As a BetterHelp affiliate, we receive compensation from BetterHelp if you purchase products or services through the links provided
Emotional support teaching is gaining more recognition in education as schools recognize the need for specialized support for students with emotional and behavioral challenges. Emotional support teachers, sometimes called behavior analysts or social-emotional learning (SEL) interventionists, work closely with students to identify and address emotional difficulties and equip them with the necessary skills to achieve their potential in the classroom.
These dedicated professionals are crucial in implementing intervention strategies and ensuring a positive learning environment for all students. Emotional support teachers collaborate with various school community members, including teachers, administrators, and parents, to develop individualized student plans based on their needs and circumstances. Focusing on social and emotional learning, they foster academic growth and vital life skills needed for personal well-being, resilience, and successful interpersonal relationships.
Key Takeaways
- Emotional support teachers specialize in addressing emotional and behavioral challenges in students.
- They collaborate with various members of the school community to develop individualized plans.
- Focusing on social and emotional learning fosters academic growth and essential life skills.
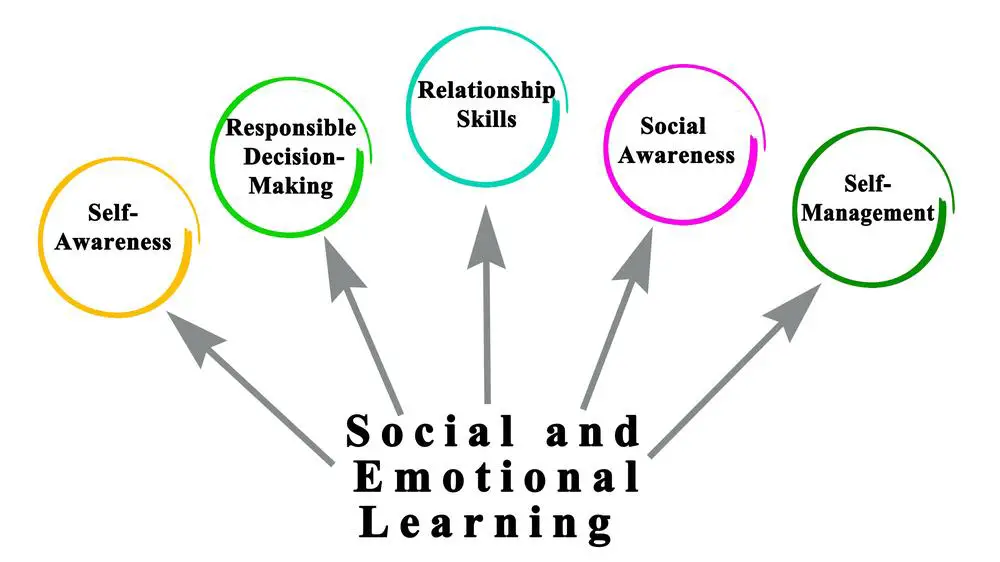
Understanding the Role of an Emotional Support Teacher
As an emotional support teacher, your role is vital in helping students develop essential life skills such as social integration, emotional management, and effective communication. You will use various models and strategies to help your students build these skills, like Michelle Garcia Winner’s Social Thinking Curriculum and the Zones of Regulation method.
One of the critical characteristics of an emotional support teacher is genuine concern and care for your students. This may involve showing empathy, understanding their feelings and points of view, and being a dependable figure in their lives. Your positive influence can significantly impact student motivation and overall well-being.
Here are some helpful approaches to consider in your role as an emotional support teacher:
- Create a nurturing environment: This means providing a safe space where students feel comfortable expressing their emotions and thoughts. Be patient, listen actively, and validate their feelings.
- Develop strong relationships: Spend time getting to know your students individually. Learn about their strengths, interests, and life circumstances. Genuine connections will make it easier to guide them and offer tailored support.
- Implement social-emotional learning (SEL) strategies: Bring SEL programs into your classroom to promote the development of self-awareness, self-regulation, relationship-building, and practical decision-making skills. Don’t hesitate to adapt these strategies to the unique needs of your students.
- Collaborate with other professionals: Work closely with counselors, psychologists, and other school staff to ensure a comprehensive approach to supporting your students’ emotional needs. Sharing insights about students’ progress and challenges can help create a more cohesive support system.
Remember that as an emotional support teacher, you play a crucial part in shaping learners’ experiences and personal growth. Your guidance, understanding, and support contribute to their overall success, not only academically but also socially and emotionally.
Role in the Classroom
Building Positive Relationships
As an emotional support teacher, your role in the classroom is crucial in ensuring students feel connected and supported. Building positive relationships with students is one of the most critical aspects of your role. To foster a strong bond with your students, consider the following tips:
- Show genuine concern and care for your students
- Respect their perspectives and feelings
- Maintain open communication
By implementing these strategies, you can create a safe, nurturing environment for students to thrive.
Instructional Methods and Curriculum
Another important aspect of your role as an emotional support teacher is creating a curriculum that caters to your student’s emotional needs and learning styles. Here are some ideas on how to achieve this:
- Design lesson plans that encourage cooperative learning and teamwork
- Integrate social-emotional learning activities into the curriculum
- Provide differentiated instruction to meet individual learning needs
- Foster a growth mindset by promoting effort and persistence over innate abilities
Remember, the goal is to make learning engaging and relevant, helping students feel connected and motivated in the classroom.
Managing Classroom Behavior
Emotional support teachers also play a vital role in managing classroom behavior and creating an environment conducive to learning. Here are some key strategies for managing behavior:
- Be a positive role model: Demonstrate patience, empathy, and respect
- Establish clear expectations and boundaries
- Develop a behavior management plan to address challenging behaviors
- Encourage positive behaviors through reinforcement and praise
Managing Classroom behavior effectively will help your students feel more secure and improve the overall learning experience.
With these practices and tips in place, you’ll be well on your way to significantly impacting your students’ lives as an emotional support teacher.

Impact on Social and Emotional Learning
Promoting Mental Health
Supporting teachers in developing their social and emotional competencies makes a difference. When teachers are emotionally healthy, they are better equipped to manage their stress levels, maintain healthy relationships, and make thoughtful decisions in the classroom. Developing your own social and emotional skills can not only benefit your well-being but also create a positive impact on your students and colleagues. Here are some tips:
- Practice self-care: Take breaks, exercise regularly, and engage in hobbies that help you relax.
- Reflect on emotions: Acknowledge your feelings and seek support from a counselor or colleagues when necessary.
- Build a support network: Cultivate relationships with colleagues who understand the challenges of teaching and can provide encouragement and advice.
Key takeaway: Enhancing your social and emotional competencies improves mental health, equipping you to manage your personal and professional challenges better.
Role in Student Well-Being
Your ability to support social and emotional learning (SEL) among students is crucial for their success and well-being. When you are attentive to their emotional needs, you have a powerful impact on their development. By embracing active listening, empathy, and trust, you promote:
- Improved self-awareness: Encouraging students to understand and express their feelings with confidence.
- Better social skills: Guiding students in building strong relationships with their peers and adults.
- Enhanced problem-solving abilities: Steering students to use critical thinking and empathy when faced with challenges.
Key takeaway: Your role in fostering SEL substantially impacts students’ well-being, equipping them with essential life skills.
Promoting a Positive Climate
You create a nurturing and inclusive classroom environment as an emotional support teacher. A favorable climate encourages students’ social and emotional growth, ultimately improving their academic performance. To promote a favorable climate, consider the following strategies:
- Set clear expectations: Establish and consistently reinforce classroom rules that reflect respect and empathy.
- Encourage open communication: Foster a safe space for students to share their thoughts, feelings, and concerns.
- Celebrate diversity: Embrace differences by incorporating activities highlighting each student’s unique qualities and contributions.
Key takeaway: By cultivating a positive classroom climate, you enable students to thrive emotionally, socially, and academically. Furthermore, these efforts also contribute to your own well-being and professional success.
 Support Services for Students
Support Services for Students
Addressing Trauma and Stress
As an emotional support teacher, you play a vital role in helping students deal with trauma and stress. One effective way to address these issues is by creating a safe and supportive learning environment. Remember to:
- Listen attentively: Encourage students to share their feelings and experiences and validate their emotions.
- Create routines: Structure and consistency can help students feel more secure and in control.
- Offer coping strategies: Teach students relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, mindfulness, and progressive muscle relaxation.
- Incorporate stress-reducing activities: Yoga, mindfulness meditation, and art therapy are some examples that can help students manage stress.
Key takeaway: Be empathetic and proactive in addressing trauma and stress to foster a supportive learning environment.
Responding to Emotional Needs
A crucial aspect of your role as an emotional support teacher is responding to your students’ emotional needs. Here are some tips to help you effectively meet their needs and promote mental well-being:
- Encourage open communication: Create an atmosphere where students feel comfortable discussing their feelings without fear of judgment.
- Offer resources: Share information on supportive services available to students, such as school counselors or mental health professionals.
- Develop social and emotional literacy: Teach students to recognize and manage their emotions and empathize with others.
- Acknowledge accomplishments: Recognize students’ achievements, big and small, to build their self-esteem and confidence.
Key takeaway: Being attuned to your students’ emotional needs allows you to support their well-being better and create a positive learning experience.
 Professional Development for Teachers
Professional Development for Teachers
Importance of Self-Care
As a teacher, it’s essential to prioritize self-care in your professional development. Juggling various responsibilities, dealing with stressors, and managing the emotional needs of students can be overwhelming. Healthy self-care habits can improve your overall well-being and support your students effectively.
Here are some self-care tips to incorporate into your routine:
- Set boundaries: Understand your limits and don’t hesitate to communicate them with others.
- Take breaks: Give yourself time to recharge by stepping away from work briefly.
- Exercise regularly: Physical activities help relieve stress and promote mental and emotional health.
- Practice mindfulness: Meditate or engage in other activities to stay present and focused.
Remember: Prioritizing self-care not only benefits you but also supports the emotional health of your students.
Building Communication and Leadership Skills
Effective communication and leadership skills are integral in your professional development as a teacher. These abilities enhance student interactions and expand your capacity to collaborate with colleagues and administrators.
Here are some strategies to develop your communication and leadership skills:
- Active listening: Pay attention, ask questions, and paraphrase to show genuine understanding.
- Empathy: Put yourself in others’ shoes to better understand their feelings and perspectives.
- Clarity: Make sure your messages are clear, concise, and jargon-free.
- Open-mindedness: Encourage feedback and be willing to adapt based on the input of others.
- Confidence: Believe in your abilities and demonstrate a positive attitude.
By focusing on self-care, communication, and leadership in your professional development, you can become a more empathetic and effective educator. Ultimately, these efforts contribute to your success, reduce overwhelmed feelings, and positively impact your students’ learning experience.
Role in the Wider School Community
As an emotional support teacher, your influence reaches beyond the classroom and into the wider school community, where you can help create a positive environment for all stakeholders. This section will discuss your role when working with administrators and coaches and developing partnerships with parents and families.
Working with Administrators and Coaches
To foster a supportive community, it’s crucial to collaborate with school administrators and coaches. They can provide valuable insights and resources to help you better understand and address students’ social and emotional needs.
- Share expertise and strategies: Work together to develop the most effective plans and programs that address emotional and social concerns.
- Professional development: Attend workshops or arrange training sessions to enhance your knowledge and skills in supporting students’ emotional well-being.
- Coordinate efforts: Ensure that everybody is on the same page so that student support remains consistent across the school.
Partnerships with Parents and Families
A strong partnership between educators, parents, and families is vital in providing emotional support to students. Engaging parents in the process creates a network of care that extends beyond the school setting.
- Communication is key: Maintain open and positive communication channels with parents to stay informed about their children’s emotional well-being and discuss concerns.
- Be approachable: Encourage parents to reach out to you if they have any questions or concerns. Create a welcoming atmosphere where they feel comfortable discussing their child’s emotional needs.
- Involve parents in school activities: Invite parents to attend school events, meetings, and workshops to support their child’s emotional well-being and engage in the community.
Remember, you play a crucial role in the overall well-being of the school community. Collaborating with administrators, coaches, and parents can foster a supportive network that ensures all students receive the emotional support they need. Keep up the great work!
Understanding the Impact of Covid-19
During the COVID-19 pandemic, teachers faced numerous challenges and opportunities while adapting to new teaching platforms and methods.
Challenges and Opportunities
Throughout the pandemic, teachers experienced various challenges, such as transitioning to remote learning, dealing with personal stress and financial burdens, and struggling to provide emotional support to their students. Additionally, they encountered the potential for burnout due to increased workloads and lack of support from administration and leadership1.
On the other hand, Covid-19 also brought about opportunities for educators to explore and utilize innovative learning resources. These resources allowed them to connect with students, enhance engagement, and maintain educational continuity during these trying times. Teachers discovered new ways of teaching and supporting their students, as well as themselves, by:
- Leveraging digital tools and learning management systems
- Participating in online professional development programs
- Collaborating with fellow educators through virtual networks
- Adapting curriculum for remote learning environments
Utilizing Remote Learning Resources
To make the most out of remote learning, teachers turned to a wide range of resources designed to support their work. These tools and platforms helped them navigate the challenges brought on by the pandemic and, in some cases, even improve their teaching methods. Some essential resources included:
- Learning Management Systems (LMS): Platforms like Google Classroom, Canvas, and Blackboard offered a centralized hub for course materials, assignments, and communication with students and parents.
- Virtual Meeting Tools: Applications like Zoom, Microsoft Teams, and Google Meet facilitated live online classes and enabled interactive discussions.
- Digital Curriculum and Content: Teachers utilized online platforms like Khan Academy, Quizlet, and Edmodo to provide engaging content and interactive assignments.
- Online Collaboration Tools: Tools like Google Docs, Padlet, and Nearpod facilitated group work and encouraged student collaboration.
Key takeaway: Although the Covid-19 pandemic posed unprecedented challenges for teachers, they found ways to adapt and make use of various tools to continue providing a quality education for their students.
What training is required to become an emotional support teacher?
To become an emotional support teacher, you typically need a bachelor’s degree in education, psychology, or a related field. Additionally, some schools and districts require special certifications, such as a certification in special education or a specific endorsement in social-emotional learning (SEL). Investing in ongoing professional development is essential to enhance your skills and stay current on best practices in the field.
How much does an emotional support teacher earn?
The salary of an emotional support teacher can vary based on factors like experience, location, and the level of education you’re working with (elementary, middle school, or high school). According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, the median annual wage for special education teachers was $61,420 in 2020. Remember that this can vary based on your role, school district, and experience.
Where can I find emotional support teachers near me?
Finding local emotional support teachers can be as simple as contacting your local school district, contacting nearby colleges or universities with education programs, or exploring online platforms dedicated to education and mental health resources. Additionally, professional organizations related to SEL and special education can guide on locating experienced emotional support teachers in your community.
What job opportunities are available for emotional support teachers?
Emotional support teachers can find job opportunities in various settings, such as:
- Public and private schools
- Learning centers or tutoring facilities
- Nonprofit organizations focused on youth mental health and SEL
- Developing and implementing training or workshops for other educators and parents
Proactively networking within education and mental health communities can lead to job opportunities.
What does the job description of an emotional support teacher include?
An emotional support teacher may have the following responsibilities:
- Developing and implementing the SEL curriculum
- Collaborating with other educators, school staff, and parents to support students’ social-emotional growth
- Regularly assess students’ progress and adjust instructional strategies based on individual needs.
- Creating inclusive, supportive, and safe learning environments
- Providing guidance and resources for addressing mental health challenges and promoting emotional well-being
How can I create an effective emotional support classroom environment?
Here are some tips for creating a supportive and inclusive environment:
- Establish clear expectations and routines: Ensure students understand what is expected of them and provide consistent structure.
- Promote empathy and understanding: Encourage students to recognize and appreciate different perspectives and emotions.
- Create a safe space: Build an atmosphere where students feel comfortable expressing themselves and seeking help when needed.
- Encourage healthy communication: Teach students effective communication techniques for resolving conflicts and expressing their feelings.
- Collaborate with other educators and parents: Foster relationships with those involved in the students’ lives to create a support system.
Key takeaway: Creating an effective emotional support classroom environment requires a combination of structure, understanding, safety, communication, and collaboration.
- 3 Ways Wearing a Hat Can Help Lower Your Stress Levels - April 19, 2025
- Breaking the Silence: Why Men’s Mental Health Matters More Than Ever - April 15, 2025
- How to Transform a Home’s Patio Space into a Relaxing Space - March 23, 2025
This site contains affiliate links to products. We will receive a commission for purchases made through these links.


 Support Services for Students
Support Services for Students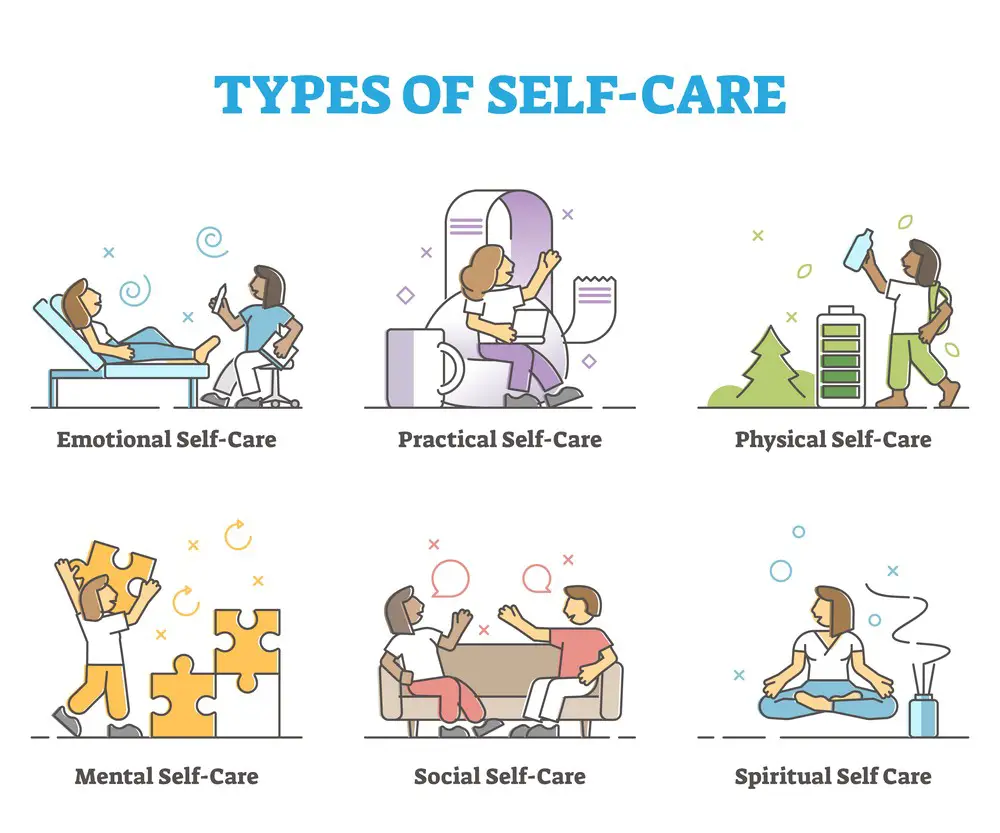 Professional Development for Teachers
Professional Development for Teachers
