As a BetterHelp affiliate, we receive compensation from BetterHelp if you purchase products or services through the links provided
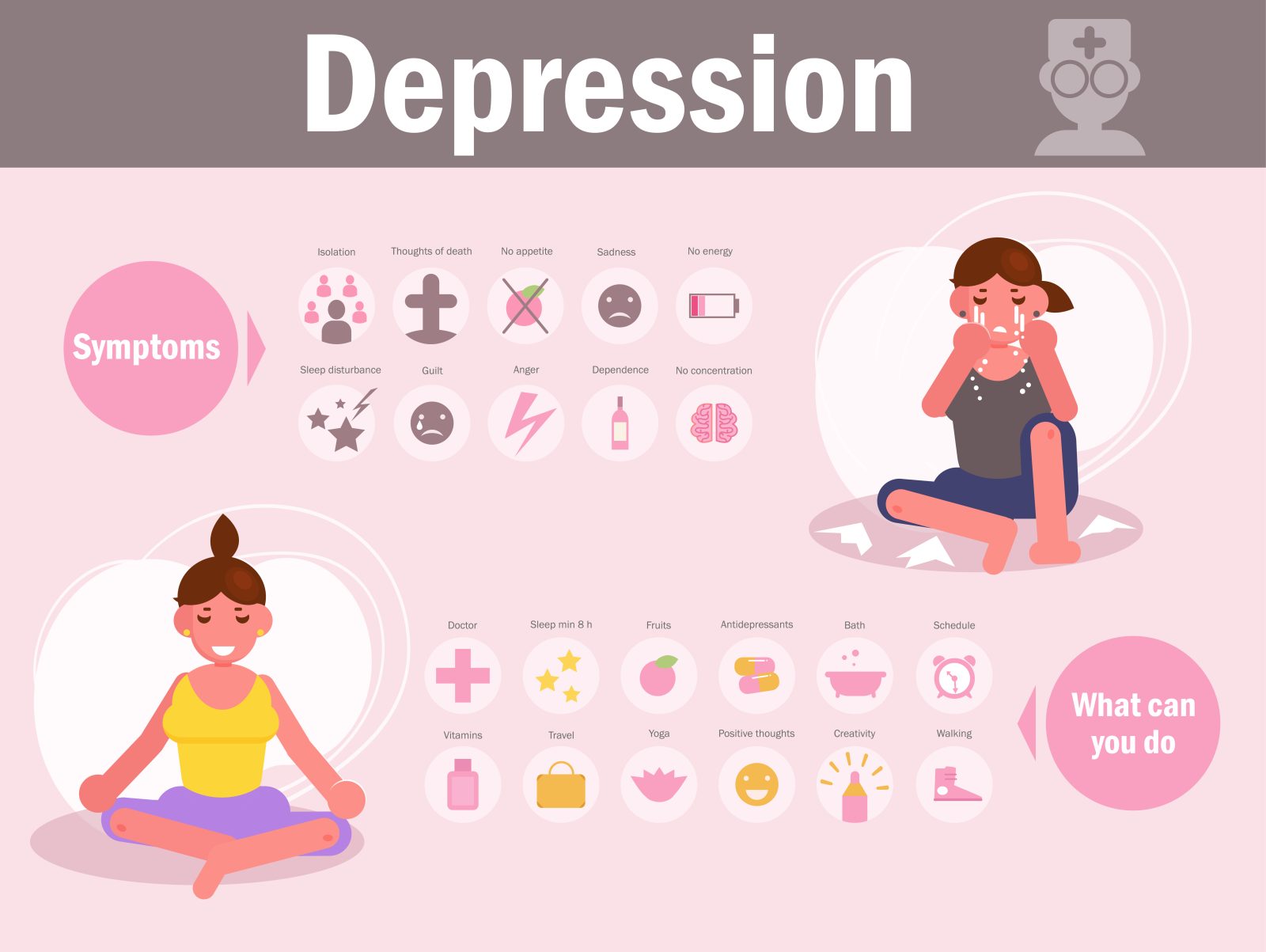
Concerns have been raised regarding the potential link between social media usage and mental health issues, particularly depression. It is imperative to investigate this possible relationship. Moreover, it is crucial to ascertain whether deleting social media accounts indicates depression or a proactive measure taken to address one’s mental health. Therefore, further research is needed better to understand social media’s effects on mental health.
Understanding the relationship between social media and depression is complex, as the impact of social media on mental health can be both positive and negative. For example, social media platforms allow individuals to connect with others, share experiences, and access information. However, they can also lead to heightened feelings of loneliness, low self-esteem, and disconnection, as users often compare their lives to the highlight reels of others. Furthermore, the widespread issue of cyberbullying on social media platforms can exacerbate feelings of depression and anxiety.
Key Takeaways
- Deleting social media can be a sign of depression or a proactive measure to improve one’s mental well-being.
- Social media has a complex relationship with mental health, with positive and negative effects.
- Balancing and managing social media use is essential for maintaining good mental health.
 Understanding the Relationship Between Social Media and Depression
Understanding the Relationship Between Social Media and Depression
The relationship between social media and depression is complex, with many aspects to consider. It is important to understand that correlation does not equal causation, which means that while there may be a connection between social media use and depressive symptoms, it does not mean that one causes the other.
Research has shown a correlation between social media use and an increased risk of depression, particularly among adolescents and young adults. Some reasons for this may include feelings of inadequacy and low self-esteem stemming from comparing oneself to others on social media platforms or the pressure to maintain a specific image online.
On the other hand, social media can provide support and a sense of belonging for individuals who may struggle with isolation or lack access to mental health resources. It has also been linked to decreased feelings of loneliness and increased social connectedness.
It is essential to recognize that not everyone who deletes social media does so because they are depressed. There may be various reasons for disconnecting from social media, such as the desire for more privacy, reduced online time, or increased focus on in-person relationships.
Furthermore, the effect of social media on an individual’s mental health is not solely determined by the amount of time spent online or negative social comparisons but also by how social media is used. For example, engaging in more positive experiences, such as sharing achievements and connecting with supportive friends, can counterbalance social media’s negative aspects.
In conclusion, the relationship between social media and depression is intricate and multi-faceted. It is crucial to understand that deleting social media is not necessarily a sign of depression but rather a personal choice that various factors may influence.
 The Impact of Social Media on Mental Health
The Impact of Social Media on Mental Health
The relationship between social media and mental health has become a growing concern in recent years. Prolonged exposure to social media can contribute to various mental health issues, such as anxiety, depression, and addiction. This section explores the potential impact of social media on mental well-being.
One of the most significant effects of social media is the increased risk of anxiety. As individuals are exposed to constant updates, images, and news, they may feel overwhelmed, causing their anxiety levels to rise. Moreover, comparing one’s own life to the highly curated lives of others on social media platforms can exacerbate feelings of inadequacy and further contribute to anxiety.
Mental illnesses, such as major depressive disorder and bipolar disorder, can also be influenced by social media usage. For example, people with depression may be prone to negative thought patterns, and the persistently idealized portrayals of life found on social media platforms can intensify those thoughts. Similarly, for those with bipolar disorder, the excessive stimulation and potential for comparison on social media can trigger mood swings.
Furthermore, a growing concern is that social media platforms may contribute to addiction. The instant gratification and reward system inherent in these platforms can lead to compulsive and excessive usage. This can increase screen time, impacting mental health and even physical well-being.
Happiness levels may also be affected by social media. While scrolling through a feed might provide initial satisfaction, it can leave users unsatisfied in the long run. This discontent can be attributed to the endless comparisons between oneself and others, leading to self-doubt and dissatisfaction with one’s life.
Finally, excessive social media use has been linked to an increased risk of suicide, particularly among adolescents and young adults. The constant exposure to others’ curated lives may lead to feelings of isolation and despair. Additionally, social media can increase the visibility of cyberbullying and hate speech, known risk factors for suicidal ideation.
In conclusion, the impact of social media on mental health is multifaceted, affecting a range of mental illnesses and emotional states. As society increasingly relies on social media platforms, it is crucial to recognize and manage the potential risks they present to mental well-being.
Influence of Popular Social Media Platforms
Social media platforms, such as Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, and blogs, have become integral to daily life for many people. They serve as a means to connect, share, and keep informed, but they can also influence mental health. In some cases, their use can contribute to feelings of depression or isolation.
Facebook is often associated with fostering a culture of comparison, where users can easily view the highlight reels of others’ lives. This can lead to feelings of inadequacy or envy, which may exacerbate depressive symptoms. Additionally, the time spent on the platform can decrease face-to-face interactions, potentially contributing to isolation and loneliness.
Instagram has a similar impact on users. Its visually-driven nature emphasizes appearances and often promotes unrealistic beauty standards. As a result, users might compare their lives to the heavily curated content they see on their feeds. This can negatively affect self-esteem and contribute to feelings of depression.
Twitter, while less centered around visuals, can also affect mental health. Constant exposure to negative news, opinions, or conflicts can cause emotional exhaustion or distress. Anxiety and depressive symptoms may increase as a result of this information overload.
Blogs, though perhaps less dominant in the social media sphere, can still contribute to feelings of depression. Users who follow personal blogs may be drawn into the lives of others and make unhelpful comparisons. Furthermore, if individuals use blogs as a platform for negative self-expression, it can reinforce depressive thought patterns.
Deleting or taking a break from social media platforms may sometimes signify a person’s attempt to cope with depressive symptoms. It can be an act of self-preservation, as distancing oneself from these platforms may reduce the negative factors that contribute to feelings of depression.
 The Dangers of Cyberbullying and Social Media
The Dangers of Cyberbullying and Social Media
Social media platforms offer numerous opportunities for connection, communication, and sharing personal experiences. However, these digital spaces also breed harmful behavior, such as cyberbullying. Cyberbullying refers to harassing, intimidating, or threatening others using digital means, typically social media. It can lead to severe consequences for both the victim and the perpetrator.
One of the primary reasons people may consider deleting their social media is the prevalence of bullying and cyberbullying. This behavior often perpetuates feelings of powerlessness, anger, and frustration. Over time, these experiences can contribute to depression, anxiety, and other mental health issues.
Another critical factor linked to social media use is doomscrolling. This term describes compulsively browsing through negative and distressing content online, even when it adversely affects one’s mood. As people engage in doom-scrolling, they may experience feelings of hopelessness and desolation, often leading to depressive symptoms.
Furthermore, social media tends to elicit envy and comparison among its users. By constantly seeing glimpses of others’ seemingly perfect lives, it’s difficult not to compare oneself to those portrayed online. This comparison can lead to feelings of inadequacy, dissatisfaction, and depression.
In this context, deciding to delete social media can be a proactive measure to improve one’s mental health. By distancing themselves from the potential dangers associated with online platforms, such as cyberbullying, doom-scrolling, and envy, individuals might experience a positive change in their overall well-being.
Analyzing Social Media Language Patterns: Machine Learning Application
Sentiment analysis is a powerful tool for studying the relationship between deleting social media and depression. By using machine learning techniques, researchers can uncover linguistic patterns associated with depressive behaviors. One popular approach is utilizing support vector machines to analyze textual data from social media platforms.
Python is an excellent programming language for implementing machine learning algorithms. It provides diverse libraries, making it easy for researchers to manipulate and analyze data. These libraries include tools for cross-validation and linguistic feature extraction, which are crucial in building an accurate model.
In this process, machine learning algorithms, such as support vector machines, are trained to understand and classify the emotional content of social media posts. To achieve this, researchers first extract linguistic features from the textual data. Techniques like n-gram models, which include unigrams and higher-order combinations, are used to generate features that best represent the data.
De Choudhury, Gamon, and Renara et al. are some scholars who have applied machine learning approaches to study language patterns in social media. Their work has demonstrated the potential of using sentiment analysis to identify early warning signs of depression in users’ behavior.
Cross-validation is another essential step in the machine-learning process. It involves dividing the dataset into multiple parts and training the algorithm on a certain portion while testing it on the remaining data. This approach helps to ensure the algorithm’s reliability and avoid overfitting.
Analyzing social media language patterns effectively studies the connection between deleting social media and depression. By utilizing machine learning techniques, such as support vector machines, and leveraging Python’s extensive libraries, researchers can accurately understand users’ emotional states and potentially detect early signs of depressive behaviors. This, in turn, can provide valuable insights for intervention strategies and promote mental well-being among social media users.
 Social Media, Sleep, and Depression
Social Media, Sleep, and Depression
A growing body of evidence suggests a connection between social media use, sleep, and depression. Social media platforms have become integral to many people’s daily lives, providing positive and negative consequences.
Sleep plays a crucial role in our overall mental health; however, excessive social media use has been linked to poor sleep quality. Studies have shown that increased screen time, especially before bedtime, can disrupt the body’s circadian rhythm and delay sleep onset. This can lead to insufficient sleep, which is a significant risk factor for depression.
Moreover, the content available on social media platforms can also affect an individual’s mental health. Constant exposure to idealized images and lifestyles may lead to feelings of inadequacy and contribute to low self-esteem. Additionally, social media platforms can sometimes be a breeding ground for online harassment and cyberbullying, negatively impacting users’ mental health.
Deleting social media accounts could be a sign of a person trying to reduce potential triggers for depression. Cutting off ties with these platforms might help improve mental health by reducing online comparisons, limiting exposure to negative content, and improving sleep quality.
In summary, deleting social media may not always be a sign of depression, but it could represent an individual taking proactive steps to protect and improve their mental health. It is essential to consider the context of the person’s situation and seek professional help when necessary.
The Role of Public Health and Pandemics on Social Media Behaviors
Public health measures significantly impact social media behaviors during pandemics, such as the COVID-19 outbreak. As people spend more time indoors and rely on digital platforms for communication, they become more active on social media. At the same time, the global crisis is a source of stress for many individuals, potentially leading some to opt for social media detox or deletion to alleviate anxiety.
Infectious diseases like COVID-19 often require implementing quarantine measures and promoting social distancing. As a result, many turn to social media for updates on the situation, to stay connected with friends and family, and even to access telemedicine services. Nonetheless, the constant barrage of news and opinions about the pandemic can take a toll on mental health, causing some users to feel overwhelmed and prompting them to step back from these platforms.
Public health authorities have recognized the importance of social media as a tool to disseminate accurate information and raise awareness about preventive measures, such as vaccination campaigns. Simultaneously, they must address the misinformation that thrives on social media. Fact-checking initiatives and collaboration with digital platforms have been indispensable in countering the spread of false data related to pandemics and understanding how the public reacts to various health issues.
Furthermore, using social media data can be crucial for public health research. Monitoring online interactions can help track the spread of infectious diseases, evaluate the effectiveness of public health campaigns, and identify vulnerable populations needing targeted interventions.
While it can be challenging to definitively say whether deleting social media is a sign of depression, it is clear that public health and pandemics play a critical role in shaping social media behaviors. Understanding these dynamics can aid in improving communication strategies during health crises and shed light on how various aspects of public health impact mental well-being.
 Managing Social Media Use for Better Mental Health
Managing Social Media Use for Better Mental Health
Exercise and physical activity are vital in maintaining physical and mental health. Incorporating regular exercise in daily routines can help reduce the negative effects of social media on mental health. Exercise releases endorphins, which help combat stress and keep the mind engaged in healthier activities.
Mindfulness practices, such as meditation and deep breathing, can aid individuals in focusing on the present moment rather than being engrossed in the virtual world. It can also help identify triggers, promote self-awareness, and manage emotionally-charged reactions to social media content.
Consulting with a therapist can provide individuals with tailored strategies to maintain a healthy balance between social media usage and mental health. Therapists can identify problematic behavior patterns and assist in setting appropriate boundaries or suggesting alternative coping mechanisms.
A qualified healthcare professional should always supervise prescription medication usage. Sometimes a person might require medication to help manage their mental health issues alongside therapy. Following the prescribed dosage and maintaining communication with the healthcare provider is essential, especially if experiencing side effects or concerns about the medication’s effectiveness.
Establishing a triage system can help prioritize and filter social media content, allowing users to focus on beneficial or relevant information. This method helps reduce the overwhelm and anxiety that often come with navigating the endless stream of information on social media platforms.
In summary, managing social media for better mental health involves incorporating exercise and mindfulness practices, seeking professional guidance, adhering to prescribed medications if needed, and implementing a triage system. Maintaining a balanced approach to social media usage will ultimately lead to a healthier mental state.
 The Isolation Paradox: More Connected, More Lonely
The Isolation Paradox: More Connected, More Lonely
In today’s digital age, it might seem counterintuitive that deleting social media could signify depression. After all, we’re more connected than ever, with friends and acquaintances just a few taps away. However, this increased connectivity can also lead to feelings of isolation and loneliness.
While social media platforms allow for constant interaction with others, research has shown that over-reliance on online connections can increase feelings of loneliness. These virtual connections often lack the depth and quality of face-to-face interactions, as they don’t provide the same level of social cues and emotional support as in-person communications. Consequently, individuals may feel more isolated from their friends and social circles.
Moreover, the prevalence of passive interactions on social media—such as scrolling through others’ posts or watching stories—can exacerbate the sense of isolation. Users may compare their lives to the seemingly perfect lives portrayed online, leading to a sense of inadequacy and self-doubt. This phenomenon, known as “social comparison,” can contribute to feelings of loneliness and depression.
Another factor contributing to the paradox of increased connectivity and loneliness is using social media to replace other, more substantial forms of social interaction. Individuals may rely on social media to fulfill their social needs instead of engaging in meaningful conversations and experiences with friends and loved ones. In the long run, they may feel increasingly lonely and disconnected.
It’s important to recognize that deleting social media accounts or taking a break from online platforms may not indicate depression. For some individuals, it could simply be an attempt to regain balance in their lives and prioritize offline relationships. In any case, it’s crucial to acknowledge the potential psychological impact of social media on our mental well-being and cultivate a healthy relationship with technology and our social connections.
Conclusion: Balance and Mindful Social Media Usage
Balancing and mindful usage are key factors in maintaining a healthy relationship with social media. Recognizing that these online platforms present a highlight reel of others’ lives can help users avoid comparing themselves to unrealistic standards. This awareness also prevents individuals from developing negative feelings or slipping into depression.
Managing notifications is one effective way to promote mindful social media usage. By controlling the frequency of alerts, individuals minimize distractions and maintain a boundary between their online and offline lives. This can improve attention span and concentration during daily tasks and activities.
Despite its many benefits, balancing a user’s social media presence and offline lives is essential. Maintaining healthy social connections outside the virtual world fosters personal well-being. Moreover, engaging in hobbies, physical activities, and relaxation techniques will reduce the chances of experiencing negative impacts, such as depression, from social media usage.
In conclusion, adopting a more thoughtful and controlled approach to using social media platforms will allow users to reap the benefits of these networks without risking their mental health. The focus should be on fostering a balanced lifestyle, both on and offline, to mitigate any potential adverse effects of excessive social media engagement.
Frequently Asked Questions

Is removing social media helpful for mental well-being?
Removing social media can be helpful for some individuals’ mental well-being. Limiting exposure to the constant stream of information and social comparison can aid in reducing stress, promoting better sleep, and encouraging healthier habits. However, the effect can vary depending on the person and their usage patterns.
Do people with depression tend to avoid social platforms?
It is not universally true that people with depression avoid social platforms. However, some individuals with depression may avoid or withdraw from social platforms due to feelings of worthlessness or a fear of being judged. Other people may use social media excessively to escape negative thoughts.
How does social media affect mental health?
Social media can have both positive and negative effects on mental health. On the one hand, it allows individuals to stay connected with friends and family, share personal content, and access information. On the other hand, excessive social media usage can lead to loneliness, anxiety, and jealousy due to the constant need for validation and social comparison.
Can taking a break from social media improve mental health?
Taking a break from social media can provide an opportunity to reflect on personal values, engage in other hobbies, and strengthen real-life connections, all of which can help improve mental health. It can relieve the constant barrage of information, the urgency to respond, and the social comparisons with social media usage.
Are there benefits to going offline during depressive episodes?
Going offline during depressive episodes may have benefits, such as reducing symptoms and allowing individuals time to focus on their mental health and self-care. Disconnecting from social media can also help prevent exposure to negativity and the urge to compare oneself to others, both of which can exacerbate depression.
How does the absence of social media impact our emotions?
The absence of social media can impact our emotions in various ways. Some people may feel a sense of relief from the constant need to stay connected and updated. For others, it might bring about feelings of loneliness and disconnect. It is essential to balance the time spent online and offline to maintain healthy emotional well-being.
About the Author: Jacob Maslow
Navigating the complex world of mental health, I’ve found solace in long daily walks and therapeutic practices. As someone who relies on Lexapro to manage my mental well-being, I understand the delicate balance that life sometimes demands. My journey has been further complicated by a prolonged court battle over the custody of my two beloved children. My ex’s severe narcissistic tendencies have led to heart-wrenching alienation, leaving me yearning for the close bond we once shared.
With a passion for educating and supporting others, I pen articles like this, touching on topics ranging from mental health to narcissism. I hope that by sharing my experiences and insights, others can find the strength and resources to overcome their challenges. Additionally, I’ve channeled my experiences into a legal platform dedicated to aiding individuals facing similar spousal non-compliance with court orders and parental alienation.
Through it all, I firmly believe that no mental health hurdle is insurmountable, and with the right tools and mindset, anyone can find their path to healing.
- Breaking the Silence: Why Men’s Mental Health Matters More Than Ever - April 15, 2025
- How to Transform a Home’s Patio Space into a Relaxing Space - March 23, 2025
- 5 Strategies to Use a Cell Phone to Help Manage Your Stress - March 23, 2025
This site contains affiliate links to products. We will receive a commission for purchases made through these links.


 Understanding the Relationship Between Social Media and Depression
Understanding the Relationship Between Social Media and Depression The Impact of Social Media on Mental Health
The Impact of Social Media on Mental Health
 The Dangers of Cyberbullying and Social Media
The Dangers of Cyberbullying and Social Media
 Social Media, Sleep, and Depression
Social Media, Sleep, and Depression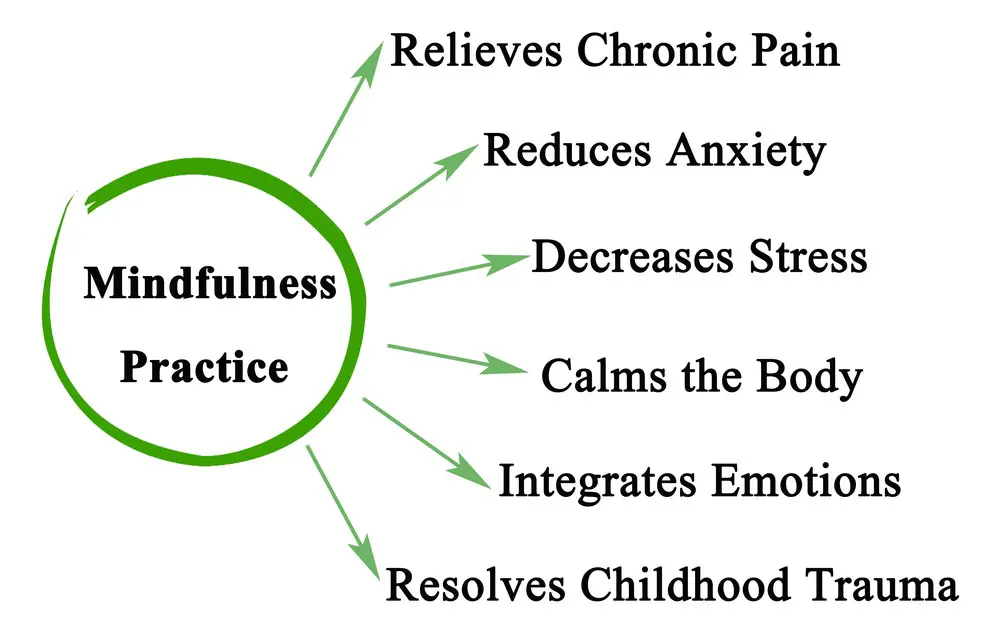 Managing Social Media Use for Better Mental Health
Managing Social Media Use for Better Mental Health The Isolation Paradox: More Connected, More Lonely
The Isolation Paradox: More Connected, More Lonely
