As a BetterHelp affiliate, we receive compensation from BetterHelp if you purchase products or services through the links provided
Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), a mental health condition, affects millions of people globally. WHO (the World Health Organization) estimates that the condition affects about 1% of the global population. Figures from NIMH (the National Institute of Mental Health) indicate that 1.2% of adults have OCD in the U.S., but it could be many more. Unfortunately, about one-third of these people don’t seek help because they feel embarrassed or self-conscious, leading to undiagnosed and unreported cases.
Fortunately, OCD is treatable. Therefore, it is imperative to reduce its stigma by providing these individuals with the understanding and treatment to relieve their symptoms.
Basic OCD Facts
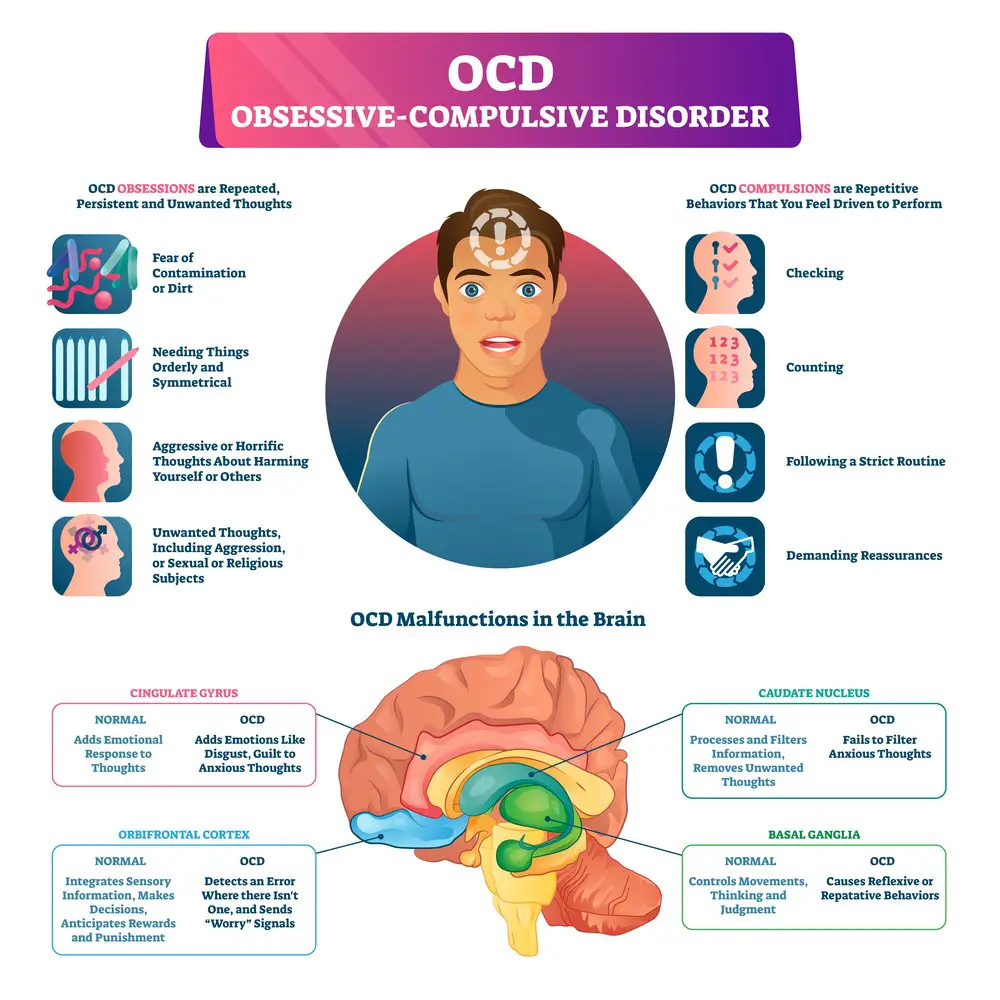
OCD causes unwanted, recurring thoughts and repetitive behaviors in the individuals affected. The average age of OCD onset is around 19, but 50% of sufferers experience their first symptoms before turning 18.
However, these symptoms cause significant distress to its sufferers, affecting their daily lives. Some of the most common topics that cause individuals frustration and anguish include:
· Hygiene and contamination
· Neatness, counting, and organization
· A constant need for reassurance
· Repeated rechecking of appliances, locks, or switches
· Catastrophizing thoughts or imagining a tragic event that happens to them or a loved one
· Taboo thinking or imagining subjects beyond commonly accepted societal norms
Severe OCD can significantly impact a person’s ability to maintain regular work life and function within a family, often leading to depression. Scientists believe several risk factors could cause OCD, but they haven’t pinned it down to one. These include genetics, brain abnormalities, environment, underlying mental health issues, and exposure to a one-off or recurring stressful situation.
Can OCD Be Cured?
When left untreated, OCD symptoms appear and disappear, becoming a chronic condition that can also change in severity. Several treatments provide the hope of relief for the symptoms of OCD, even though a complete cure is rare.
In this article in Brains Way, we read that the American Psychiatric Association (APA) and other sources indicate that up to 20% of patients can reach full recovery or remission. Treatments aim to significantly reduce the symptoms of OCD, allowing patients to manage their compulsions and obsessions to live happier lives.
Exploring Treatment Options for OCD
Currently, OCD sufferers can seek several recognized OCD treatments. However, since these vary in effectiveness and side effects, sufferers should consult a physician before embarking on one, ensuring that it suits their needs and symptoms.
1. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy
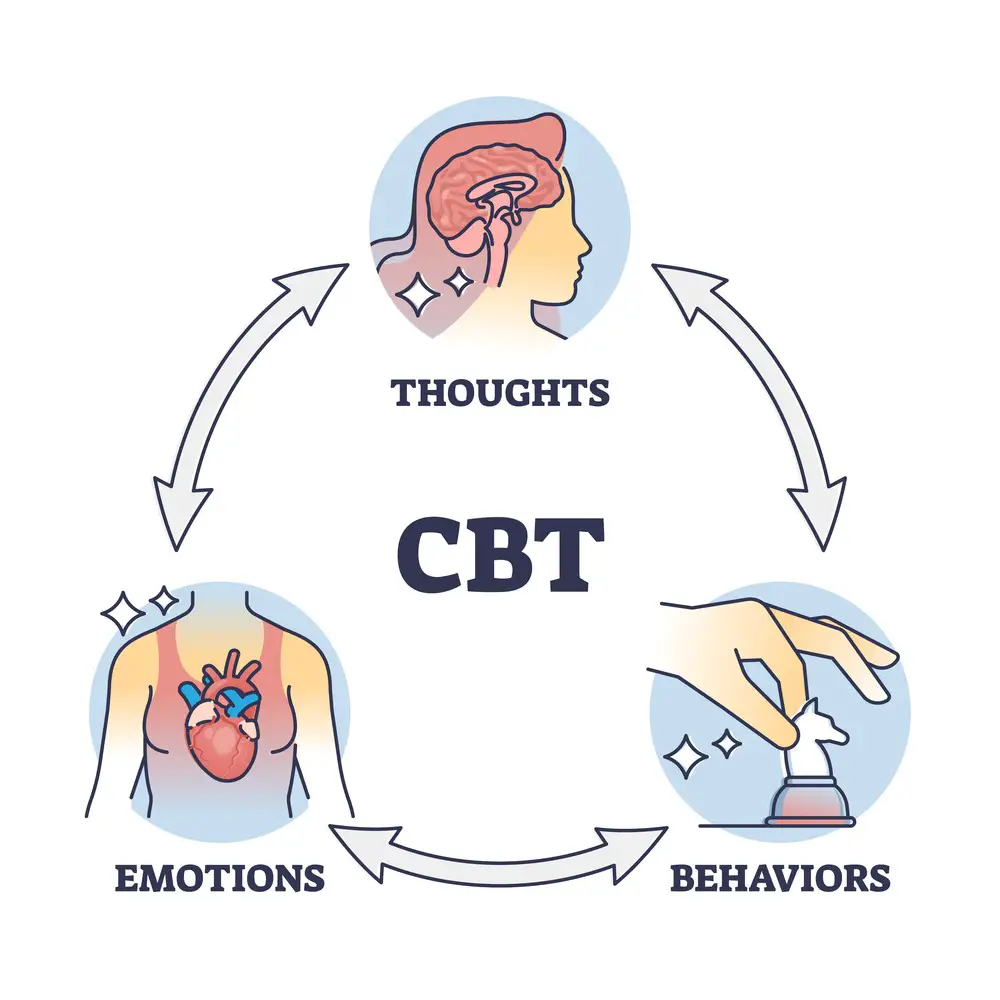
CBT, a type of talking therapy, involves working with a trained mental health professional to break down problems into thoughts, physical feelings, and actions. Patients are encouraged to confront the thoughts that lead to compulsive behavior, progressively helping alleviate their symptoms.
Therapists start by helping patients to familiarize themselves with the different aspects of their condition, beginning with the ones causing minor distress before moving to more difficult ones.
CBT has branched into different therapies, offering OCD sufferers with better symptom relief. Acceptance and commitment therapy (ACT) is notable since it works based on openness and flexibility in managing the symptoms. The patient works with the therapist to define their obsession and work toward a commitment to improving their well-being.
The patient must make a rigorous effort, but the sessions and exercises practiced at home can offer relief after up to 20 sessions for people with milder OCD. Severe cases usually require longer treatment.
2. Deep Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (Deep TMS™)
Deep TMS uses magnetic fields to safely and effectively help promote healing for conditions like OCD, PTSD, depression, addiction, anxiety, etc., non-invasively. The treatment uses magnetic fields to stimulate different brain areas associated with these mental health issues, requiring no downtime for the patients.
The ease and effectiveness of incorporating Deep TMS into a patient’s daily routine without causing any significant or long-lasting side effects have made it an efficient treatment method for OCD.
Thanks to its ability to provide substantial relief for OCD sufferers, the FDA cleared Deep TMS in 2018. A multicenter clinical study published in the American Journal of Psychiatry followed a year later, reaching the same conclusion on the effectiveness and safety of Deep TMS on patients who had seen no improvement from therapy or medication courses.
3. Exposure and response therapy (ERP)
Another form of therapy, ERP, has also proven effective in effectively treating OCD. Patients are exposed to the problems that stimulate their anxiety-raising behavior and are encouraged to manage their reactions to these stimuli.
The basis of the therapy is to prevent avoidance of situations that produce OCD but rather to find a safe way to deal with their distressing emotions. Depending on the severity of the OCD, it can take anything from one session to several months to see improvement, but ERP is a reliable and fast OCD treatment.
4. Medication
In reasonably severe cases of OCD where the above forms of therapy have minimal effect, doctors may prescribe FDA-approved selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) like Prozac or Zoloft. Rarely, doctors may prescribe tricyclic antidepressants.
SSRIs increase the brain’s serotonin level, helping to improve the symptoms of OCD. However, it can take up to twelve weeks before patients notice a difference. Therefore, the treatment may continue for anything from one year onwards, depending on the severity of the OCD symptoms.
Medication does provide relief for many patients, but it also presents many side effects. One major drawback to SSRIs is that patients must stop the medications gradually because sudden cessation also comes with unpleasant side effects.
5. Psychodynamic Therapy
Talkspace therapist Reshwana Chapple states, “Psychodynamic therapy explores the relationships and events of a patient’s life to find the trigger to their anxiety and OCD symptoms.”
The treatment aims to help them understand the reasons for their thoughts and behaviors. As a result, with time, patients learn to be more flexible and soothed to the situations that induce their anxiety.
6. Invasive Treatments
In very rare cases where any of the above non-invasive treatments have proven non-effective, patients battling with severe OCD may seek help in the form of neurosurgical interventions from healthcare professionals.
Invasive procedures are still limited to studies where a limited number of patients join trials, meaning their efficacy in alleviating OCD symptoms has yet to be determined. Some neurological lesion methods tested so far include radioactive seed implants that cause local ablation, coagulative lesions made with a gamma knife, stereotactic ablation, and deep brain stimulation. Outcomes are usually only assessed after several months to two years post-surgery. Research is ongoing, and researchers continue to improve the effectiveness and safety of these procedures, giving hope for severe cases.
All these treatments have their advantages and drawbacks, but they help OCD patients take back control of their lives. As with any condition, the key to effective treatment is an accurate diagnosis and timely intervention from healthcare professionals. With the right medical advice and therapy, most patients can lead relatively normal life without OCD-related worries. Whatever type of therapy you decide to pursue, it is important to remember that success depends on your commitment and willingness to confront your fears to overcome them. With knowledge about OCD treatment options available today, you’re sure to find one that works best for you!
Tips & Advice:
The most important thing to remember is that OCD is manageable. With the right combination of treatment and therapy, OCD sufferers can work towards a better quality of life and have their symptoms managed or even eliminated. Many treatments are available, so talking to a healthcare professional about the best option for you is important. No matter what type of treatment you choose, you must remain committed and diligent with your course of action to achieve success. Keep in mind that recovery is possible if given enough time and effort. With patience and dedication, individuals with OCD can lead productive lives!
Strategies for Living With OCD:

– Acknowledge and accept the condition.
– Develop a routine of healthy habits that can be maintained regardless of intrusive thoughts or urges.
– Avoid triggers such as people, places, things, or situations that could cause anxiety.
– Engage in activities that distract from obsessive thoughts and provide relaxation.
– Connect with other individuals who have OCD to gain support and advice.
– Practice cognitive behavioral techniques to reframe irrational beliefs and reduce symptoms associated with OCD.
While many treatments are available for those suffering from OCD, finding the right combination of therapies or medications to treat the condition effectively can be difficult. Those with OCD must seek an accurate diagnosis and consult a professional healthcare provider to receive the most appropriate individualized treatment plan. With the right combination of therapy and medication, most people living with OCD can find relief from their symptoms and lead more functional lives. By committing to a course of treatment, those suffering from OCD can regain control and live a happier life free from obsessive-compulsive worries.
FAQs
- 3 Ways Wearing a Hat Can Help Lower Your Stress Levels - April 19, 2025
- Breaking the Silence: Why Men’s Mental Health Matters More Than Ever - April 15, 2025
- How to Transform a Home’s Patio Space into a Relaxing Space - March 23, 2025
This site contains affiliate links to products. We will receive a commission for purchases made through these links.



