concern over physical fragility feels genuine to the person experiencing it.
Key Takeaway: Recognize the importance of empathy in responding to someone’s concerns about their perceived physical fragility while maintaining a realistic perspective on their actual health.
Pain and Suffering
For someone grappling with both narcissism and hypochondria, the experience of pain can be complex. They may report:
- Intense discomfort
- Persistent bodily complaints
It’s not uncommon for them to perceive normal bodily sensations or minor aches as severe pain, and these experiences are often amplified by the attention and sympathy these feelings might garner from others. It is challenging but vital to differentiate between expressed suffering and clinically identifiable causes, such as a stroke, which requires immediate professional attention.
Key Takeaway: Listening and providing support is critical, but guiding someone to appropriate medical care when symptoms may indicate severe conditions like a stroke is essential.
Narcissistic Coping Mechanisms
Navigating the rocky terrain of emotional distress, you may find narcissistic coping mechanisms particularly intricate. They’re designed to shield one’s self-esteem from the sharp edges of criticism and the uncomfortable reality of imperfection.
Dealing with Imperfection and Criticism
It’s human nature to experience discomfort when faced with imperfection or criticism. However, for a narcissist, this pain can be acute, triggering a response to manage the psychological distress.
- Self-Image Maintenance: Imperfection threatens the idealized self-image. To navigate this, narcissists often:
- Reconstruct criticism to suit their worldview.
- Attribute flaws to external factors.
- Mitigating Self-Fragmentation: Feeling ‘whole’ is crucial. When faced with real or perceived criticism, there’s a drive to quell self-fragmentation through:
- Denial of shortcomings.
- Affirmations of personal superiority.
Key Takeaway: To counter criticism, strategies often involve preserving an unblemished self-view and dismissing external negative input.
Narcissistic Defense Strategies
Protection against emotional threats is vital, and defense strategies are the armor. This section sheds light on common tactics used to deflect perceived attacks.
- Deflection and Projection: You might notice a tendency to:
- Dodge accountability by shifting blame.
- Accuse others of one’s flaws to redirect focus.
- Idealization and Devaluation: The balance between admiration and disdain can be:
- Initially, placing someone on a pedestal.
- Swiftly devaluing them to regain a sense of dominance after any criticism.
Key Takeaway: Defense mechanisms are diverse; however, they converge to avoid internal turmoil and maintain a facade of perfection.
 Conceptualizing the Ideal Self
Conceptualizing the Ideal Self
In considering the ideal self, especially in the context of narcissistic hypochondria, the influence of early familial relationships and the pursuit of an unattainable standard become central themes.
Ideal Mother Influence
Your conception of an ideal self is often rooted in childhood, with the ‘ideal mother’ archetype playing a pivotal role. This mythical mother figure represents an archetype of perfection against which all other relationships are measured.
- Empathy and Approval: The ideal mother is envisioned as the epitome of empathy and unconditional love.
- Expectations: She sets high standards, inadvertently fostering a compulsive chase for perfection in her offspring.
Here’s a brief look at how this can manifest:
| Ideal Mother Traits | Narcissistic Hypochondriac’s Internalization |
|---|---|
| Unconditional support | Perpetual dissatisfaction when support is perceived as lacking |
| High Achiever | Self-inflicted pressure to excel beyond reasonable limits |
Takeaway: The longing for an ideal mother’s approval can drive you toward an unyielding quest for an impeccable self-image.
 Pursuit of Perfection
Pursuit of Perfection
Chasing the ghost of perfection is a path of ambition and frustration. Here’s what it typically entails:
- Unreachable Standards: You may set benchmarks so high that they’re virtually unachievable.
- Self-Righteous Superiority: To compensate, a sense of inflated self-importance and superiority may develop.
Reflect on these features in the context of a narcissistic hypochondriac:
| Pursuit of Perfection | Narcissistic Behaviors |
|---|
- Incessant striving * A relentless journey toward ever-moving goalposts
- Judgement of others * A critical eye on those not aligning with their high standards
The outcome? It is a cycle of reaching for an ever-elusive ideal and the resulting dissatisfaction when it is not attained.
Key takeaway: Your relentless pursuit of perfection might lead you to a superiority complex, which can become both a shield and a burden.
Diagnosis and Analysis
When navigating the complexities of psychoanalytic diagnosis in individuals with both narcissistic and hypochondriac characteristics, you’ll find it’s vital to understand the interplay of their personality structure. It’s not just the symptoms that are analyzed but also the underlying personality dynamics that sustain them.
Psychoanalytic Diagnosis
Personality Structure: At the heart of a psychoanalytic diagnosis, the personality structure is a cornerstone. For someone who may be described as a narcissist with hypochondriacal tendencies, this refers to how they organize their thoughts and feelings about themselves and their health.
- Self-Image: Often, such individuals possess a fragile self-image that they vigorously protect through grandiosity or preoccupation with health.
- Defense Mechanisms: Defense mechanisms, notably denial, and projection, are robust enough to maintain self-esteem and manage anxieties about health and competence.
Symptoms Analysis: Your symptoms aren’t just gauged at face value but are seen as symbolic expressions of deeper conflicts.
- Anxiety Manifestations: Physical symptoms typically manifest underlying psycho-emotional distress and unmet narcissistic needs.
- Attention Seeking: Illnesses serve as a vehicle for gaining attention and sympathy, bolstering their self-importance.
Through this lens, treatment strategies often involve addressing the deeper psychic structures rather than just the overt hypochondria or narcissistic behaviors. Establishing a nuanced understanding of such a personality structure is pivotal for effective therapeutic interventions.
Key Takeaway: Remember, behind every symptom is a story rooted in the psyche, and unlocking it can be the first step toward healing.
Theories and Causes
When you’re looking at the complex weave of personality and health anxieties embodied by narcissistic hypochondria, you find a spectrum of theories and causes. These address why an individual might exhibit a profound preoccupation with themselves and an excessive concern for their health.
Alternative Theories
Various psychological frameworks have been proposed to understand narcissistic hypochondria better. One approach views it as a construct overlapping features of narcissistic personality disorder and illness anxiety disorder. Another theory hypothesizes that the hypochondriacal tendencies stem from an underlying need for attention and validation, which aligns with the core traits of narcissism.
- Psychoanalytic Perspective: Some experts propose that narcissistic hypochondria could develop from early childhood experiences. The struggle between a desire for acknowledgment and the fear of vulnerability might translate into an adult life where both narcissistic and hypochondriac traits manifest strongly.
- Modern Approaches: Contemporary psychologists often lean towards a biopsychosocial model, which considers genetic, environmental, and psychological factors. This model suggests that an interplay between biological predisposition, social interactions, and psychological state could give rise to this condition.
Causes of Narcissistic Hypochondria
The causes behind narcissistic hypochondria are as multi-layered as the condition itself. Here’s what we know:
- Genetic Factors: While genetics can predispose one to certain personality traits, the direct genetic link to narcissistic hypochondria remains a topic of ongoing research.
- Environmental Influences: Childhood experiences, including parenting styles and early interactions, can significantly mold your personality. Trauma, neglect, or excessive pampering might contribute to narcissistic and hypochondriacal tendencies later in life.
- Sociocultural Dynamics: With the advent of social media and the rise of ‘the self’ in cultural discourse, there is a greater external emphasis on personal health and image, potentially exacerbating narcissistic and hypochondriacal behavior.
Key takeaway: Understanding the theory behind narcissistic hypochondria helps in recognizing that it’s not just about vanity or seeking attention. A complex interplay of past experiences and psychological states often drives a person’s behavior.
Frequently Asked Questions
When diving into the topic of narcissistic hypochondria, you’ll find that specific patterns emerge. Below, you’ll get answers to some of this complex behavior’s most commonly inquired aspects.
Are individuals with narcissistic tendencies more likely to exaggerate their health issues?
People with a narcissistic disposition may indeed amplify health concerns to garner attention or sympathy. It’s not unusual for them to describe everyday aches as severe illnesses.
Key Takeaway: Watch for overstatements in health matters that may serve to attract notice or create drama.
What are the typical behaviors exhibited during a narcissistic breakdown?
During a narcissistic breakdown, you might witness extreme mood swings, a relentless search for admiration, or impulsive actions. The individual often feels vulnerable and may react with heightened emotions.
Key Takeaway: Expect erratic behavior and intense emotional responses during these periods.
Why might someone exhibiting narcissism tend to magnify minor problems or concerns?
Magnifying minor issues often satisfies a narcissistic individual’s need for constant validation and attention. Inflating problems can place them at the center of others’ concerns.
Key Takeaway: This magnification serves their desire to be the ongoing focus of interest.
How do narcissistic individuals typically cope with rejection or separation from a partner?
Coping with rejection, a narcissist might deny the loss or react with anger. Emotional volatility is common, and they may try to regain control or attention through manipulation.
Key Takeaway: Anticipate a struggle with acceptance and potential persuasive tactics to reclaim a sense of power.
Can narcissism influence a person’s perception and reporting of their own health?
Absolutely. A narcissist’s self-reported health issues might be distorted by their need for attention. Their perception may not align with medical assessments.
Key Takeaway: Discrepancies between personal accounts and clinical evaluations can arise from their attention-seeking behavior.
What’s the correlation between narcissism and hypochondriac behavior?
Narcissism is linked to hypochondriac behavior as individuals may obsess over or exaggerate illnesses to satisfy their craving for admiration or as tools for emotional manipulation.
Key Takeaway: Narcissism can heighten self-focus on health, leading to exaggerated medical concerns.
- 3 Ways Wearing a Hat Can Help Lower Your Stress Levels - April 19, 2025
- Breaking the Silence: Why Men’s Mental Health Matters More Than Ever - April 15, 2025
- How to Transform a Home’s Patio Space into a Relaxing Space - March 23, 2025
This site contains affiliate links to products. We will receive a commission for purchases made through these links.


 Understanding Narcissism
Understanding Narcissism Object Relations and Narcissism
Object Relations and Narcissism Exploring Hypochondria
Exploring Hypochondria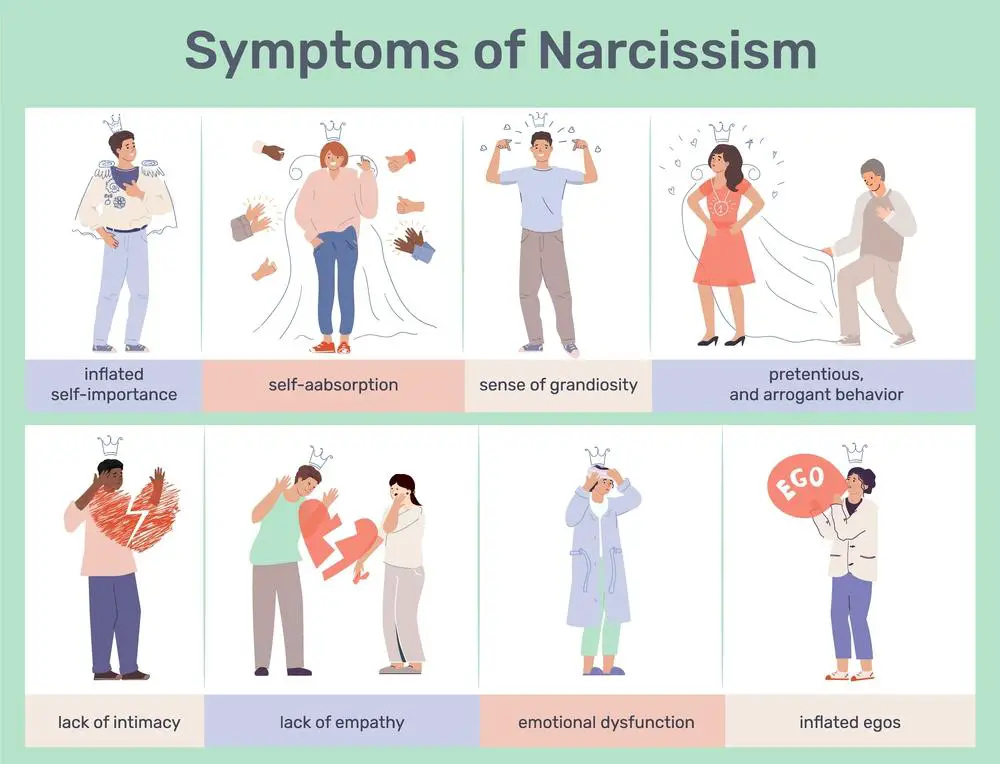 Intersection of Narcissism and Hypochondria
Intersection of Narcissism and Hypochondria Physical and Psychological Health
Physical and Psychological Health Conceptualizing the Ideal Self
Conceptualizing the Ideal Self Pursuit of Perfection
Pursuit of Perfection
