When discussing Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD), the conversation often leads to the question of whether PTSD is considered a disability. This consideration is crucial because it ties directly into access to resources, support, and legal protections for those affected. PTSD, a disorder that can develop after a person has experienced or witnessed a traumatic event, has profound effects on an individual’s daily life and functioning.
Understanding PTSD is fundamental to recognizing why it might be classified as a disability. Symptoms can include severe anxiety, flashbacks, uncontrollable thoughts about the event, and emotional numbness, which can hinder one’s ability to function in work and social settings. Recognizing the impact of these symptoms is key in appreciating why and how various institutions and laws acknowledge PTSD as a disabling condition.
For individuals living with PTSD, knowing the parameters for disability benefits can be empowering. It helps you navigate the complexities of applying for and receiving assistance and is essential for maintaining stability in both personal and professional spheres. Jobs, relationships, and general quality of life can be significantly impacted, and the proper support and therapy options are instrumental in managing the condition over the long term.
Key Takeaways
- PTSD can significantly impact an individual’s daily functioning, potentially qualifying it as a disability.
- Recognition of PTSD as a disability facilitates access to necessary resources and support.
- Understanding eligibility criteria for disability benefits and available support options can aid in long-term PTSD management.
 Understanding PTSD
Understanding PTSD
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) is a serious condition that can develop after you witness or experience a traumatic event. This event could be a natural disaster, a severe accident, a terrorist act, war/combat, rape, or other violent personal assault.
PTSD is classified as a trauma- and stressor-related disorder. The crux of coping with PTSD is understanding its various aspects:
- Exposure to trauma: Encountering or witnessing a life-threatening event.
- Symptoms of PTSD: These can be emotional (like sadness and anger) and physical (such as headaches or stomachaches). Symptoms generally fall into four categories:
- Intrusive thoughts
- Avoidance behaviors
- Negative alterations in mood or cognition
- Changes in arousal and reactivity
It’s not uncommon for these symptoms to cause significant stress or problems in social or work settings. They can start soon after the traumatic event or even years later. PTSD symptoms must last for more than one month and be severe enough to impair your ability to function in daily life to be considered PTSD.
Key Takeaway: If you’re experiencing distressing symptoms following a traumatic event, it’s important to seek help. Recognizing signs of PTSD early can lead to timely support and treatment.
 PTSD as a Recognized Disability
PTSD as a Recognized Disability
Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) has a significant impact on the lives of those it touches. Recognizing this, PTSD is classified as a disability under certain circumstances. If you’re grappling with this condition, it’s crucial to understand how it’s viewed in the context of disability.
- Legally Defined: Under the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA), PTSD is indeed regarded as a disability. This means you’re protected against discrimination based on your condition.
The condition manifests after events or situations that can shatter your sense of well-being, sometimes overwhelming your ability to cope. As a result, if your PTSD substantially limits one or more of your major life activities or bodily functions, it falls under the umbrella of disabilities.
- Criteria for Recognition: Not everyone with PTSD is automatically granted disability status. For this recognition:
- Your mental health condition must significantly limit your daily activities.
- It should be on record.
- You may be asked to provide medical documentation to support your claim.
- Rights and Accommodations: With PTSD recognized as a disability, your employer or service provider must provide reasonable accommodations to help you perform your job effectively.
Remember, being diagnosed with PTSD doesn’t make you any less capable or valuable. It simply means you have a mental condition that requires understanding and support, much like a physical disability.
Key Takeaway: If your post-traumatic stress disorder affects life’s major facets, it is viewed legally as a disability, and with that designation comes a framework of support to assist you in your daily life and employment.
Eligibility Criteria for Disability Benefits
When seeking disability benefits, you’re facing specific criteria that must be met. Here’s how you can align your situation with the requirements.
Medical Documentation Requirements
Your journey to receiving disability benefits starts with thorough medical documentation. You need to provide:
- A formal diagnosis from a healthcare professional.
- Comprehensive records detailing your condition’s history.
- Evidence showing how your condition affects your daily functions, like concentrating, interacting with others, and remembering.
Remember, your documentation must reflect a severe injury or condition that significantly limits your daily activities or has lasted, or is expected to last, at least one year or result in death.
Key takeaway: Ensure your medical evidence is detailed and up-to-date to demonstrate the impact of your condition clearly.
The Social Security Administration’s Blue Book
The Social Security Administration (SSA) maintains a manual known as the Blue Book, listing medical conditions that automatically qualify you for Social Security Disability Insurance (SSDI) or Supplemental Security Income (SSI). The Blue Book also details the criteria for each condition, including:
- Specific clinical and laboratory findings.
- The required intensity, persistence, and limiting effects of your condition.
If you’ve experienced depression, violence, or sexual trauma that leads to a marked limitation of your abilities, this resource can be pivotal in your claim.
Key takeaway: Use the Blue Book to cross-reference your condition and prepare your claim based on its standardized criteria.
Qualifying Under the Americans with Disabilities Act
The Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) provides a broader spectrum for a disability. Under the ADA, you’re eligible if your condition substantially limits one or more major life activities. The ADA also makes room for mental impairments, which may not be as clearly measured as physical ones.
- Does your condition hinder your ability to perform activities compared to an average person?
- Are the impacts of your condition on activities like work, social interactions, and self-care significant and long-term?
If you can answer yes to these questions, you might have a valid claim for disability benefits under the ADA.
Key takeaway: Your disability’s effect on daily life activities, not just your medical diagnosis, is critical under the ADA.
 PTSD Symptoms Affecting Functional Capacity
PTSD Symptoms Affecting Functional Capacity
Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) can significantly impair your daily functioning across various aspects of life. Here’s how some PTSD symptoms could limit your capabilities:
- Flashbacks and Nightmares: These can disrupt your sleep patterns, leading to fatigue that hinders your ability to concentrate during the day.
- Intrusive Memories: Unexpected and frequent recall of traumatic events may distract you from tasks, affecting your work performance and social interactions.
- Arousal and Reactivity: Hypervigilance or increased startle response can make you constantly feel ‘on edge’, impacting your comfort and effectiveness in social situations.
- Concentration Problems: PTSD can make it challenging for you to focus, remember details, and complete tasks that require sustained attention.
- Interacting with Others: The discomfort in social settings can strain relationships, as you might find it tough to connect with colleagues, friends, and family.
Symptoms of PTSD are persistent and can impede your ability to adapt and apply information in various contexts. A heightened state of arousal, often a result of trauma, might lead you to react in ways that seem disproportionate to the actual situation. This reactivity can make routine adaptation to changes a hurdle. Moreover, the energy required to manage these symptoms often leaves little room for other activities, reducing your overall functional capacity.
Key Takeaway: Your symptoms of PTSD are not simply emotional responses but have real, tangible impacts on daily life. Recognizing the challenges is crucial for seeking appropriate support and accommodations.

Support and Therapy Options
Navigating through the challenges of PTSD requires a multifaceted approach to treatment, ensuring that you receive the support and therapy that aligns with your needs. Below, you’ll find strategies and interventions designed to aid your journey to recovery.
Mental Health Interventions
Evidence-Based Psychotherapies:
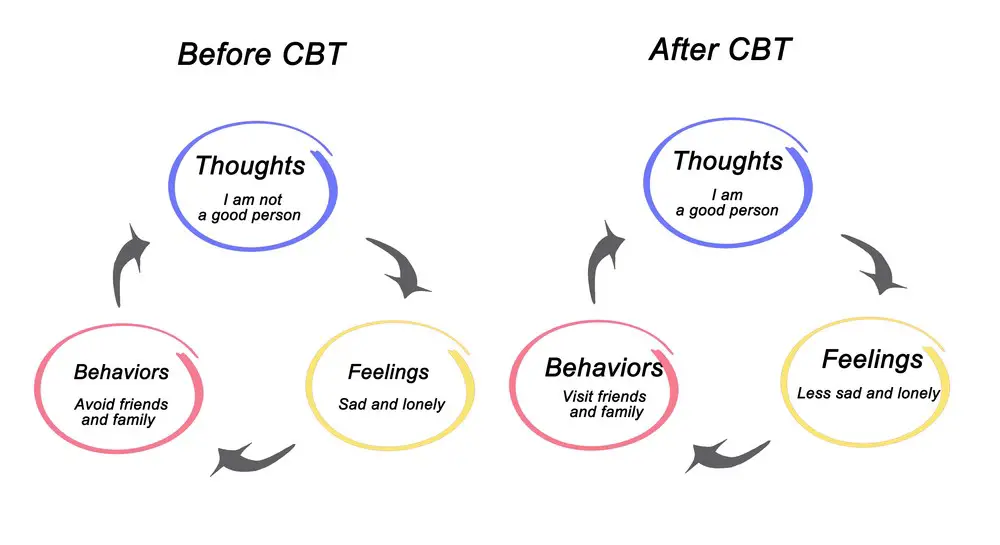
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): In CBT, you’ll work with a therapist to identify and understand your thought patterns, learning strategies to cope with difficult emotions.
- Prolonged Exposure Therapy: This method teaches you to gradually approach trauma-related memories and feelings to diminish their power over you.
- Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR): EMDR incorporates elements of CBT with eye movements or other forms of rhythmic, left-right stimulation to help process traumatic memories.
Medications:
- Antidepressants such as SSRIs and SNRIs are commonly prescribed to help manage symptoms.
- Medication isn’t a one-size-fits-all solution, so be open with your doctor about how different prescriptions affect you.
Key Takeaway: Connect with a mental health professional to discuss the therapy options most effective for your unique condition.
Alternative and Complementary Therapies
Exploring Beyond Conventional Treatment:
- Art Therapy: Engage in creative activities to express emotions that might be hard to verbalize.
- Yoga: Find a yoga practice to help you connect with your body and regulate stress responses.
- Nature Therapy: Spend time in natural settings to improve mood and reduce anxiety.
Combining practices can often create a comprehensive support system catering to your mental and physical well-being. Remember, therapy is personal, and finding the right combination of treatments is crucial for your path to healing.
Key Takeaway: Alternative therapies can supplement traditional treatment, offering a holistic approach to managing PTSD.
Navigating Disability Benefits and Compensation
Before diving into the intricacies of disability benefits and compensation, it’s imperative to grasp the application process, understand veterans’ specific routes for claims, and recognize when legal expertise may enhance your case.
The Social Security Disability Application Process
To obtain Social Security Disability Insurance (SSDI) or Supplemental Security Income (SSI), you must submit a structured application through the Social Security Administration (SSA). The key steps include:
- Gathering Documentation: You’ll need comprehensive medical records, work history, and identification documents.
- Completing the Application: Forms can be submitted online, by mail, or in person if you schedule an appointment with an SSA office.
- Review Process: The SSA evaluates your application against disability standards reflecting your work capacity.
Key Takeaway: Ensure your documentation is thorough to streamline the SSA’s application assessment.
Veterans Affairs and Disability Compensation
As a military veteran, you may be eligible for VA disability benefits through the Department of Veterans Affairs (VA). This process involves:
- Initial Filing: You can file a claim online, by mail, or at a VA office with evidence of a service-connected disability.
- Compensation & Pension Exam: A key part of evaluating your condition to confirm service connection and degree of disability.
- Awaiting a Decision: The VA will review your claim, after which you’ll receive a decision regarding your compensation rate.
Key Takeaway: Participate in all evaluations to ensure your claim accurately reflects your disability.
Legal Assistance and Representation
Regarding disability claims, having a qualified disability lawyer can be pivotal. Here’s why:
- Expert Guidance: Lawyers understand the complex language and requirements of applications for SSDI, SSI, and VA benefits.
- Appeal Support: If your initial claim is denied, a lawyer can help file an appeal and represent you in hearings.
- Maximizing Compensation: An experienced disability lawyer will know strategies to help you receive the full benefits you’re entitled to.
Key Takeaway: Seeking a lawyer’s assistance can help you navigate the complexities of disability claims more effectively.
Long-Term Management and Prognosis
Managing PTSD is an evolving process requiring both understanding and adjustment. Successful long-term outcomes often hinge on recognizing ongoing disability while fostering work and social reintegration.
Ongoing Disabilities and Adjustment
Disability and PTSD: Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) can result in disabilities that may need ongoing management. Disabilities range from marked limitations in day-to-day activities to more extreme limitations that severely impact one’s life. You might be easily startled, or certain situations might trigger a significant stress response.
- Treatment and Support: Long-term therapy is essential.
- Consistent counseling
- Medication management, when appropriate
- Support groups
Adjusting to New Realities:
- Understanding your triggers
- Learning coping strategies
- Creating a tailored support system
Key Takeaway: Therapy and support systems are vital for adjusting to the disabilities caused by PTSD.
Work and Social Integration
Navigating Work Requirements:
Under the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA), you have rights that protect from discrimination based on disability. Here’s how you can navigate work requirements:
- Inform your employer of your situation.
- Request reasonable accommodations.
- Understand that you might have to balance work expectations with your capabilities.
Social Integration Challenges:
- Engaging with others may be tough, but it is an important step.
- Find social activities or groups that are sensitive to your needs.
- Build a support network of friends, family, or colleagues.
Key Takeaway: Your rights under the ADA and a supportive social network are key components in achieving successful work and social integration with PTSD.
 Challenges Beyond the Diagnosis
Challenges Beyond the Diagnosis
Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) presents multifaceted challenges that extend far beyond receiving a diagnosis. Your journey to cope and manage PTSD can be complex, often involving more than just the primary symptoms of the disorder.
PTSD and Associated Conditions
When you’re living with PTSD, you may also experience a host of associated conditions that compound your daily challenges. These can include:
- Anxiety and Depression: A heightened state of worry and a persistent low mood can accompany PTSD, making it harder for you to find balance.
- Insomnia: Difficulty in falling or staying asleep is common, disrupting your body’s need for rest and recovery.
- Addiction: You might seek solace in alcohol or drugs, which can offer temporary relief but often lead to addiction.
Key Takeaway: Managing PTSD also means being vigilant about these associated conditions.
The Impact of Trauma on Daily Living
Trauma impacts your life in ways that can be subtle or all-encompassing. Here’s how it may manifest:
- Interacting with Others: You might find it harder to trust people or maintain relationships, making socializing a major hurdle.
- Concentration: Regular tasks might seem overwhelming as concentrating becomes more challenging.
- Reactivity and Arousal: Normal environments may suddenly feel threatening, leading to increased stress and agitation.
Key Takeaway: Understanding how trauma influences your daily activities is crucial for seeking appropriate support.
Recognition and Dealing with Triggers
Triggers can be unpredictable, and recognizing them is a step towards regaining control:
- Identify Patterns: Keep a journal to track when you’re triggered. This can help identify patterns related to places, memories, or dreams.
- Develop Coping Strategies: Create a list of strategies, like breathing exercises, to use when feeling triggered.
- Seek Professional Help: Therapy can aid in reducing the intensity of your reactions to triggers over time.
Key Takeaway: Being proactive with triggers can significantly reduce their impact on your life.
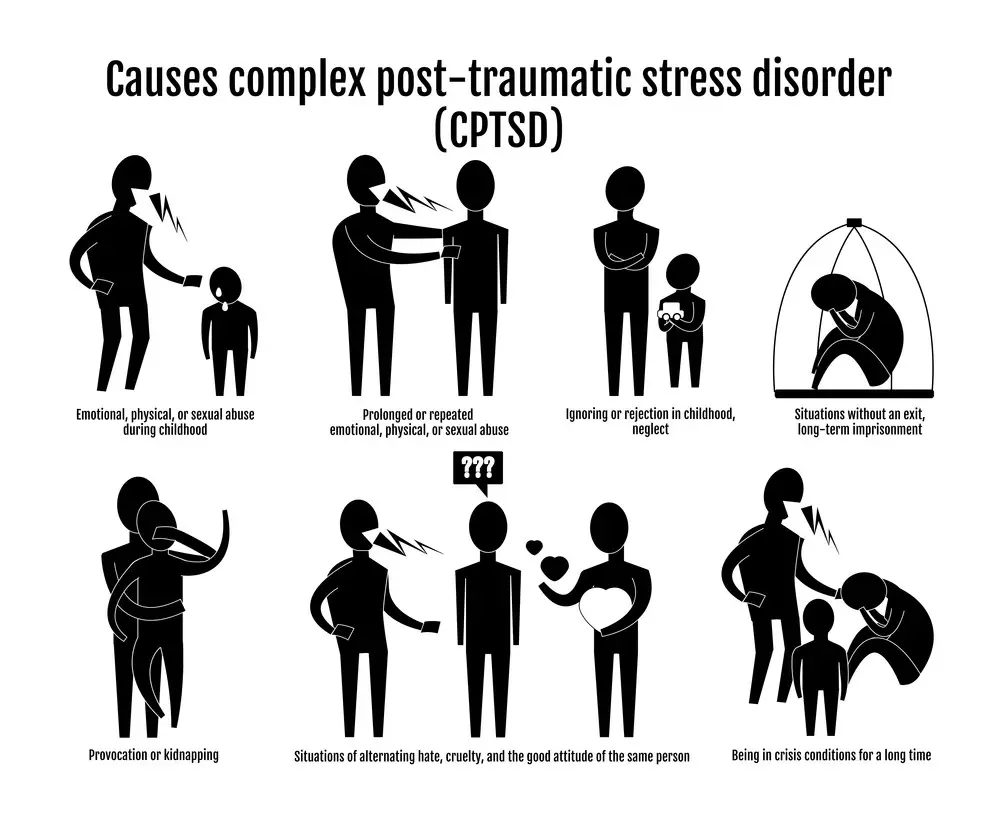
Understanding C-PTSD: Navigating the Complexities of Chronic Trauma
When discussing the nuances of Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD), it’s essential to delve into a specific subtype of this condition: Complex PTSD (C-PTSD). This condition often arises from prolonged exposure to traumatic circumstances, which might include long-term abuse, captivity, or repeated betrayal. Understanding C-PTSD is crucial not only for those who suffer from it but also for their loved ones and healthcare providers.
The Nature of C-PTSD
C-PTSD shares many symptoms with traditional PTSD, such as severe anxiety, flashbacks, and avoidance of trauma reminders. However, it also includes additional layers of emotional distress that stem from prolonged trauma. These may include:
- Deep-seated feelings of shame or guilt: Often, victims of prolonged trauma internalize the abuse, leading to persistent negative self-perception.
- Chronic emotional regulation difficulties: People with C-PTSD might struggle to manage their emotions, leading to sudden bursts of anger, persistent sadness, or suicidal thoughts.
- Complex relational issues: Trust issues, difficulty in maintaining relationships, or even a tendency to seek out harmful relationships can be a hallmark of C-PTSD.
Why C-PTSD is Often Misunderstood
C-PTSD can be challenging to diagnose and treat for several reasons:
- Overlap with other mental health conditions: Symptoms of C-PTSD often mimic those of other disorders like borderline personality disorder or major depression, leading to misdiagnosis.
- Lack of awareness and understanding: Not all mental health professionals are equally trained in recognizing and treating C-PTSD.
- Stigma and misunderstanding in society: There’s a tendency to overlook or simplify the complexities of trauma, mainly when it occurs over an extended period.
The Impact of C-PTSD on Daily Life
The effects of C-PTSD can permeate every aspect of life:
- Workplace challenges: Difficulty in concentrating, trust issues with colleagues, or fear of authority figures can impair professional performance.
- Social and relational difficulties: Forming and maintaining healthy relationships can be a significant challenge for those with C-PTSD.
- Self-care struggles: Individuals might neglect personal care, struggle with substance abuse, or engage in self-harming behaviors as a way of coping.
Seeking Help and Managing C-PTSD
Dealing with C-PTSD requires a comprehensive and empathetic approach:
- Specialized therapy: Therapies like trauma-focused cognitive behavioral therapy, dialectical behavior therapy, or EMDR can be more effective.
- Support groups: Connecting with others who have similar experiences can provide a sense of understanding and community.
- Patient, ongoing care: Recovery from C-PTSD is often a long-term process, requiring patience and sustained effort from both the individual and their support network.
Key Takeaways
- C-PTSD is a complex and often misunderstood condition resulting from prolonged exposure to trauma.
- It affects an individual’s emotional regulation, relationships, and self-perception significantly.
- Proper diagnosis and specialized treatment are crucial for effective management.
- Support and understanding from society, loved ones, and healthcare providers are vital in the healing process.
Frequently Asked Questions
Suppose you’re navigating the complexities of PTSD as it relates to disability. In that case, you’ll find that understanding the nuances of benefits, service accommodations, and the impact on life expectancy can be crucial in managing your situation.
How is PTSD rated for disability benefits?
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) is rated for disability benefits based on the severity of symptoms and their impact on social and occupational functioning. The VA rates PTSD on a scale from 0% to 100%, taking into account factors like work impairments and social interaction.
Key takeaway: The more severe the symptoms and their impact on your daily life, the higher the disability rating you may receive.
Can individuals with PTSD qualify for Social Security disability benefits?
Yes, individuals with PTSD can qualify for Social Security disability benefits if they meet the SSA’s criteria. Your PTSD must be diagnosed by a professional and cause significant impairment in your ability to perform any work.
Key takeaway: A thorough diagnosis and evidence of the impact on your work life are essential for qualifying for Social Security disability benefits.
Are service dogs allowed for individuals with PTSD as a disability?
Service dogs are indeed allowed for individuals with PTSD. They are recognized as a form of support that can perform tasks and alleviate symptoms, such as providing safety checks or interrupting self-harm behaviors. Access rights can vary by region.
Key takeaway: You have the right to a service dog to aid with PTSD; however, be aware of specific regional access regulations.
Can you receive disability benefits for PTSD stemming from domestic violence?
PTSD resulting from domestic violence is considered for disability benefits like PTSD from other causes. Documentation and evidence of PTSD as a diagnosis and its resulting limitations are required for benefit consideration.
Key takeaway: With proper documentation, PTSD from domestic violence can lead to disability benefits, just like other forms of PTSD.
Is a 100 percent disability rating possible for PTSD cases?
A 100 percent disability rating for PTSD is possible if you have extreme symptoms that ultimately impair your ability to function in a work environment. Ratings are based on the severity and frequency of PTSD symptoms.
Key takeaway: If PTSD severely disrupts your work and personal life, a 100% rating is within reach.
How does PTSD impact long-term life expectancy?
The long-term impact of PTSD on life expectancy can vary. Chronic stress from PTSD may contribute to health conditions that potentially reduce life expectancy, but this isn’t a guarantee and varies with individual circumstances and coping mechanisms.
Key takeaway: The relationship between PTSD and life expectancy is complex, highlighting the importance of effective management and support.11
About Jacob Maslow
After surviving the traumatizing events of 9/11, I took it upon myself to heal through helping others. I’m the primary caregiver of my children and understand from first-hand experience the lonely paths you have to walk as a partner and parent when leaving an unhealthy relationship.
We’re all echoing in a dark space that doesn’t have to be this empty, and that’s been my mission since finding solace and recovery in therapy: To help comfort others who are still in shock and at the prime of their struggle.
I came across BetterHelp after searching for this type of community. I wanted to belong to a body of proactive therapists and supportive therapy veterans who allowed me to see other sides of the story.
It was unconventional, and that’s what attracted me most. During my most challenging times, when my ex-wife completely cut me off from my children, I found comfort and clarity through BetterHelp.
Instead of being chained to a strict therapist recommendation, I was in charge of who I felt understood my struggle most. That allowed me to find my true peace, as I was reunited with those who read behind my words and had first-hand experience with my trauma.
Recovery is a choice; with BetterHelp, that choice will be a few clicks away. You can join their couples-oriented platform, Regain.us, for those stuck with family estrangement and toxic relationship patterns.
- The Burnout Epidemic: Why We’re All Feeling Overwhelmed and How to Cope - February 9, 2024
- How to Live a Peaceful Life - February 9, 2024
- Useful Information You Should Know About Health Screenings - February 8, 2024
This site contains affiliate links to products. We will receive a commission for purchases made through these links.

 Understanding PTSD
Understanding PTSD PTSD as a Recognized Disability
PTSD as a Recognized Disability PTSD Symptoms Affecting Functional Capacity
PTSD Symptoms Affecting Functional Capacity Challenges Beyond the Diagnosis
Challenges Beyond the Diagnosis