As a BetterHelp affiliate, we receive compensation from BetterHelp if you purchase products or services through the links provided
Low testosterone is a hormone deficiency that affects many men, especially as they age. It can cause several physical and mental issues, such as loss of libido, muscle mass, energy, and the ability to maintain a healthy emotional balance. One lesser-known side effect of low testosterone is anxiety, which may be an indirect result of several other symptoms related to testosterone deficiency.
Anxiety is a natural stress response, but it can become overwhelming and debilitating for some individuals. While it is often considered a condition unrelated to hormones, the link between low testosterone and anxiety warrants exploration. Understanding the roles and functions of testosterone in the body can shed light on how low levels of this hormone may contribute to developing or exacerbating anxiety.
Key Takeaways
- Low testosterone levels can lead to various physical and mental health issues, possibly contributing to anxiety.
- Diagnosing low testosterone and anxiety requires a thorough evaluation by a medical professional.
- Treatment options for low testosterone and anxiety include hormone therapy, medications, and lifestyle changes.
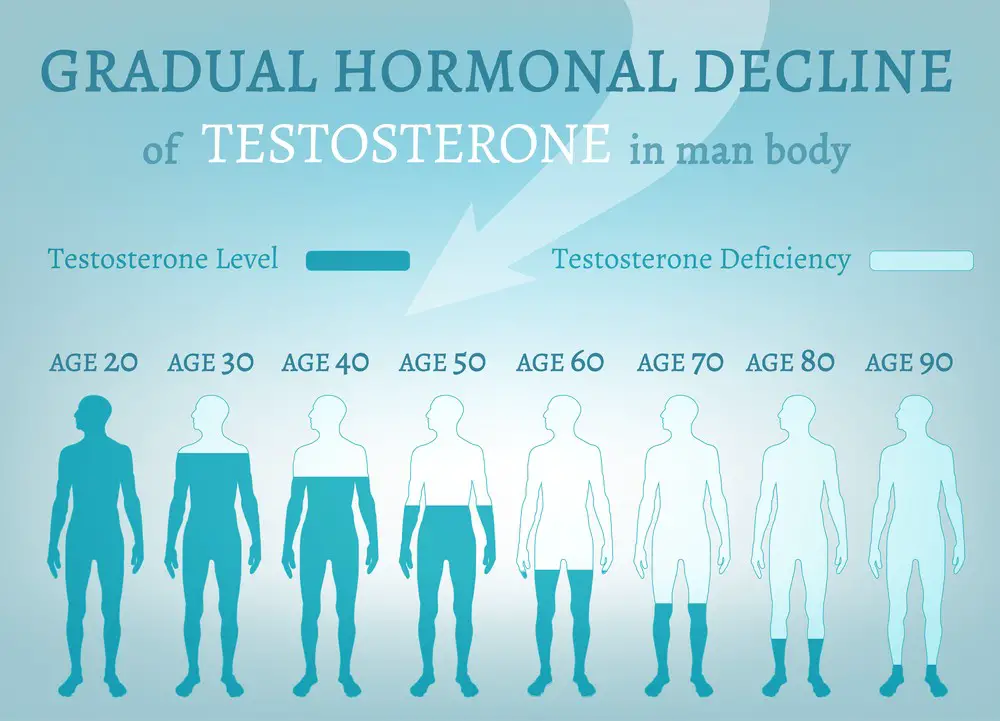
Understanding Low Testosterone
Low testosterone, also known as hypogonadism, is a condition in which a man’s body produces insufficient amounts of the male hormone testosterone. Testosterone is one of the primary androgens, hormones responsible for regulating various bodily functions, including developing male sex characteristics, muscle mass, and bone density.
As men age, it is normal for their testosterone levels to decline gradually. This decrease usually occurs at a rate of about 1% per year after the age of 30. However, some men may experience a more rapid decline or have naturally low testosterone levels, which can lead to various health issues.
Multiple factors contribute to low testosterone levels, including aging, obesity, certain medical conditions, and lifestyle choices. It is essential to recognize the symptoms of low testosterone and consult with a healthcare professional for diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Low testosterone levels can impact an individual in several ways, both physically and mentally. Some common physical symptoms include fatigue, decreased muscle mass, increased body fat, and reduced bone density. These physical changes can significantly affect a person’s overall quality of life and well-being.
In addition to the physical symptoms, low testosterone levels can contribute to psychological and emotional issues such as anxiety. It is essential to note that anxiety is a complex condition, and low testosterone may not always be the direct cause. However, hormonal imbalances can exacerbate anxiety and mood swings in some individuals, creating a greater need to understand the relationship between testosterone and mental health.
In conclusion, low testosterone levels can contribute to various physical and mental health issues, including anxiety. Addressing these hormonal imbalances through proper medical evaluation and treatment may help improve those affected’s overall well-being and quality of life.
Symptoms of Low Testosterone
Low testosterone can manifest through various symptoms, affecting physical and mental health. One common symptom is depression, which may also lead to anxiety. Individuals with low testosterone might experience mood swings and irritability, making it even more challenging for them to cope with daily stressors.
Fatigue is another typical symptom of low testosterone, causing an overall lack of energy and motivation. This sense of exhaustion can contribute to decreased work performance and affect one’s personal life.
Physically, low testosterone levels can negatively impact the body in numerous ways. Some men may experience erectile dysfunction or low sex drive, leading to difficulty maintaining healthy romantic relationships. They may also observe decreased muscle mass and strength, affecting their fitness abilities and overall health.
The reduction in muscle mass and strength can further result in the development of excess breast tissue, a common symptom in men with low testosterone. Additionally, low testosterone levels may cause infertility issues, posing a challenge for couples trying to conceive.
Low testosterone can also affect cognitive functions, such as memory and motivation. Those with low testosterone might struggle to concentrate or recall facts and details. This cognitive decline can create added frustration and contribute to the anxiety experienced by individuals with low testosterone.
Low testosterone can cause many symptoms, ranging from mood-related issues like anxiety and depression to physical changes, such as erectile dysfunction or decreased muscle strength. By recognizing these symptoms, individuals can proactively address their low testosterone levels and manage any accompanying anxiety.

Low Testosterone and Anxiety
Low testosterone is a hormonal imbalance that can contribute to anxiety and related symptoms. Anxiety encompasses a range of negative emotions, including stress, worry, fear, and restlessness, which can manifest as anxiety disorders, mood changes, and emotional disturbances. Individuals may sometimes experience panic attacks or social anxiety due to low testosterone levels.
It is important to note that anxiety is a complex condition with various causes, including genetic, environmental, and psychological factors. While low testosterone may not be the sole cause of anxiety in individuals, research has indicated a possible connection between hormonal imbalances and anxiety symptoms. As testosterone plays a pivotal role in regulating mood, maintaining energy levels, and influencing emotional well-being, the deficiency of this hormone can lead to negative emotional outcomes.
Although low testosterone has been linked to anxiety and emotional changes, it is not universally experienced. In some cases, individuals with normal or high testosterone levels may also encounter anxiety disorders or related symptoms. Individuals need to consider all possible factors and seek professional advice to determine the underlying cause of their anxiety.
Treatment options for low testosterone-induced anxiety may include hormone replacement therapy, medications, and lifestyle modifications. These therapies aim to balance the hormonal levels and alleviate anxiety symptoms ultimately. However, consulting healthcare professionals before treatment is important to ensure proper evaluation and comprehensive guidance on appropriate therapy.
Low testosterone can be associated with anxiety and its many manifestations. By addressing hormonal imbalances and seeking professional help, individuals may find relief from the debilitating effects of anxiety and improve their overall emotional well-being.

Risk Factors for Low Testosterone and Anxiety
Age is a significant risk factor for low testosterone levels. As men get older, their testosterone levels tend to decrease naturally. This decline usually begins around 30 and continues to decrease with age. In some cases, a reduced testosterone level can lead to anxiety symptoms.
Another factor that contributes to the decrease in testosterone levels is obesity. Excess body fat can cause a hormonal imbalance, lowering testosterone levels. This imbalance can also contribute to the development of anxiety disorders. Maintaining a healthy weight is essential in regulating hormonal levels and reducing the risk of anxiety.
Lifestyle choices can also impact testosterone levels and may lead to anxiety. Alcohol use affects hormone levels negatively and can lower testosterone levels and increase anxiety symptoms. Limiting alcohol consumption is essential for maintaining healthy testosterone levels and mental well-being.
Similarly, smoking can also harm testosterone levels. Chemicals in cigarettes and tobacco products can affect hormone production, lowering testosterone levels. Quitting smoking or avoiding secondhand smoke exposure is crucial for maintaining healthy hormone levels and reducing anxiety symptoms.
Several risk factors contribute to low testosterone levels and anxiety, including age, obesity, alcohol use, and smoking. These factors can negatively affect hormone production and ultimately lead to anxiety disorders. By making healthier lifestyle choices and managing factors such as weight and alcohol consumption, individuals can minimize the risk of experiencing low testosterone levels and anxiety.

Diagnosis of Low Testosterone and Anxiety
Diagnosing low testosterone and anxiety can be crucial in helping individuals manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life. To accurately diagnose these conditions, healthcare professionals assess the patient’s medical history, perform physical examinations, and conduct various tests.
One method for diagnosing low testosterone involves identifying the symptoms commonly associated with this condition. Some of the most common symptoms of low testosterone include fatigue, decreased sex drive, erectile dysfunction, muscle weakness, and mood changes. However, it is important to note that these symptoms can also be attributed to various other factors, and a definitive diagnosis requires laboratory testing.
Blood tests are essential in determining testosterone levels. Healthcare providers usually require a blood sample to measure the total testosterone concentration in the patient’s blood. According to the Cleveland Clinic, a normal testosterone range for adult men is typically between 300 and 1,000 ng/dL. Results lower than 300 ng/dL may indicate a potential issue with testosterone production. It is important to note that these reference ranges may vary among different laboratories and healthcare providers.
In some cases, a medical professional, such as a urologist, might be consulted to assess a patient’s low testosterone levels further. Urologists specialize in diagnosing and treating conditions that affect the male reproductive system and urinary tract. They can provide thorough evaluations and recommend appropriate treatment options based on a patient’s needs.
Diagnosing anxiety often involves a psychological evaluation in which healthcare professionals assess the patient’s symptoms and experiences. Anxiety can manifest as persistent worry, restlessness, irritability, and sleep disturbances, among other signs. Medical professionals may utilize diagnostic criteria from the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5) or other standardized evaluation tools to determine if a patient’s symptoms align with an anxiety disorder diagnosis.
In conclusion, diagnosing low testosterone and anxiety requires thoroughly assessing a patient’s symptoms, medical history, and laboratory test results. Collaboration between healthcare professionals, including primary care physicians, urologists, and mental health providers, is essential in accurately diagnosing these conditions and establishing appropriate treatment plans.
Treatment Options
In cases where low testosterone is causing anxiety, several treatment options are available to help address both the hormonal imbalance and anxiety symptoms.
One popular treatment is testosterone replacement therapy (TRT). This involves supplementing the individual’s testosterone levels with external sources in various forms, such as injections, gels, or patches. TRT can help alleviate anxiety and improve overall mood by balancing the hormone levels in the body. Patients must consult a healthcare professional to determine the appropriate dosage and delivery method.
In addition to TRT, medications can be prescribed to help manage anxiety symptoms. Commonly prescribed medications include anxiolytics, benzodiazepines, and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs). These medications can help alleviate anxiety by targeting specific neurotransmitters in the brain, thus promoting relaxation and improving mood. As with TRT, a healthcare professional should be consulted to determine the appropriate medication and dosage.
Addressing mental health is also essential to treating anxiety related to low testosterone levels. Working with a therapist or counselor can help individuals develop coping strategies for managing anxiety and identify and address any underlying factors contributing to their symptoms. Depending on the individual’s needs and preferences, therapy options might include cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), psychodynamic therapy, or mindfulness-based practices.
In summary, treatment options for anxiety caused by low testosterone levels may include testosterone replacement therapy, medications, and addressing mental health concerns. Combining these approaches enables patients to manage their symptoms and improve their overall well-being. It is imperative to consult with healthcare professionals to develop a personalized treatment plan tailored to each individual’s needs.
The Role of Testosterone in Men’s Health
Testosterone is a vital hormone for men’s health, crucial in many aspects of their lives. It is responsible for developing secondary sexual characteristics and contributes significantly to a man’s overall well-being.
One of the primary functions of testosterone is to regulate sex drive. A healthy hormone level ensures a robust libido, enabling men to engage in satisfying sexual experiences. It also plays a critical role in sexual health, as it governs sperm production and helps maintain the functioning and growth of the penis and testicles.
Testosterone is also essential for muscle growth and overall body strength. It stimulates muscle mass development and influences how muscles repair and grow. Men with adequate testosterone levels often experience improved physical performance and stamina, positively impacting their daily activities and athletic abilities.
In addition to muscle growth, testosterone contributes to body and facial hair development. This hormone induces hair growth during puberty in specific areas, such as the face, chest, and underarms. The presence and density of body and facial hair are often associated with masculinity and can vary depending on the individual’s testosterone levels.
Testosterone plays a significant role in men’s health, affecting aspects such as sex drive, muscle growth, body and facial hair, and sexual health. Maintaining healthy testosterone levels is crucial for a man’s overall well-being and can influence his life’s physical, emotional, and social aspects.
Secondary Effects of Low Testosterone
Low testosterone levels can lead to secondary effects on the body and mind. One notable effect is weight gain, often accompanied by increased body fat. This can result from decreased muscle mass and a slower metabolism, which are common consequences of low testosterone. The additional weight and body fat can exacerbate anxiety, as individuals may feel self-conscious or concerned about their health.
Insomnia and sleep apnea are also potential side effects of low testosterone. A lack of quality sleep can negatively impact one’s mood and contribute to anxiety. Furthermore, sleep apnea, characterized by periods of interrupted breathing during sleep, is often seen in individuals with excess body fat, creating a link between low testosterone, weight gain, and sleep disturbances.
Infertility is another possible outcome of low testosterone levels, as it can affect sperm production and reproduction capabilities in men. This can be a significant source of stress and anxiety for those trying to conceive.
Gynecomastia, or the enlargement of breast tissues in men, might occur due to an imbalance in estrogen and testosterone levels. This condition can cause significant emotional distress and feelings of anxiety, especially in social situations.
Osteoporosis, characterized by weak and brittle bones, can be a secondary effect of low testosterone. Testosterone plays a crucial role in bone density, and its deficiency can heighten the risk of fractures, leading to increased worry and anxiety about one’s physical health.
Lastly, low testosterone can contribute to menopause-related issues, as it has been linked to hot flashes and other menopausal symptoms. These discomforts can result in anxiety and mood disturbances, further highlighting the connection between low testosterone and anxiety.
In summary, low testosterone can lead to multiple secondary effects such as weight gain, insomnia, infertility, and osteoporosis, all of which can contribute to or exacerbate anxiety. It’s crucial to consult with a healthcare professional to receive appropriate guidance and treatment if experiencing these symptoms.
Impact on Physical and Mental Health
Low testosterone can significantly impact an individual’s physical and mental health. It is associated with decreased muscle mass and bone density and affects emotional well-being. This section will discuss the effects of low testosterone on physical changes, mental and emotional changes, and self-confidence.
Physical changes related to low testosterone include reduced muscle mass, decreased bone density, and increased body fat. These changes can lead to a decreased ability to perform physical activities, subsequently contributing to anxiety.
Mental and emotional changes resulting from low testosterone can manifest as mood swings, irritability, and even depression. Anxiety may become more pronounced as individuals experience these emotional fluctuations, and their overall well-being can be negatively affected.
Low testosterone can also impact self-confidence, as the physical and emotional changes can make individuals feel less capable in various aspects of their lives. This lack of confidence can exacerbate anxiety, creating a cycle where physical and emotional factors reinforce one another.
In summary, the relationship between low testosterone and anxiety can be explained through the physical and mental changes when testosterone levels decline. The effects on muscle mass, bone density, mood stability, and self-confidence contribute to heightened anxiety levels. Encouraging proper assessment and management of low testosterone can greatly improve an individual’s overall quality of life.

Frequently Asked Questions
Can low testosterone lead to mood swings?
Yes, low testosterone can lead to mood swings. Testosterone plays a crucial role in managing stress and maintaining emotional stability. When the testosterone level decreases, it may result in difficulties with mood regulation, including mood swings.
How does low testosterone affect mental health?
Low testosterone can negatively affect mental health by contributing to psychological symptoms such as irritability, mood swings, and depression. Moreover, low testosterone levels can also result in decreased motivation, lack of focus, and difficulty concentrating.
Does low testosterone contribute to fatigue?
Indeed, low testosterone can contribute to fatigue. Testosterone maintains energy levels, and a decrease in this hormone can lead to excessive tiredness and a lack of energy. It is essential to consult a medical professional if experiencing persistent fatigue, as other factors might be involved.
Can low testosterone impact cognitive function?
Low testosterone can impact cognitive function, particularly in memory, attention, and reasoning. Research has shown a correlation between low testosterone levels and a decline in cognitive function, although more studies are needed to understand this relationship’s mechanisms and extent fully.
Is there a connection between low testosterone and depression?
There is evidence suggesting a connection between low testosterone and depression. Decreased testosterone levels can lead to mood disorders, including depression, and some studies have shown that testosterone replacement therapy might be beneficial in treating depressive symptoms.
How can low testosterone levels influence emotions?
Low testosterone levels can influence emotions, contributing to mood swings, irritability, and depression. Testosterone plays a vital role in emotion regulation, and when the hormone level is low, an individual may struggle to maintain emotional balance. Seeking medical advice and appropriate treatment can help manage these emotional changes.
- 7 Ideas to Help You Relax and Unwind on a Family Vacation - April 27, 2025
- How Having Cybersecurity Protection Helps You Relax - April 25, 2025
- 8 Reasons Why Spending Time Outside Calms You Down - April 25, 2025
This site contains affiliate links to products. We will receive a commission for purchases made through these links.



