As a BetterHelp affiliate, we receive compensation from BetterHelp if you purchase products or services through the links provided
Headaches can slow you down, making it hard to get through your day. You might wonder if feeling anxious is causing these headaches.
Interestingly, anxiety can indeed lead to headaches, including tension type and migraines. Anxiety doesn’t just affect your mind; it manifests physically, often as painful tension headaches or debilitating migraines.
In this article, we will look into how and why this happens.
We’ll explore different types of headaches linked with anxiety, what causes them, and most importantly – how you can manage or even prevent them. Ready for some relief? Let’s find out more!
Headaches and Anxiety: Understanding the Connection
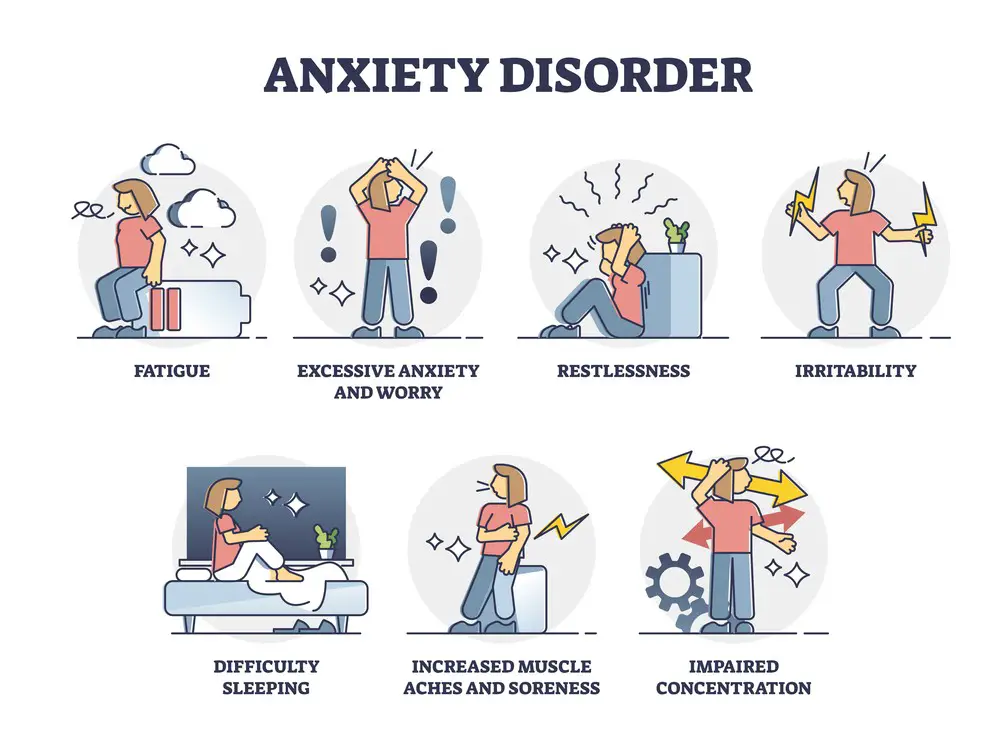
Headaches often accompany anxiety, creating discomfort that affects daily life. Exploring how stress triggers these headaches reveals insights into our body’s response to psychological distress.
Headaches As A Common Symptom Of Anxiety
Experiencing anxiety can lead to various physical symptoms, with headaches being a commonly reported issue. These aren’t just any headaches; they often manifest as tension headaches or migraines, making it hard to concentrate and go about daily activities.
The discomfort can range from pain in the neck and behind the eyes to an uncomfortable pressure around the head.
Muscle tension increases with higher levels of anxiety, contributing significantly to these headache episodes. Studies show that people suffering from generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) frequently report headaches as a symptom of their condition.
This connection highlights the need for a holistic approach to managing mental health and physical manifestations to ensure overall well-being.
The Bidirectional Relationship Between Anxiety And Migraines

The relationship between anxiety and migraines is complex and goes both ways. People with generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) often find that their condition includes headaches as a common symptom.
These aren’t just ordinary headaches; they can escalate to full-blown migraines marked by intense pain, sensitivity to light, and sometimes nausea. On the flip side, those suffering from migraines are at a higher risk of developing anxiety and depression.
This cycle creates a positive feedback loop where anxiety triggers migraines, which in turn amplifies stress levels, leading to more frequent or severe episodes of anxiety.
Migraine sufferers report not only physical discomfort but also significant emotional strain. The anticipation of migraine attacks can cause considerable psychological distress, further elevating nervous tension—a known trigger for both anxiety episodes and tension headaches.
This bidirectional link underscores the importance of managing both conditions proactively to mitigate the impact on individuals’ daily lives and overall well-being.
Understanding Different Types of Anxiety Headaches
Understanding the different types of anxiety headaches is crucial for finding the proper treatment and relief. Anxiety can trigger several headache varieties, such as tension headaches and migraines.
Tension headaches bring a persistent dull ache around the head or neck, often described as feeling like a tight band around your forehead. They’re linked to muscle tension from stress or anxiety.
Conversely, migraines present a more intense pain that throbs or pulses in one area of the head and might be accompanied by sensitivity to light and sound. They can last from hours to days.
For people experiencing generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), these headaches become an all-too-common symptom, affecting daily life significantly. Children with anxiety disorders are also likely to face frequent headaches compared to their peers without anxiety issues, indicating how essential it is to manage not only physical but also psychological well-being in coping with such conditions.
Managing Anxiety-Induced Headaches
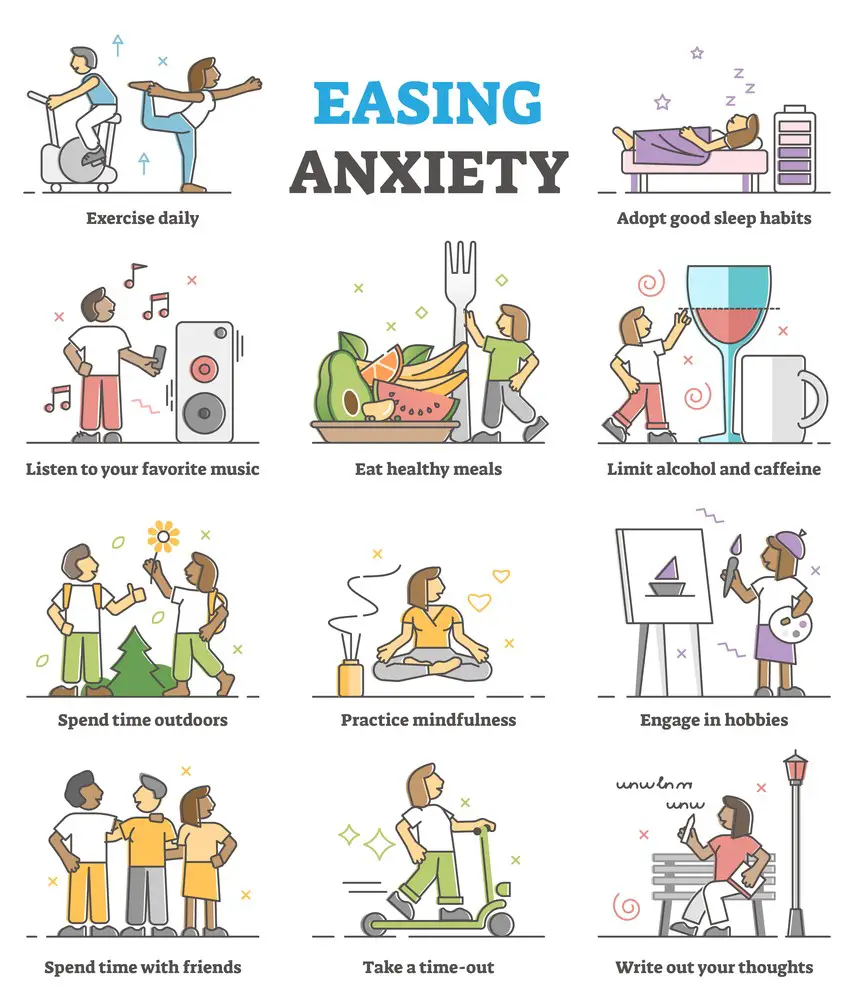
Tackling anxiety-induced headaches starts with recognizing the role of stress and nervous tension in triggering migraines and tension headaches. Deep breathing, engaging in regular physical activity, and setting aside time for relaxation each day can significantly reduce the intensity and frequency of these headaches.
Mental health strategies such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) also show promise in managing both the psychological distress and physical symptoms that come with generalized anxiety disorder (GAD).
Coping with anxiety-related headaches is not just about pain relief; it’s about addressing the root causes of stress.
Practicing mindfulness meditation has been proven to lower levels of stress and, by extension, alleviate headache pain caused by anxiety. Additionally, ensuring a healthy sleep schedule reinforces your body’s resilience against stress-induced headaches.
For many individuals facing both GAD and migraine challenges, integrating these approaches into daily life creates a comprehensive strategy for reducing both the emotional strain and associated headache discomfort.
Natural Remedies for Anxiety-Related Headaches

Anxiety and stress can undoubtedly trigger or exacerbate headaches. When the body experiences prolonged periods of tension and worry, it can lead to muscle tightness, jaw clenching, and increased blood pressure, all contributing to headache development. Fortunately, several natural remedies can help alleviate anxiety-related headaches.
One effective approach is practicing relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing exercises, progressive muscle relaxation, or mindfulness meditation. These methods can help reduce muscle tension, lower stress levels, and promote a sense of calm, potentially alleviating or preventing anxiety-induced headaches.
Incorporating these practices into daily routines not only fosters a resilient stress management system but also enhances one’s ability to cope with anxiety in healthier ways.
Over time, individuals who engage in these relaxation techniques may experience a noticeable decrease in the frequency and severity of their headaches, illustrating the significant impact that managing stress and anxiety can have on physical health.
Furthermore, establishing a regular mindfulness practice can improve overall quality of life, with increased emotional balance and reduced anxiety-related symptoms.
Additionally, incorporating regular physical activity, such as yoga, can help release pent-up tension and improve overall well-being.
Herbal remedies can also offer relief for anxiety-related headaches. Chamomile tea, known for its calming properties, can help reduce anxiety and promote relaxation. When inhaled or applied topically, lavender essential oil can have a soothing effect on the mind and body.
Magnesium supplementation can also be beneficial, as magnesium deficiency is linked to both anxiety and headaches.
By exploring these natural remedies and addressing the underlying anxiety, individuals may find relief from persistent headaches.
Tips for Preventing Headaches Triggered by Anxiety

Exploring ways to prevent anxiety-triggered headaches can lead to fewer disruptions and more peace in daily activities. Understanding your body’s signals and implementing stress-reducing strategies is key to keeping those pesky headaches at bay.
Identifying Triggers
Knowing your own triggers is one of the best strategies to avoid headaches brought on by worry. Although they might differ from person to person, typical triggers include:
- Stress.
- Lack of sleep.
- Certain foods or drinks.
- Environmental factors such as noise or bright lights.
Keeping a headache diary can be a valuable tool for pinpointing your triggers. Note details such as the time, location, activities, foods consumed, and any emotional or physical factors that may have preceded the onset of the headache.
By recognizing your triggers, you can take proactive steps to avoid or manage them. This could involve implementing stress management techniques, maintaining a regular sleep schedule, adjusting your diet, or making environmental modifications to reduce exposure to potential triggers.
Armed with this personalized knowledge, individuals can tailor their preventive strategies more effectively, creating a lifestyle that minimizes the risk of headache occurrences. This proactive approach not only aids in avoiding specific headache triggers but also contributes to a broader sense of control over one’s mental health.
By adjusting daily habits and environments to accommodate personal sensitivities better, individuals can significantly improve their capacity to manage anxiety and stress, leading to a more balanced and headache-free life.
Self-care
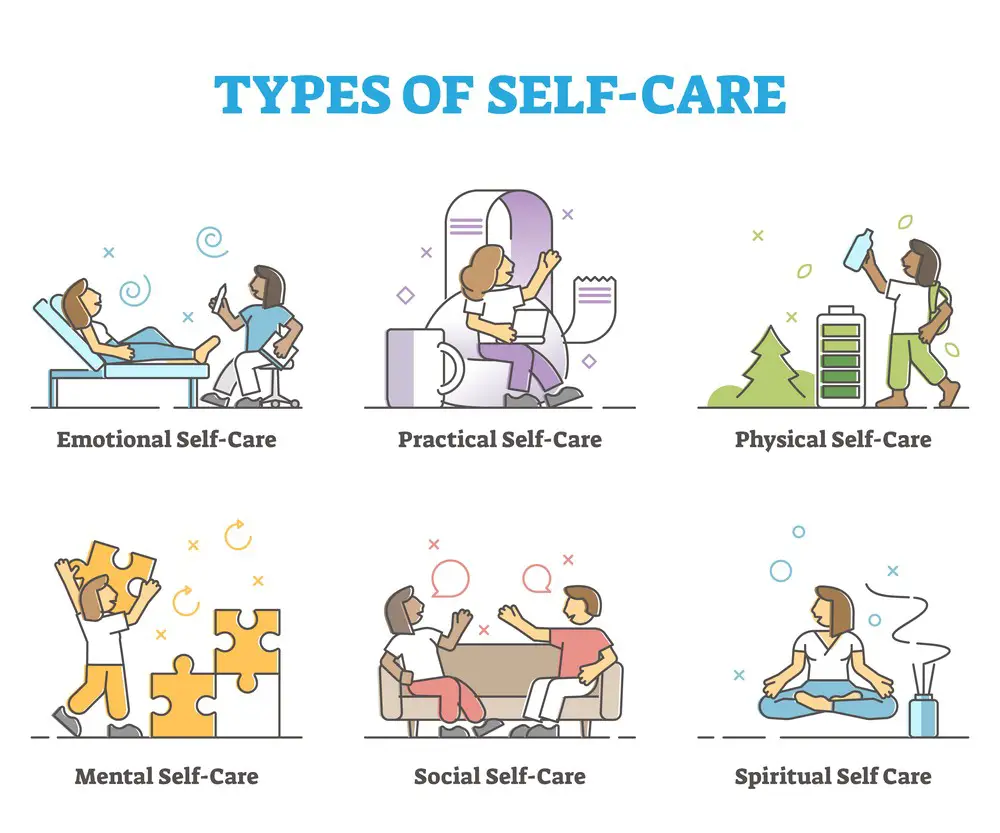
Practicing self-care is an essential aspect of preventing anxiety-induced headaches. When we neglect our physical, emotional, and mental well-being, we become more susceptible to stress and anxiety, which can trigger or exacerbate headaches. Engaging in self-care activities can help reduce stress levels, promote relaxation, and improve overall health, thereby reducing the likelihood of headaches.
One self-care strategy is to prioritize adequate sleep. Lack of sleep can amplify anxiety and increase the risk of headaches. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night by establishing a consistent sleep routine, creating a calming sleep environment, and avoiding stimulants close to bedtime.
Additionally, incorporating relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing exercises, yoga, or meditation, can help calm the mind and release tension, which can prevent headaches from occurring.
Another essential aspect of self-care is maintaining a balanced diet and staying hydrated. Certain foods and beverages, such as caffeine, alcohol, and processed foods, can trigger headaches or exacerbate anxiety. Opt for a diet rich in whole, nutrient-dense foods and drink plenty of water to support overall health and well-being.
Regular exercise can also be beneficial. It releases endorphins and reduces stress, which can help prevent anxiety-related headaches.
Recognizing When to Seek Help for Anxiety-Induced Headaches

Anxiety can manifest in numerous physical symptoms, including headaches, which can significantly impact quality of life. Understanding when these symptoms require professional help is crucial for effective management and treatment. This section explores when to consider therapy or medication, the advantages and disadvantages of each, and how to set goals and recognize progress in managing anxiety-induced headaches.
When to Seek Professional Help:
- Persistent Symptoms: If headaches and anxiety are frequent, impacting daily functioning, it’s time to consult a healthcare provider.
- Escalation in Severity: When headaches become more frequent or intensify, professional intervention may prevent further complications.
- Ineffectiveness of Home Remedies: Professional treatment may be necessary if natural remedies and lifestyle changes fail to alleviate symptoms.
Choosing Between Medication and Therapy:
- Medication:
- Pros: Quick relief of symptoms, effective for reducing the frequency and severity of anxiety-induced headaches.
- Cons: Potential side effects, dependency risks, and may not address the underlying causes of anxiety.
- Appropriate for: Individuals experiencing severe symptoms that need immediate relief, or those whose daily life is significantly impaired.
- Therapy:
- Pros: Offers tools and strategies to manage not only symptoms but also the root causes of anxiety, provides long-term solutions, and no dependency risks.
- Cons: Requires time and commitment, which may take longer to see results than medication.
- Appropriate for: Individuals looking to develop coping strategies, understand the underlying issues of their anxiety, and who prefer a drug-free approach.
Setting Goals and Recognizing Progress:

- Goal Setting: Effective management starts with clear, achievable goals. These might include reducing headache frequency, managing anxiety triggers more effectively, or improving overall emotional well-being.
- Tracking Progress: Keeping a diary of symptoms can help track what triggers headaches and measure how changes in management strategies reduce their frequency or severity. Regular check-ins with a mental health professional can provide professional insight into progress and further adjustments to treatment plans.
- Adaptive Strategies: As individuals work through therapy or adjust to medications, strategies might need to be adapted based on effectiveness and side effects. Open communication with healthcare providers ensures that treatments are adjusted to best suit individual needs.
- Celebrating Successes: Recognizing small improvements is crucial for motivation. Whether it’s fewer headache days, better handling of anxiety in stressful situations, or feeling more positive overall, acknowledging these milestones encourages continued effort towards managing anxiety and its physical manifestations.
Conclusion
Understanding the connection between anxiety and headaches opens up avenues for better management and prevention strategies. Acknowledging that stress, particularly from anxiety disorders like Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD), can lead to both tension headaches and migraines is crucial.
Effective coping mechanisms, including relaxation techniques and cognitive-behavioral therapy, offer relief and reduce headache frequency. Managing anxiety not only alleviates psychological distress but also diminishes the physical symptoms associated with it, such as headaches.
Focusing on both mental health and headache prevention enriches overall well-being.
- Breaking the Silence: Why Men’s Mental Health Matters More Than Ever - April 15, 2025
- How to Transform a Home’s Patio Space into a Relaxing Space - March 23, 2025
- 5 Strategies to Use a Cell Phone to Help Manage Your Stress - March 23, 2025
This site contains affiliate links to products. We will receive a commission for purchases made through these links.



