As a BetterHelp affiliate, we receive compensation from BetterHelp if you purchase products or services through the links provided
Appendicitis is a medical emergency that demands immediate attention. It is a condition characterized by inflammation of the appendix, a small, finger-shaped pouch that protrudes from the colon on the lower right side of the abdomen. The causes of appendicitis can vary, and it is generally attributed to blockage, infection, or decreased blood supply to the appendix. However, it is crucial to acknowledge that stress could also lead to appendicitis, and it is essential to take appropriate action to manage stress levels to avoid such a medical emergency.
Understanding the effects of stress on the body is crucial to exploring the link between stress and appendicitis. Acute stress, for instance, is more closely associated with the onset of acute appendicitis than chronic stress. Severe, short-term stressors, like goal frustration, may contribute to the development of the condition, although the connection is relatively weak and arguable.
Key Takeaways
- Appendicitis is an inflammation of the appendix that various factors can cause.
- The link between stress and appendicitis is weak but suggests acute stress may be more closely associated with the condition.
- Understanding the effects of stress on the body is important in determining its potential role in causing appendicitis.

Definition of Appendicitis
Appendicitis is a medical condition involving the inflammation of the appendix. The appendix is a small, narrow tube-like structure about 3 to 4 inches long and attached to the large intestine. It comprises lymphoid tissue, which is vital to the body’s immune system.
When you have appendicitis, your appendix becomes inflamed, swollen, and filled with pus. This can lead to severe pain, primarily in the lower right part of your abdomen, though the location of the pain may vary depending on factors such as age and the position of the appendix. Other symptoms that you may experience with appendicitis include nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, constipation, or diarrhea.
The exact cause of appendicitis is still unclear, but it is generally believed that the inflammation occurs due to an obstruction, such as a fecal matter or infection buildup. It’s important to seek medical attention if you suspect appendicitis because untreated appendicitis can lead to severe complications.
Some complications that may arise from untreated appendicitis include a burst appendix, which can be life-threatening, or the development of an appendiceal abscess. Additionally, peritonitis, a serious infection that can spread throughout your abdomen, can result from a ruptured appendix.
In summary, appendicitis is the inflammation of the appendix, a small organ of lymphoid tissue, and it can lead to life-threatening complications if not promptly treated.
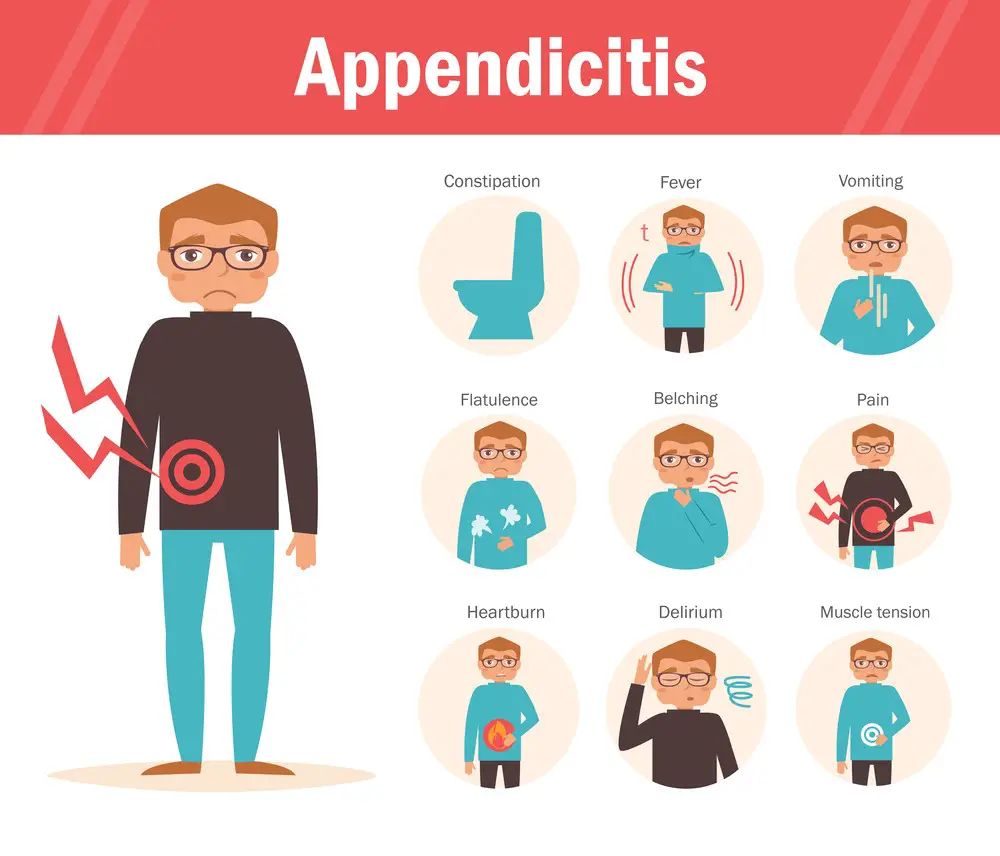
 Appendicitis Symptoms
Appendicitis Symptoms
Experiencing appendicitis symptoms can be quite distressing. You may feel a sharp, sudden pain in the lower right part of your abdomen. But it’s important not to ignore these signs, as this condition can become serious if left untreated. Here’s what you should look out for:
One of the most common symptoms is abdominal pain. It usually starts around your navel and then moves to the lower right area. This pain may worsen if you move, cough, or take deep breaths. It can range from mild discomfort to severe, debilitating pain.
You might also feel nausea and vomiting alongside the abdominal pain. These symptoms can make it challenging to maintain a healthy appetite, often leading to loss of appetite. Don’t be alarmed if you’re not as hungry as usual, but be sure to seek medical attention if the pain persists.
Gas and bloating are other symptoms you may notice. Your abdomen may appear swollen, and it could be difficult to pass gas or feel relief from the built-up pressure. If you’ve tried at-home remedies but still experience discomfort, it’s time to consult a healthcare professional.
Apart from the abdominal symptoms, you may develop a fever. A fever is a sign that your body is fighting an infection, which an inflamed appendix could cause. Be vigilant and monitor your temperature regularly if experiencing other appendicitis symptoms.
Your abdomen may also be tender to touch, or you might notice guarding – an involuntary tensing of your abdominal muscles when someone tries to touch the area. This tenderness and guarding can be indicative of the inflammation of the appendix.
Lastly, you may feel an overall sense of malaise. This is a general feeling of being unwell, uncomfortable, fatigued, or weak. While various reasons can cause malaise, don’t disregard it if it accompanies other appendicitis symptoms.
In short, if you’re experiencing abdominal pain, nausea, gas, fever, vomiting, loss of appetite, bloating, tenderness, guarding, and malaise, don’t hesitate to visit your healthcare provider. Remember, it’s better to be safe than sorry about your health.
The Causes of Appendicitis
Appendicitis is an appendix inflammation, a small pouch-like structure in the lower right side of the abdomen. Its exact cause is unclear, but several factors can contribute to appendicitis.
One of the main causes of appendicitis is blockage. This can occur when the opening of the appendix is obstructed by a fecalith, a hardened stool, or appendicoliths, also known as calcified fecal deposits. In some cases, foreign objects or parasites can also lead to blockage.
When blockage occurs, bacteria can multiply and cause an infection. This, in turn, causes the appendix to become swollen and inflamed, which results in pain and potentially dangerous complications, such as abscess formation.
Another factor that can contribute to appendicitis is a diet that’s low in fiber. A low-fiber diet may form fecaliths, as the body has difficulty moving waste through the digestive system. Consuming a diet rich in fiber can help prevent fecaliths and, consequently, reduce the risk of appendicitis.
In some cases, appendicitis can be caused by infections, such as bacterial, parasitic, or viral infections. These infections can make the appendix swollen and inflamed, making it more prone to blockage and the onset of appendicitis.
While major stressful events have been weakly associated with the onset of appendicitis, research studies have not found any concrete evidence to support stress as a direct cause. It’s always essential to stay informed and listen to your body to maintain your overall health and well-being.
 Understanding Stress
Understanding Stress
Stress is a natural response your body experiences when it perceives a threat or a challenge. There are different types of stress, such as anxiety and emotional stress, and when managed effectively, they can have minimal effects on your overall well-being. In moderate amounts, stress helps you adapt and improve in various aspects of life.
Anxiety is a type of stress characterized by worry, unease, or tension, especially when facing a difficult or uncertain situation. Similarly, emotional stress results from adverse emotional situations, such as breakups or personal conflicts. These forms of stress can impact your physical health and overall well-being.
The brain-gut axis is a critical concept to understand when discussing stress and its relationship with the digestive system. This remarkable communication network between the brain and the gut influences mental and gastrointestinal health. It is important to recognize that stress can negatively affect this brain-gut axis, causing disruptions to your digestive system.
When you’re under stress, your body releases specific hormones that can impact your gastrointestinal system. These hormones may cause or intensify pre-existing inflammation, potentially contributing to gastrointestinal issues such as indigestion or irritable bowel syndrome. Although stress does not directly cause appendicitis, understanding the relationship between stress and gastrointestinal health is crucial in maintaining a healthy lifestyle and preventing inflammation-related issues.
Finding a balance between your personal and professional life is essential to manage your stress levels effectively and preserve your gastrointestinal health. Incorporating relaxation techniques, such as mindfulness meditation and deep breathing exercises, can help alleviate stress and maintain a harmonious brain-gut connection. Additionally, regular physical activity and a well-balanced diet can support a healthy lifestyle that reduces the risk of stress-related complications.
 The Link Between Stress and Appendicitis
The Link Between Stress and Appendicitis
It’s natural for you to wonder if there’s a connection between stress and appendicitis. Although stress and anxiety can’t directly cause appendicitis, they may contribute to problems with your gastrointestinal system, which can sometimes lead to appendicitis or other related health issues.
Inflammation in the appendix is the main cause of appendicitis. While there isn’t any solid scientific proof that stress directly causes appendicitis, some researchers have theorized that acute stressors could be associated with acute episodes of appendicitis. This connection may be because a weakened immune system, which can result from high-stress levels, makes the body more susceptible to inflammation.
Another possible connection between stress and appendicitis is the immune system’s response to various stressors. Inflammation is a natural response of the immune system, and when your immune function is compromised due to stress, it might play a role in the development of chronic appendicitis.
Now, let’s consider oxidative stress, which has been linked to appendicitis in some research. Oxidative stress refers to an imbalance between free radicals and antioxidants in your body, and this type of stress has been associated with a higher risk of appendicitis, particularly in cases of trauma. However, it’s important to note that this link is not the same as the stress we experience in our daily lives, such as work or relationships.
In conclusion, while there isn’t a direct, proven link between stress and appendicitis, you must manage your stress levels for overall health. A well-functioning immune system prevents inflammation and other health complications, including appendicitis.
 Effects of Stress on the Body
Effects of Stress on the Body
Stress can affect many aspects of your life, including your physical well-being. Stress can cause issues with your gastrointestinal system, which can sometimes lead to or exacerbate existing conditions. Although stress alone doesn’t directly cause appendicitis, it may contribute to problems in your gut.
When you experience stress, your body undergoes numerous changes. One of those is an altered functioning of the colon, which is part of the lower abdomen. Stress might cause you to have abnormal bowel movements or experience abdominal discomfort. This shows how stress can impact gut health, including your colon.
Your appendix is on your lower right side, near the belly button. This small, finger-like pouch extending from your large intestine can become inflamed due to factors such as fecal blockage or infection. When stressed, your body’s response may exacerbate gastrointestinal issues, indirectly increasing the likelihood of problems with your appendix.
Taking care of your gut health and managing stress in your life is essential. Chronic stress can lead to long-term health consequences, so it is crucial to find ways to minimize it. Whether through exercise, relaxation techniques, or spending time with loved ones, taking steps to reduce stress can ultimately benefit your overall well-being, including your abdomen and lower right side where the appendix is located.
Remember, while stress doesn’t directly cause appendicitis, it can contribute to disturbances in your gut health. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle and managing stress are vital aspects of preventing issues with your lower abdomen and colon.
Diagnosis and Tests for Appendicitis
When you suspect appendicitis, reaching out to your healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis is crucial. They will begin with a physical exam to determine the severity of your symptoms. During this exam, they may apply gentle pressure on the painful area, and if the pain worsens upon releasing the pressure, it may indicate appendicitis.
To confirm the diagnosis, your doctor may order several tests, including blood and urine tests. Blood tests check your white blood cell count, which may be elevated during an appendicitis episode. A urine test helps rule out other conditions with similar symptoms, such as a urinary tract infection or kidney stone.
Imaging tests also play a vital role in diagnosing appendicitis. These can include:
- Abdominal ultrasound: An ultrasound uses sound waves to create images of your internal organs. This non-invasive test helps doctors examine your appendix and detect inflammation or blockages.
- CT scan: A computed tomography (CT) scan combines multiple X-ray images to create cross-sectional images of your abdomen. This detailed view allows healthcare professionals to see if your appendix is swollen or has an abscess.
- MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) uses magnetic fields and radio waves to produce detailed images of your organs and tissues. While MRIs are not as common as ultrasounds and CT scans for diagnosing appendicitis, they may be used if other tests are inconclusive.
Remember that early diagnosis is essential in treating appendicitis. Timely intervention helps prevent complications such as a ruptured appendix or an infection spreading through your abdominal cavity. If you experience symptoms of appendicitis, like severe lower abdominal pain, nausea, and fever, contact your healthcare provider immediately.
Appendicitis and Other Medical Conditions
An inflamed appendix, or appendicitis, can be a serious health concern. If left untreated, it might rupture, leading to a condition called peritonitis, which can be fatal. Although stress has not been proven to cause appendicitis directly, other factors, such as infections, tumors, or obstructions, can contribute to this condition.
You may already be familiar with some common symptoms of appendicitis, such as abdominal pain, loss of appetite, constipation, diarrhea, and bloating. However, it is essential to remember that appendicitis is not the only medical condition with similar symptoms. For example, irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) can cause abdominal pain, bloating, constipation, and diarrhea. Still, they are not directly linked to appendicitis.
Additionally, the cause of appendicitis can vary. Bacterial infections can lead to inflammation of the appendix, while viruses and parasites may play a role in some cases. Trauma to the abdominal area is another possible cause of appendicitis but is relatively rare.
Tumors can also be responsible for appendicitis. If a tumor blocks the tube connecting the large intestine and the appendix, it can lead to inflammation and, eventually, an infection. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial to prevent the appendix from rupturing.
In conclusion, while stress is not a direct cause of appendicitis, it is essential to be aware of the various factors and medical conditions that can contribute to this potentially dangerous condition. If you experience any symptoms associated with appendicitis, consult your healthcare professional immediately. They will guide you through the necessary steps to ensure your health and well-being.
Complications and Risks of Appendicitis
If you’re dealing with appendicitis, you must be aware of the complications and risks that may arise. One of the most concerning complications is a burst appendix. If left untreated, the inflammation can cause your appendix to rupture, which is life-threatening. This can lead to further complications, such as necrosis and gangrene.
Necrosis is when the tissues in your appendix begin to die, and gangrene is tissue death caused by a lack of blood supply and bacteria. These complications can be extremely dangerous and can lead to sepsis. Sepsis is a severe blood infection caused by the body’s response to bacteria, which can be life-threatening if not addressed promptly.
It’s not unusual to feel confused about the symptoms and risks associated with appendicitis – it’s a complex health issue. To mitigate the risks and potential complications, it’s important to seek medical advice as soon as you suspect appendicitis. Prompt treatment can help you avoid life-threatening situations and ensure a smoother recovery.
Remember, being aware of the complications and risks associated with appendicitis is crucial in taking care of your health. Stay informed, and don’t hesitate to contact a healthcare professional if you’re ever concerned about your symptoms.
 Treatments for Appendicitis
Treatments for Appendicitis
If you’re experiencing appendicitis, the primary treatment options include antibiotics and surgery. In most cases, an appendectomy is performed to remove the inflamed appendix. Before surgery, you might receive antibiotics to help combat any infection.
Two main types of surgery are used to treat appendicitis: laparoscopic surgery and laparotomy. Laparoscopic surgery is a minimally invasive procedure that involves making small incisions in your abdomen. A tiny camera and surgical instruments are inserted to remove your appendix. This method typically has a faster recovery time and less postoperative pain than laparotomy.
On the other hand, a laparotomy involves making a single, larger incision in your abdomen to access and remove the appendix. This method may be chosen if your appendix has already burst or if other complications are present.
When managing the pain associated with appendicitis, your healthcare team may recommend over-the-counter pain medications or prescribe stronger pain relievers depending on the severity of your symptoms.
Alternative methods for treating appendicitis are rare, as this condition often requires prompt medical attention and surgical intervention. However, in some cases, when the appendix is only mildly inflamed, healthcare providers may choose to treat the swelling with antibiotics alone. This approach is more common in people who may not be ideal candidates for surgery, such as the elderly or those with significant medical comorbidities.
Always consult with your healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate treatment plan for your situation.
Appendicitis in Specific Populations
Due to various factors, appendicitis may affect different population groups differently. This section will examine some specific scenarios and settings where appendicitis might occur.
Pregnant Women: During pregnancy, it can be challenging to diagnose appendicitis as the growing fetus may displace the appendix, causing it to shift from its usual position. Additionally, the symptoms of appendicitis during pregnancy may mimic other common pregnancy issues, such as gastrointestinal discomfort. Still, if you suspect appendicitis, seeking medical attention is crucial to avoid possible complications.
Children and Infants: Appendicitis is common in children between the ages of 10 and 19. Recognizing the symptoms in young children can be difficult as they might not communicate their pain. Furthermore, the symptoms, such as vomiting and diarrhea, may be mistaken for other conditions in infants. Consulting a pediatrician as soon as possible is essential in these cases.
Older Adults: Appendicitis in older adults can present with atypical symptoms, making it challenging to diagnose in this population. Delayed medical attention may increase the risk of complications, so seeking professional advice is essential if any appendicitis-related symptoms arise.
People with E. Coli Infections: Although it is not the primary cause of appendicitis, E. coli infections can sometimes contribute to the inflammation of the appendix. If you are diagnosed with an E. coli infection and experience symptoms of appendicitis, it’s critical to seek prompt medical help.
In summary, appendicitis can affect people of all ages, ranging from weeks to years. It is essential to seek medical attention promptly, as delays can turn this condition into a severe medical emergency. Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent complications and ensure a successful recovery.
Frequently Asked Questions
 What are common appendicitis triggers?
What are common appendicitis triggers?
Appendicitis is usually triggered by an obstruction in the appendix, such as poop (feces) blocking the entrance to the appendix. Other causes include infections, tumors, and gastrointestinal problems. While stress does not directly cause appendicitis, it may contribute to gastrointestinal issues that can sometimes lead to appendicitis.
Does constipation lead to appendicitis?
Constipation is not a direct cause of appendicitis, but it can increase the risk of fecal matter blocking the appendix, resulting in inflammation. If you experience constipation frequently, consider adopting a high-fiber diet and staying hydrated to support healthy bowel movements.
Can certain foods cause appendicitis?
No conclusive evidence links specific foods to the onset of appendicitis. However, a healthy diet that includes fiber-rich foods, such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, can help support overall digestive health and reduce the risk of constipation, a potential appendicitis trigger.
Is it possible for appendicitis to go away on its own?
In some rare cases, appendicitis may resolve itself if the inflammation is mild and the body can naturally clear the infection or obstruction. However, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional if you suspect that you have appendicitis, as untreated appendicitis can be life-threatening.
Are there conditions that mimic appendicitis?
Several conditions can present symptoms similar to appendicitis, such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), Crohn’s disease, urinary tract infections, and ectopic pregnancies. Accurate diagnosis is crucial, so if you experience symptoms like abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and fever, seek medical attention immediately.
Can alcohol consumption lead to appendicitis?
Excessive alcohol consumption is not a direct cause of appendicitis. However, drinking alcohol can contribute to gastrointestinal issues and impair your body’s ability to fight infections, which may indirectly increase the risk of developing appendicitis. It’s important to consume alcohol in moderation to safeguard your overall health.
Cracking Under Pressure: Spotting the Signs of Unhealthy Stress
Stress is a normal part of life, and in small doses, it can even be beneficial, pushing us to achieve our goals and sharpen our focus. However, when stress becomes too much, it can wreak havoc on our physical and emotional well-being. Here are some clear signs that stress might be reaching unhealthy levels and possibly leading to physical issues:
- Constant Fatigue: If you’re tired all the time, even after a good night’s sleep, stress might wear you down.
- Frequent Headaches: Persistent headaches might indicate stress overloading your system.
- Digestive Problems: Stress can affect your gut, leading to heartburn, bloating, or irritable bowel syndrome (IBS).
- Mood Swings and Anxiety: Erratic emotions or an inexplicable sense of dread can indicate that stress is taking its toll on your mental health.
- Muscle Tension and Pain: Feeling tense and experiencing muscle pain, particularly in the neck and shoulders, can signify chronic stress.
- Difficulty Concentrating: Struggling to focus or make decisions is a common symptom of excessive stress.
- Changes in Appetite: Both overeating and loss of appetite can signal that stress harms your body.
- Sleep Disturbances: Stress might be the culprit if you’re having trouble falling or staying asleep or experiencing nightmares.
- Skin Issues: Conditions like acne, eczema, or hives might flare up due to increased stress levels.
- Heart Palpitations: Feeling your heart race or experiencing palpitations can be a frightening indication that stress affects your cardiovascular system.

Strategies to Manage Unhealthy Stress
Recognizing the signs of unhealthy stress is the first step. Implementing healthy coping strategies is equally important. Consider:
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity can boost your mood and reduce stress.
- Mindfulness and Meditation: Taking time to breathe and center yourself can help you regain control.
- Balanced Diet: Eating well nourishes your body and mind, making you more resilient to stress.
- Seeking Professional Help: If stress interferes with daily life, consider seeking professional counseling or therapy.
Remember, stress isn’t inherently bad, but too much can lead to serious health issues. Being aware of your body and mind and taking proactive steps to manage stress can help you maintain a balanced, healthy life.
 Navigating the Healing Journey: Goals and Milestones in Therapy
Navigating the Healing Journey: Goals and Milestones in Therapy
Embarking on the path of therapy is a courageous step toward self-discovery and healing. Therapy isn’t just about solving problems; it’s about growth, understanding, and creating a better life. Recognizing the goals and signs of progress along this journey is vital for the therapist and the client. Here’s how you can chart your course:
Defining Clear Goals
Setting clear and achievable goals is the foundation of successful therapy. These goals might include:
- Improving Relationships: Building better communication skills and emotional connections with loved ones.
- Managing Stress or Anxiety: Learning techniques to cope with daily pressures or anxiety triggers.
- Overcoming Trauma: Working through past traumas and finding ways to heal.
- Boosting Self-Esteem: Focusing on self-love, acceptance, and growing confidence.
- Substance or Addiction Recovery: Creating strategies and support systems to overcome addictions.
Recognizing Signs of Progress
Progress in therapy isn’t always linear, but certain signs can indicate that you’re moving in the right direction:
- Improved Emotional Well-being: Feeling a general sense of contentment or having more good days than bad.
- Increased Insight and Understanding: Gaining clarity on patterns, behaviors, or feelings that have been confusing or troublesome.
- Enhanced Relationships: Noticing improved connections, empathy, and communication with friends and family.
- Reduced Symptoms: Experiencing fewer anxiety symptoms, depression, or other mental health conditions.
- Utilizing New Skills: Successfully applying new coping strategies or techniques learned in therapy.
- Feeling Empowered: Taking control of your life and making decisions aligned with your values and needs.
- Positive Feedback from Others: Hearing from friends or family that they notice positive changes in you.
Embracing the Journey, Not Just the Destination
It’s crucial to recognize that therapy is a process, not just a quick fix. The road might be filled with twists and turns, but even small advancements are worth celebrating. Be patient and communicate openly with your therapist to adjust goals as needed.
Final Thoughts
Therapy is a deeply personal and transformative experience. The journey might seem daunting, but by setting clear goals and acknowledging progress, you empower yourself to navigate the healing path confidently and gracefully. It’s about embracing the journey, celebrating the milestones, and recognizing that growth often happens one step at a time.
 Navigating Personal Chaos: A Battle with Stress and Survival
Navigating Personal Chaos: A Battle with Stress and Survival
Hi, I’m Jacob Maslow, and my life has been a whirlwind of personal challenges and growth. Balancing my mental health has become essential, thanks to the daily dosage of Lexapro and being a therapy veteran.
As someone who has faced the ugly specter of narcissism in my own family, I’ve been through tough battles. My ex, trapped in a severe narcissism, has wreaked havoc in our lives, from chasing community leaders for affairs to alienating our children and breaching court-ordered shared custody.
I’ve had a close relationship with my children over the years, even after our separation, and living in two households was once normal. But recently, it’s changed. The refusal of my ex to communicate or comply with custody orders has led to a painful, ongoing court battle.
Taking long walks every day has cleared my head, giving me the strength to face my daily struggles. While the road has been rough, I channel my experiences into writing about mental health, narcissism, and legal battles.
I’m committed to helping others navigate similar challenges. I believe anyone can overcome mental health issues, and I’ve also created a legal site to support others who face spouses refusing to comply with court orders.
My journey might be unique, but the lessons I’ve learned and the insights I’ve gained fuel my writing and my will to help others. Whether it’s a question of appendicitis caused by stress or the broader mental health challenges, I’m here to explore, understand, and share my knowledge.
- 7 Ideas to Help You Relax and Unwind on a Family Vacation - April 27, 2025
- How Having Cybersecurity Protection Helps You Relax - April 25, 2025
- 8 Reasons Why Spending Time Outside Calms You Down - April 25, 2025
This site contains affiliate links to products. We will receive a commission for purchases made through these links.

 Appendicitis Symptoms
Appendicitis Symptoms Understanding Stress
Understanding Stress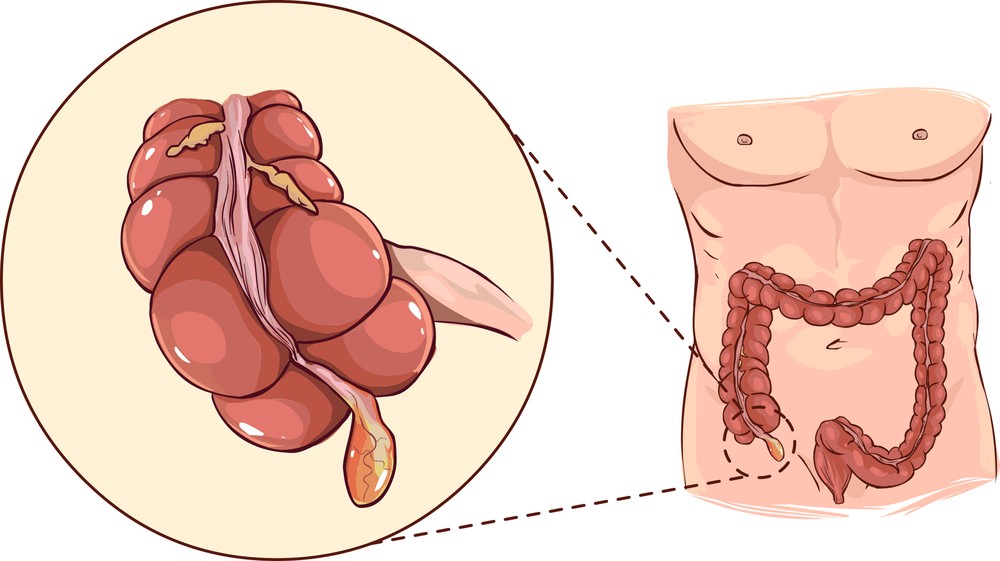 The Link Between Stress and Appendicitis
The Link Between Stress and Appendicitis Effects of Stress on the Body
Effects of Stress on the Body Treatments for Appendicitis
Treatments for Appendicitis What are common appendicitis triggers?
What are common appendicitis triggers? Navigating the Healing Journey: Goals and Milestones in Therapy
Navigating the Healing Journey: Goals and Milestones in Therapy Navigating Personal Chaos: A Battle with Stress and Survival
Navigating Personal Chaos: A Battle with Stress and Survival
