As a BetterHelp affiliate, we receive compensation from BetterHelp if you purchase products or services through the links provided
Feeling nauseous or even throwing up when you’re stressed or anxious might have you wondering, “Can anxiety cause vomiting?” Yes, it can. Anxiety goes beyond just feeling worried or nervous; it has physical effects on the body, too.
This includes symptoms like nausea and vomiting, which, though unpleasant, are common ways your body responds to stress.
One crucial fact to understand is that anxiety can indeed affect your digestive system and may lead to conditions such as nausea, diarrhea, constipation, or general stomach upset. Vomiting usually happens with extreme levels of anxiety and is often preceded by feelings of nausea.
This blog sheds light on this troubling connection between anxiety and vomiting. It’s packed with information on why these symptoms occur and offers practical tips for managing them effectively.
Ready to feel better? Keep reading!
The Gut-Wrenching Effects of Anxiety
Anxiety doesn’t just cloud your thoughts; it can also wreak havoc on your digestive system. Symptoms like nausea, diarrhea, constipation, and general stomach upset are common when anxiety strikes.
These signs show how deeply stress and psychological distress impact the body.
Your digestive tract is especially vulnerable to emotional turmoil. Stress-induced nausea precedes vomiting in extreme cases of anxiety, demonstrating a direct link between your mental state and gastrointestinal symptoms.
This intricate connection highlights why managing stress is crucial for both mental health and physical well-being.
Nausea and Anxiety: A Troubling Connection

Anxiety takes a toll on your body, often leading to nausea or an upset stomach. This unsettling connection begins in the brain and signals distress through your digestive system. When you’re anxious, the body releases stress hormones that can accelerate heart rate and digestion.
This rapid shift might lead to gastrointestinal symptoms of anxiety, such as nausea from stress, or even trigger conditions like cyclic vomiting syndrome. Scientists have found that imbalances in the gut microbiome might also contribute to these uncomfortable symptoms, highlighting how psychological distress manifests physically.
Dealing with severe anxiety can sometimes escalate to panic-induced vomiting, a situation where intense worries overwhelm physical control. For some people, subconscious anxiety triggers nausea without any apparent reason, making daily tasks challenging.
Anxiety-related vomiting is not just restricted to adults; teenagers experience it too, suggesting that anyone dealing with high levels of stress or panic could face these problems regardless of age.
Understanding this link underscores the importance of addressing both mental health issues and physical well-being together for comprehensive care and relief from these distressing symptoms.
Vomiting: A Physical Manifestation of Anxiety

Extreme anxiety doesn’t just unsettle the mind; it physically manifests in our bodies, sometimes leading to vomiting. This intense physical reaction often follows episodes of severe stress or panic, signaling how deeply our psychological state affects our gastrointestinal health.
The connection between nausea and anxiety underscores the complex dialogue between the brain and the gut. Stress-induced nausea transforms into actual vomiting for some individuals when their anxiety reaches a peak, making it more than just an uncomfortable sensation but a visible sign of internal turmoil.
Anxiety may not have a voice, but it cries out through our bodies in ways we can’t ignore.”
Vomiting from anxiety goes beyond mere discomfort; it highlights a significant impact on one’s daily life and well-being. Adults and teenagers alike face this distressing symptom during heightened moments of fear or stress, suggesting that age does not shield one from the physical consequences of mental battles.
Whether preceded by simple nervousness or full-blown panic attacks, such responses point to the urgent need for strategies to manage both immediate symptoms and underlying anxieties effectively.
Understanding the Link Between Anxiety and Upset Stomach

Anxiety doesn’t just stop at causing vomiting; it digs deeper, affecting your entire digestive system.
This connection hinges on the body’s stress response, which can trigger gastrointestinal symptoms like nausea, diarrhea, constipation, and general stomach discomfort. The gut-brain axis plays a significant role here; feelings of anxiety can send signals to your gut that disrupt its normal functioning.
Your digestive system is sensitive to emotions and mental states such as stress and panic. Stress-induced nausea or an upset stomach isn’t just uncomfortable—they’re signs of how closely linked our gastrointestinal health is with our mental state.
Imbalances in the gut microbiome may exacerbate these symptoms, highlighting indigestion as another layer of complexity in the anxiety-digestive system relationship. Understanding this link explains why managing one’s mental health is critical for emotional well-being and maintaining a healthy digestive system.
Coping with Anxiety-Induced Nausea

Anxiety can manifest in various physical symptoms, and nausea is a common one. When the body experiences heightened levels of stress and anxiety, it can trigger an upset stomach, queasiness, and even vomiting in some cases.
This anxiety-induced nausea can be incredibly uncomfortable and debilitating, making it challenging to go about daily activities. However, several coping strategies can help alleviate this unpleasant symptom.
One practical approach is to practice deep breathing exercises or meditation. These relaxation techniques can help calm the mind and body, reducing the intensity of anxiety and its associated physical symptoms.
Additionally, staying hydrated by sipping on ginger tea or water can help settle the stomach and prevent dehydration, which can exacerbate nausea. Light physical activity, such as gentle walks or stretching, can also help redirect focus and alleviate tension.
In more severe cases, over-the-counter medications like ginger supplements or anti-nausea remedies may provide relief from anxiety-induced nausea. However, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional before taking new medicines, especially if you have pre-existing conditions or are taking other medications.
Identifying and addressing the root causes of anxiety through therapy, lifestyle changes, or stress management techniques can also help prevent recurrent episodes of nausea and vomiting related to anxiety.
Overcoming Anxiety-Related Vomiting
Anxiety can trigger a host of physical symptoms, including nausea and vomiting. While uncomfortable and disruptive, anxiety-related vomiting is a treatable condition. The first step in overcoming this issue is to address the underlying anxiety through effective coping strategies.
Practicing relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, or progressive muscle relaxation, can help calm the mind and body, reducing the likelihood of anxiety-induced vomiting. Additionally, identifying and avoiding potential triggers, such as stressful situations or anxiety-provoking stimuli, can help prevent episodes from occurring.
In some cases, seeking professional help from a therapist or counselor may be beneficial. Cognitive-behavioral therapy can provide tools to manage anxiety and its physical manifestations effectively.
If vomiting persists or is severe, consult a healthcare professional. They may prescribe anti-nausea medications or suggest dietary adjustments to alleviate symptoms.
Seeking Relief: Tips for Managing Anxiety-Induced Upset Stomach

Anxiety can manifest in various physical symptoms, including an upset stomach, nausea, and even vomiting in some cases.
When the body experiences heightened levels of stress and anxiety, it can disrupt the normal functioning of the digestive system, leading to these unpleasant and often debilitating symptoms. However, there are several strategies you can employ to find relief and manage an anxiety-induced upset stomach.
One of the most effective approaches is incorporating relaxation techniques into your daily routine. Practices such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, or progressive muscle relaxation can help calm the mind and body, reducing the intensity of anxiety and its associated physical symptoms.
Additionally, it can be beneficial to pay attention to your diet and avoid potential trigger foods or beverages that may exacerbate digestive issues. Staying hydrated by sipping ginger tea or water can help soothe an upset stomach.
Over-the-counter medications like antacids or anti-nausea remedies may temporarily relieve more severe cases. Still, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional before taking any new medicines, especially if you have pre-existing conditions or are taking other medications.
Identifying and addressing the root causes of anxiety through therapy, lifestyle changes, or stress management techniques can also help prevent recurrent episodes of an upset stomach and other anxiety-related digestive issues.
Finding Calm: Addressing the Physical Symptoms of Anxiety
Anxiety not only upsets your digestive system but also creates a host of physical symptoms that require attention.
As part of your body’s response to stress, you might experience nausea, sweating, trembling, and even panic-induced vomiting. These manifestations are signals from your body urging you to seek calm and restore balance.
Addressing these symptoms starts with recognizing their source: psychological distress. Implement strategies such as deep breathing exercises, regular physical activity, and mindfulness techniques to mitigate the impact of anxiety on your body.
Engaging in activities like yoga or meditation can help soothe the mind and gastrointestinal issues by enhancing overall well-being. Always consider professional guidance if self-help methods do not bring relief; sometimes, external support is necessary to navigate the complexities of anxiety-related challenges effectively.
Quick Tips for Managing Anxiety and Its Gastrointestinal Effects
Anxiety’s impact on the gastrointestinal system can be profound, leading to symptoms like nausea and vomiting. These are not just distressing but can also interfere significantly with daily life. Understanding how to manage anxiety and its effects can help alleviate these symptoms and improve overall well-being. Here are some strategies that might help:
- Identify and Address Triggers: Understanding what triggers your anxiety can be the first step in managing it. Once you identify these triggers, you can work on strategies to avoid them or reduce their impact through various coping mechanisms.
- Develop a Routine: Consistency can help manage anxiety. Establishing a regular schedule for meals, exercise, and sleep can stabilize your body’s rhythms and reduce anxiety levels, thereby mitigating its physical symptoms.
- Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques: Practices like yoga, meditation, and deep-breathing exercises can reduce stress and anxiety. These techniques help center your thoughts and calm your body, which can lessen the impact of anxiety on your digestive system.
- Dietary Adjustments: Sometimes, what you eat can affect how you feel. Foods that are high in fat, caffeine, or sugar might exacerbate anxiety symptoms. Conversely, a balanced diet rich in vegetables, fruits, whole grains, and lean proteins can support a healthy mind and body.
- Professional Help: If anxiety and its symptoms become overwhelming, seeking help from a mental health professional can be beneficial. Therapies like Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) are effective in treating anxiety disorders. A therapist can provide tools and strategies to cope with anxiety healthily and productively.
- Medication: In some cases, medication may be necessary to manage anxiety. It’s important to consult with a healthcare provider about the possibilities and what might work best for you.
By incorporating these strategies into your life, you can better manage anxiety and reduce its impact on your digestive system. It’s important to remember that dealing with anxiety is a process, and what works for one person might not work for another. Be patient with yourself and open to finding the combination of techniques that works best for you.
Knowing When to Seek Professional Help for Anxiety

Dealing with anxiety and its physical symptoms can sometimes require more than self-management strategies. Knowing when to seek professional help and the options available can significantly improve your quality of life. Here’s a guide on when to consider professional intervention, and how to set goals and recognize progress in your journey toward managing anxiety:
When to Seek Help:
- Persistent Symptoms: If anxiety symptoms persist and significantly interfere with your daily activities, such as work, school, or relationships, it may be time to seek professional help.
- Physical Health Impact: When anxiety leads to physical symptoms like persistent nausea, vomiting, or a drastic change in appetite, professional assessment is crucial.
- Deterioration of Quality of Life: If you find your quality of life diminishing—avoiding social situations, increased worry about future attacks, or a general sense of unhappiness—it’s essential to seek help.
Therapy and Medication:
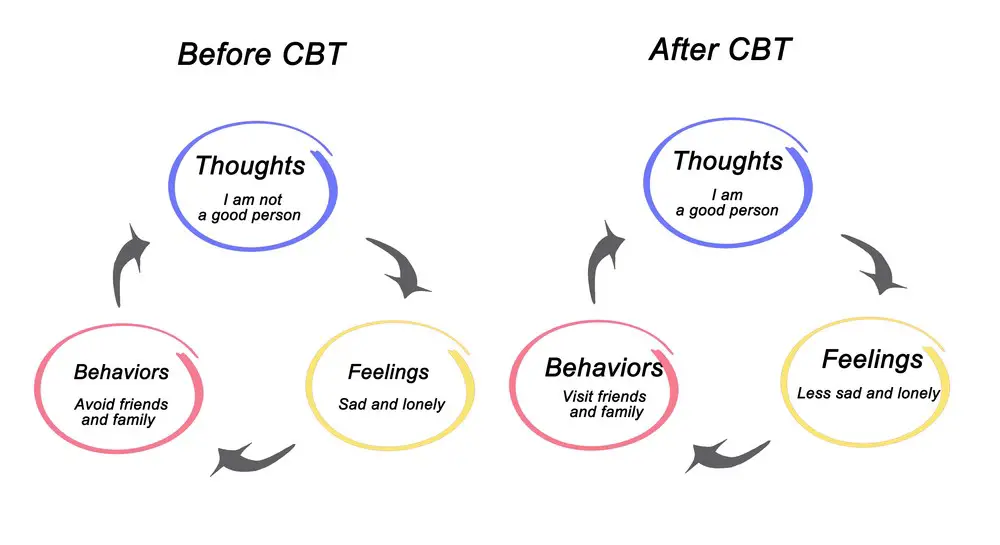
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): CBT is highly effective for treating anxiety. It involves working with a therapist to identify and challenge negative thought patterns and behaviors that cause anxiety.
- Medication: Medications such as antidepressants and anti-anxiety drugs can be prescribed when symptoms are severe or CBT alone is not sufficient. Always discuss the benefits and risks with a healthcare provider.
- Combination Treatments: A combination of therapy and medication is often the most effective treatment. This approach tackles both the mental and physical symptoms of anxiety.
Setting Goals and Recognizing Progress:
- Set Realistic Goals: Start with small, achievable goals contributing to larger objectives. For example, if social interactions cause anxiety, start by engaging in small, structured social situations.
- Monitor Progress: Record your symptoms and note any changes over time. This can help you and your healthcare provider determine what is working and what is not.
- Celebrate Successes: Recognize and celebrate improvements, no matter how small. This can boost your motivation and help in building more positive experiences.
Other Considerations:
- Holistic Approaches: Include lifestyle changes such as regular exercise, adequate sleep, and balanced nutrition, which can help manage anxiety symptoms.
- Support Networks: Leverage support from friends and family or seek out support groups where you can share experiences and strategies with others facing similar challenges.
Conclusion:
Recognizing when to seek professional help for anxiety is a critical step in managing not only the mental aspects but also the physical symptoms like nausea and vomiting. With the right combination of professional care, self-help strategies, and supportive approaches, managing anxiety becomes a more attainable goal. Stay proactive about your mental health, and remember that seeking help is a sign of strength, not weakness.
- Stress Management: What is the Relationship Between Stress and Addiction? - June 28, 2024
- Exploring Techniques to Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle without Drugs - May 28, 2024
- How Acupuncture Helps Treat Chronic Fatigue Syndrome - May 28, 2024
This site contains affiliate links to products. We will receive a commission for purchases made through these links.



