Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) and Narcissistic Personality Disorder (NPD) are distinct conditions, each with unique challenges and characteristics. ASD is a developmental disorder that affects communication and behavior, and it’s considered a “spectrum” because there’s a wide variation in the type and severity of symptoms people experience. On the other hand, NPD is a personality disorder characterized by a long-term pattern of exaggerated feelings of self-importance, an excessive need for admiration, and a lack of empathy for others.
While these disorders seem fundamentally different, individuals with either diagnosis may face misconceptions and stigma. There is an opportunity for better understanding when comparing their social aspects and relationships, coping mechanisms, and the journey to adulthood. Knowing how to navigate these conditions can lead to more effective support strategies, including therapy and advocacy.
Key Takeaways
- ASD is a neurodevelopmental disorder that varies widely in how it presents, while NPD involves persistent patterns of self-centeredness.
- There is a need for increased understanding to reduce the stigma and misconceptions associated with both ASD and NPD.
- Effective coping strategies and support are crucial for individuals with ASD or NPD.
 Understanding Autism Spectrum Disorder
Understanding Autism Spectrum Disorder
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a complex developmental condition that involves persistent challenges in social interaction, speech and nonverbal communication, and the presence of restricted and repetitive behaviors. The spectrum nature of ASD means that each individual with the condition has a distinct set of strengths and challenges.
Defining Autism Spectrum Disorder
ASD is a neurodevelopmental disorder that affects individuals across gender, race, and socioeconomic status. It’s characterized by:
- Diverse Behaviors: Ranging from highly skilled to severely challenged.
- Social Communication Difficulties: You may notice this as trouble with conversations or making eye contact.
Key Takeaway: ASD is a broad spectrum, and no two individuals experience it the same way.
Diagnosing ASD Using DSM-5
The DSM-5 provides criteria for clinicians to diagnose ASD, focusing on two core areas:
- Deficits in social communication and interaction that are not accounted for by general developmental delays.
- Restricted, repetitive patterns of behavior, interests, or activities.
Diagnosis considers the individual’s developmental level and may involve:
- Assessments: Both behavioral and developmental evaluations.
- Observations: Across multiple settings.
Key Takeaway: An accurate diagnosis involves careful observation and assessment based on DSM-5 criteria, considering the person’s developmental level.
Spectrum of Autism Behaviors
ASD encompasses a range of behaviors that can include:
- Repetitive Activities: Such as lining up toys or echoing phrases.
- Intense Interests: Often in specific topics or objects.
- Response to Sensory Input: Like aversion to specific sounds or textures.
Different people on the spectrum may display a mix of behaviors and degrees of severity, which is why it’s termed a ‘spectrum.’
Key Takeaway: The spectrum aspect of ASD reflects a variety of behaviors, sensitivities, and interests.
 Social Interaction and Communication Challenges
Social Interaction and Communication Challenges
Individuals with ASD might find social interactions and communication more challenging than their neurotypical peers due to:
- Understanding Nuances: Like body language or tone of voice.
- Expressing Themselves: Both verbally and non-verbally.
These challenges do not indicate a lack of desire for connection but rather a difference in processing social information.
Key Takeaway: Even though you might face communication hurdles if you have ASD, it doesn’t mean you’re not interested in forming relationships. It’s just that interacting can be tricky and might require support.
 Exploring Narcissistic Personality Disorder
Exploring Narcissistic Personality Disorder
In this section, you’ll learn about the hallmarks and diagnostic criteria of Narcissistic Personality Disorder (NPD), including its implications on empathy.
Characteristics of Narcissism
Narcissism involves a range of traits characterized by an inflated sense of one’s importance and a deep need for excessive attention and admiration.
- Self-Importance: You might notice that individuals with narcissistic traits often display a grandiose sense of self-importance. They may talk about personal achievements and talents as though they’re unmatched, even when such claims are unfounded.
- Fantasies of Success: Their inner world can include fantasies of unlimited success, power, brilliance, beauty, or ideal love.
- Sense of Entitlement: Narcissists often expect special treatment. They believe they’re entitled to it and want others to comply with their expectations.
Key Takeaway: Narcissism can show up as arrogance or an inflated self-image, with individuals often expecting preferential treatment and harboring unrealistic dreams of success.
 Diagnostic Criteria for NPD
Diagnostic Criteria for NPD
According to the DSM-5, the diagnostic criteria for Narcissistic Personality Disorder encompass a persistent pattern of grandiosity, a constant need for admiration, and a lack of empathy.
- Criteria Overview:
- A grandiose sense of self-importance
- Preoccupation with fantasies of unlimited success and power
- Belief in being special and unique and can only be understood by, or associated with, high-status people
- A need for excessive admiration
- A sense of entitlement
- Interpersonally exploitative behavior
- Lack of empathy
- Envy of others or belief that others are envious of them
- Demonstrating arrogant and haughty behaviors or attitudes
Key Takeaway: To be diagnosed with NPD, an individual must meet certain criteria that mainly focus on grandiosity, the need for admiration, and lack of empathy.
 Empathy and Narcissism
Empathy and Narcissism
Empathy refers to the ability to understand and share the feelings of another, a trait that can be significantly impaired in those with Narcissistic Personality Disorder.
- Understanding Empathy: Empathy allows you to put yourself in someone’s shoes. With NPD, the capacity to do so is often compromised, leading to challenges in personal relationships.
- Lack of Empathy: Individuals with NPD may struggle to recognize the desires and feelings of others; they may dismiss them, prioritize their own needs, or exploit others without guilt.
Key Takeaway: Empathy is generally low in people with NPD, which can affect their social interactions and relationships. Understanding this can be the key to navigating relationships with individuals showing narcissistic tendencies.
Common Traits and Misconceptions
In exploring autism and narcissism, it’s essential to discern their unique characteristics and the frequent misconceptions that surround them.
Autism vs. Narcissism Misunderstanding
Autism is often characterized by challenges in social interaction, communication, and restricted interests or repetitive behaviors. Narcissism, on the other hand, involves an inflated sense of self-importance and a deep need for admiration coupled with a lack of empathy for others. Misconceptions arise when people mistakenly attribute a lack of social response from individuals with autism to narcissism. One may perceive this as self-centered behavior when it’s usually not about ego but rather about dealing with sensory and processing differences.
Key Traits of Autism:
- Communication: You might notice limited eye contact or difficulty in understanding social cues.
- Behavior: Repetitive actions or strict adherence to routines can be expected.
Key Traits of Narcissism:
- Relationships: There may be a pattern of manipulative behaviors or entitlement.
- Empathy: A noticeable lack of understanding or concern for others’ feelings.

Importance of Differential Diagnosis
Differential Diagnosis is crucial for distinguishing between autism and narcissistic personality disorder, as treatment strategies differ significantly. The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5) is a guideline for professionals to diagnose these conditions accurately.
Diagnostic Criteria for Autism (according to DSM-5):
- Persistent deficits in social communication and interactions across various contexts.
- Restricted, repetitive patterns of behavior, interests, or activities.
Diagnostic Criteria for Narcissism:
- Grandiosity and constant need for admiration.
- Lack of empathy for others and exploitative of relationships.
When considering therapy, people with autism may benefit from behavioral strategies that enhance communication and social skills. In contrast, therapy for narcissism often focuses on developing empathy and building healthier relationship patterns.
Key Takeaway: Accurate diagnosis informs effective therapy. Understanding that someone may have social and communication difficulties for reasons other than self-absorption is essential. Seeking professional help for a proper evaluation is often the best action.

Social Aspects and Relationships
Building meaningful connections and navigating social landscapes can be uniquely challenging for individuals with autism, while those with narcissistic traits may experience difficulties in maintaining empathetic and reciprocal relationships.
Navigating Social Interactions
You might find social interactions to be a complex dance, guided by unspoken rules that everyone else seems to understand instinctively. For individuals on the autism spectrum, decoding these subtle cues can be puzzling:
- Eye contact: To some, it’s engaging; for you, it might feel overwhelming.
- Body language: Others use it to express feelings silently, which perhaps you interpret more literally.
- Social cues: Overseeing these can lead to misunderstandings.
Key takeaway: Navigating social interactions involves recognizing the unwritten rules and finding your rhythm.
Autism and Relationship Building
Building relationships is a journey, one that may feel less like a sprint and more like a scenic route when you’re autistic:
- Maintaining conversations might require extra focus, as understanding and keeping up with the give-and-take of dialogues might not come as naturally to you.
- Adapting to social norms doesn’t always align easily with how you process the world, but small steps toward empathy can open big doors in relationships.
Key takeaway: Relationship building is forging connections where your unique perspective is valued and reciprocated.
 Narcissistic Relationships and Empathy
Narcissistic Relationships and Empathy
If you’re dealing with narcissistic relationships, you might sometimes feel that your emotional needs are playing second fiddle to someone else’s self-focus:
- Relationships with narcissistic individuals often feel one-sided, with a lack of genuine empathy for your feelings.
- Understanding emotions might not be their strong suit, and you might notice a pattern of them twisting situations to their benefit.
Key takeaway: Healthy relationships require a balance of empathy and mutual respect, which may be lacking in narcissistic dynamics.
 Coping Mechanisms and Therapy
Coping Mechanisms and Therapy
In managing both autism spectrum disorder (ASD) and narcissistic traits, therapy plays a pivotal role. Effective coping mechanisms and tailored therapeutic approaches can significantly improve daily functioning and relationships.
Therapeutic Interventions for ASD
Therapy for ASD often involves a team of specialists. Your main point of contact could be a therapist who specializes in behavioral therapy. Behavioral therapy focuses on your specific needs and may include:
- Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA):
- It aims to improve social, communication, and learning skills through positive reinforcement.
- Occupational Therapy:
- Helps you master everyday tasks and improve your independence.
- Speech Therapy:
- Enhances communication abilities, both verbal and non-verbal.
Joining support groups can also be helpful. They provide a safe space to share experiences and coping strategies with others who understand your challenges.
Key takeaway: Behavioral therapy and the support of occupational therapists and support groups are essential for improving daily life and communication for individuals with ASD.
 Approaches to Managing Narcissism
Approaches to Managing Narcissism
Narcissism, as a mental health condition, requires tailored approaches to encourage empathy and healthier relationships. Strategies that therapists might employ include:
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT):
- Helps you identify and change negative thinking and behavior patterns.
- Group Therapy:
- Provides a platform to understand and improve interpersonal dynamics.
- Empathy Training:
- Encourages the development of compassion and understanding of others’ feelings.
Find a therapist who is experienced in treating personality disorders. They’ll guide you in exploring coping strategies and nurturing more meaningful connections with others.
Key takeaway: Techniques like CBT and empathy training worked on with a skilled therapist can aid you in managing narcissism and fostering healthier relationships.
Genetic and Environmental Influences
Understanding the interplay between genetics and the environment is crucial in unraveling the complexities of autism and narcissism.
Genetics of Autism and Narcissism
Genetic Makeup:
- You inherit your genetic code from your parents, which can predispose you to certain traits, including developmental and personality disorders like autism and narcissism.
- Research indicates there’s considerable genetic overlap between autism and narcissism, suggesting that if you have a family history of one, your genetic risk for the other might also be elevated.
Key Takeaway: Your genes could be a shared factor that influences both autism and narcissism risk.
The Role of Environment
Lifestyle and Social Factors:
- Environmental triggers, which encompass everything from your prenatal environment to your early childhood experiences, play a role alongside genetic factors in the development of both autism and narcissism.
- For example, complications during birth, parental care styles, and social interactions can all impact the expression of these conditions.
Key Takeaway: The setting you grow up in can interact with your genetic predisposition, shaping the emergence of autism and narcissism.
The Journey to Adulthood
Transitioning to adulthood is a multifaceted process, influenced significantly by individual experiences. For those with autism and individuals showing narcissistic traits, this journey presents distinct challenges and milestones.
From Childhood to Adulthood with Autism
As you move from childhood to adulthood, having autism means facing unique developmental stages. During this time, it’s crucial to have strong support networks and access to resources tailored to your needs. Here are essential aspects to consider:
- Education and Employment: Finding inclusive educational settings and workplaces that understand the value of neurodiversity can pave the way for success.
- Strategies may include seeking out special education services or job coaches.
- Social Interactions: Developing social skills is a continual process, which can involve:
- Engaging in social skills training or therapy groups.
- Utilizing peer mentorship opportunities.
- Independent Living: Gaining independence often requires planning and practice, involving:
- Learning daily living skills early.
- Exploring different living arrangements, such as assisted living or shared housing.
Key Takeaway: Embrace your unique journey, seek accommodations when needed, and remember that progress is personal and non-linear.
 Narcissism in Different Stages of Life
Narcissism in Different Stages of Life
Narcissism can present differently as you traverse through life’s stages. Here are some observations:
- Childhood and Adolescence: Disruptive patterns can emerge early but often blend with typical developmental behavior.
- It’s imperative to differentiate between self-esteem development and potential narcissistic traits.
- Young Adulthood: This life stage can magnify personal ambition and self-focus.
- Building healthy relationships and setting realistic goals are strategies to keep in check.
- Mid-life and Beyond: Often a time for reflection, possible adjustments may be made in self-perception.
- Prioritizing connections with others and community engagement can foster a sense of balance.
Key Takeaway: Be aware of how narcissistic traits can evolve, and proactively nurture empathy and self-awareness.
 Mental Health and Comorbid Conditions
Mental Health and Comorbid Conditions
Navigating the complexities of mental health can be challenging, especially when more than one condition is involved. This section sheds light on the intricacies of such overlapping diagnoses, specifically how autism spectrum disorder (ASD) and narcissistic personality disorder (NPD) can exist alongside other mental health challenges.
Co-occurrence of ASD and Other Disorders
When you have ASD, it’s not uncommon for other conditions to tag along. This is known as comorbidity. Professionals in mental health recognize that anxiety, depression, and ADHD are frequent companions of ASD, including Asperger’s syndrome, which is a subset of the autism spectrum.
- Anxiety often amplifies the social and communication challenges associated with ASD.
- Depression may emerge as a response to the persistent struggles and misunderstandings faced by individuals with ASD.
- ADHD often presents with ASD, potentially compounding difficulties with focus and impulse control.
Substance use disorders and borderline personality disorder are also seen with greater frequency in those with ASD than in the general population.
Key Takeaway: Understanding that ASD can coincide with other mental health issues is crucial for developing effective treatment plans and support strategies.
NPD and Associated Mental Health Challenges
In the case of NPD, comorbidity is also common. If you or someone you know has NPD, it’s vital to be aware that this condition doesn’t exist in isolation.
- Depression can be a covert issue for those with NPD, as their self-esteem might heavily depend on the recognition and approval of others.
- Substance Use Disorders are sometimes utilized by individuals with NPD in an attempt to self-medicate their emotional pain.
- Borderline Personality Disorder and NPD can overlap, leading to a complex treatment landscape that requires careful navigation.
Mental health professionals are trained to identify and address these overlapping challenges, offering hope for those grappling with the implications of their intertwined conditions.
Key Takeaway: An awareness of comorbid conditions with NPD helps in seeking holistic care tailored to address all facets of one’s mental well-being.
Impact of Narcissism and Autism on Family
Navigating family life with members affected by Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) or narcissism brings unique challenges. Understanding these can foster a more supportive environment for everyone involved.
 Family Dynamics with ASD
Family Dynamics with ASD
When a family member has ASD, recognizing and adapting to their needs is crucial. People with autism may struggle with social cues, which can lead to misunderstandings within family interactions. Here are specific considerations:
- Awareness: Educate yourself and your family members about the social challenges of ASD.
- Routine: Strive for a consistent daily routine to provide a sense of stability for your loved one with autism.
- Communication: Use clear, direct language to avoid confusion and help articulate feelings and needs.
Key Takeaway: Supporting a family member with ASD involves patience, education, and establishing a predictable environment.
Challenges in Families with Narcissistic Members
In contrast, narcissism can disrupt family balance through a lack of empathy and emotional abuse. A narcissistic family member may create a pattern of hostile dependency, where their need for admiration strains relationships. To navigate these challenges:
- Recognize Manipulative Behaviors: Be alert to tactics like guilt-tripping or gaslighting.
- Set Boundaries: Establishing limits to protect your emotional well-being is essential.
- Seek Support: Find a therapist or support group that understands the dynamics of narcissistic relationships.
Key Takeaway: Managing relationships with narcissistic family members requires setting firm boundaries and seeking external support when needed.
Empowerment and Advocacy
Empowerment and advocacy are crucial elements in addressing the challenges faced by individuals with autism and those labeled with narcissism. Self-advocacy promotes personal growth and empowerment while challenging stigma contributes to societal changes.
Self-Advocacy and Autism
You may feel that the world is often tailored to neurotypical standards, making self-advocacy a vital tool for individuals with autism. Here’s why:
- Success Through Self-Awareness: By fostering self-awareness, you can better understand and communicate your needs effectively.
- Theory of Mind Development: It involves recognizing and appreciating different perspectives, which enhances communication skills.
Key Takeaway: By advocating for yourself and increasing your understanding of autism, you not only pave the path for your successes but also assist others in developing a nuanced theory of mind.
Challenging the Stigma of Narcissism
While narcissism is often seen through a negative lens, it’s essential to understand the various dimensions:
- Recognizing the Spectrum: Narcissism ranges from healthy self-esteem to extreme self-absorption.
- Addressing Misconceptions: Challenging stigma involves separating destructive behaviors from the individual and acknowledging the capacity for change, like developing remorse.
Key Takeaway: By actively challenging the stigma surrounding narcissism, you encourage a balanced view that acknowledges the complexities of the trait and the individual’s potential for positive power and passion.
Advancements in Autism and Narcissism Research
Recent studies have illuminated our understanding of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) and narcissism, focusing on behavioral patterns and cognitive processes.
Latest Research in ASD
Autism research has made significant strides towards understanding how you interact with the world. Here’s what’s new:
- Eye Contact: You may find maintaining eye contact challenging. Studies show it’s not about disinterest but how sensory information is processed.
- Routine: Changes in routine can be stressful if you have ASD. Recent interventions aim to equip you with strategies to handle disruptions with less anxiety.
- Social Skills and Verbal Communication: Innovative behavioral therapies have been developed to enhance your social interactions and verbal abilities through structured yet flexible programs.
- Social Skills: Role-playing games and peer-mediated learning.
- Verbal Communication: Use of visual aids and technology-based tools.
Key Takeaway: Personalized interventions are crucial and are now being tailored to suit your unique needs and preferences better.
 Understanding Narcissism in Modern Psychology
Understanding Narcissism in Modern Psychology
Narcissism, once narrowly defined, is now viewed through a complex lens:
- Behavior: Your tendency to seek admiration and a sense of superiority is now linked to underlying insecurities and past experiences.
- Objects and Nonverbal Communication: How you interact with objects and use nonverbal cues is being studied. It might signify more than self-focus, reflecting how you connect with others.
- Nonverbal Communication: Body language in narcissism tells of your emotional state and intentions.
Key Takeaway: The research moves beyond stereotypes, understanding why you may feel and behave like you do.
Frequently Asked Questions
When diving into the intricacies of autism and narcissism, you’re bound to have a lot of questions. This section aims to unpack some common curiosities, focusing on how these two conditions differ and how they interact in varied contexts.
How do the traits of narcissistic personality disorder differ from those seen in individuals with autism?
Narcissistic Personality Disorder (NPD) is characterized by a deep need for admiration and a sense of superiority, often with little empathy for others. On the flip side, autism spectrum disorder involves challenges with social communication and behavior but doesn’t inherently include a desire for admiration or a lack of empathy.
Key takeaway: NPD and autism differ mainly in empathy and the desire for admiration, with NPD individuals seeking validation and autistic individuals facing social communication challenges.
What are the challenges in a relationship between someone with narcissistic personality disorder and an individual with autism or Asperger’s syndrome?
Balancing a relationship where one partner has NPD and the other has autism can be tough. The narcissistic partner may feel frustrated by their partner’s social communication difficulties, while the autistic partner might feel overwhelmed by the narcissist’s emotional needs.
Key takeaway: Patience and understanding from both sides are vital in navigating the unique challenges in such a relationship.
Can being raised by a narcissistic parent affect the development of a child with autism?
Absolutely. The emotional environment created by a narcissistic parent may impact an autistic child’s development. This child might struggle with self-esteem issues or become more susceptible to stress due to potential emotional neglect or manipulation.
Key takeaway: A nurturing environment is crucial for an autistic child’s growth, and a narcissistic parent’s behavior can compromise this.
What are some signs to differentiate between covert narcissism and autism in adults?
Covert narcissism may present as sensitivity to criticism and a quiet sense of superiority. While autism in adults can also include social challenges, it’s not typically linked with a hidden self-centered agenda or fragile ego.
Key takeaway: Look for a hidden sense of entitlement in covert narcissism, as opposed to straightforward social challenges in autism.
How does having a sense of entitlement manifest differently in individuals with autism compared to those with narcissistic tendencies?
In autism, any perceived sense of entitlement may stem from a need for routine or fairness. People with narcissistic tendencies, on the other hand, may display entitlement as a belief in their inherent superiority and expectation of special treatment.
Key takeaway: The root of entitlement in autism is different from narcissism, focusing on comfort in routine rather than self-importance.
What are the most common comorbid disorders associated with autism, and how do they interact with traits of narcissism?
Common comorbid disorders with autism include ADHD, anxiety, and depression. These can all magnify social challenges and may interact with narcissistic traits by complicating communication and emotional regulation.
Key takeaway: Awareness of comorbid conditions is essential, as it helps you understand the layered experiences of an autistic individual.
- The Burnout Epidemic: Why We’re All Feeling Overwhelmed and How to Cope - February 9, 2024
- How to Live a Peaceful Life - February 9, 2024
- Useful Information You Should Know About Health Screenings - February 8, 2024
This site contains affiliate links to products. We will receive a commission for purchases made through these links.


 Understanding Autism Spectrum Disorder
Understanding Autism Spectrum Disorder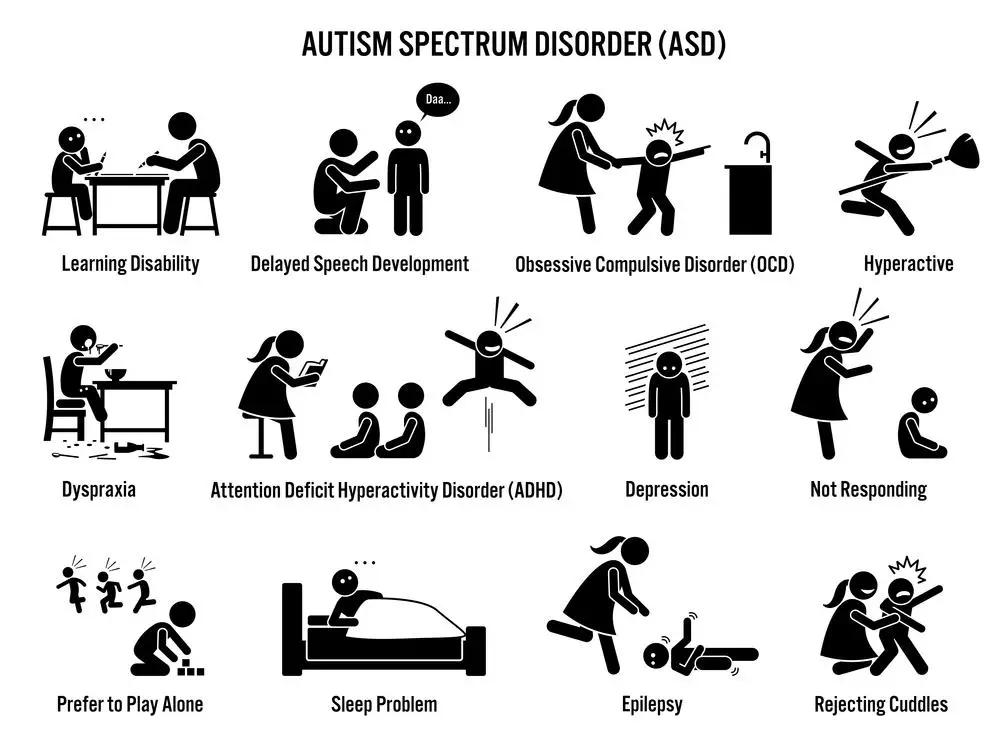 Social Interaction and Communication Challenges
Social Interaction and Communication Challenges Exploring Narcissistic Personality Disorder
Exploring Narcissistic Personality Disorder Diagnostic Criteria for NPD
Diagnostic Criteria for NPD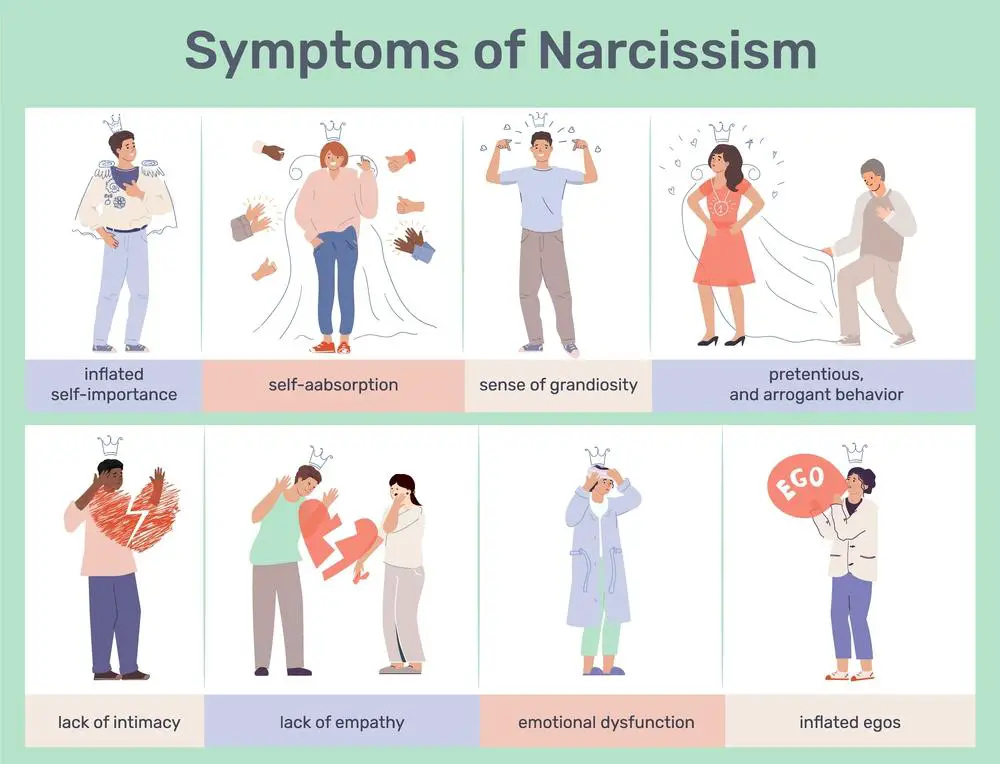 Empathy and Narcissism
Empathy and Narcissism Narcissistic Relationships and Empathy
Narcissistic Relationships and Empathy Coping Mechanisms and Therapy
Coping Mechanisms and Therapy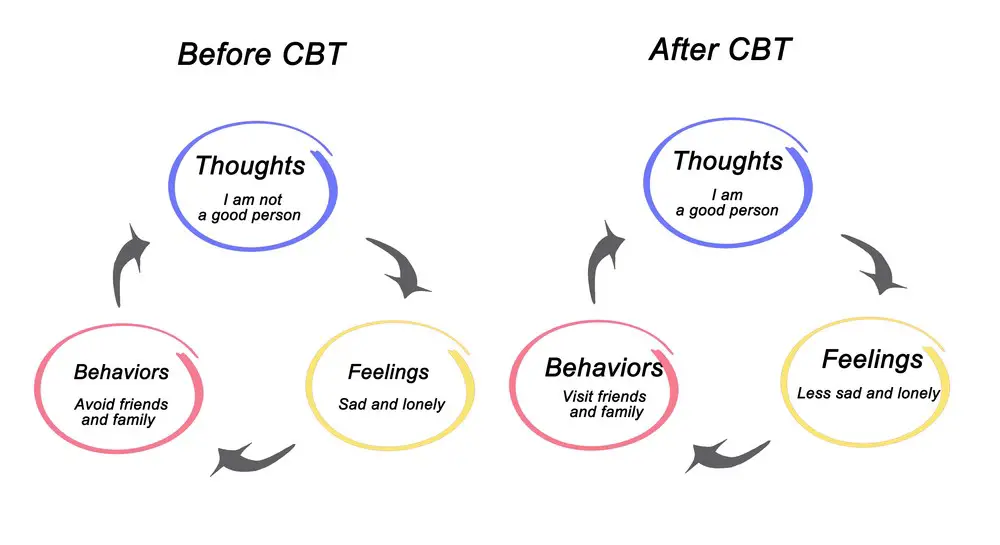 Approaches to Managing Narcissism
Approaches to Managing Narcissism Narcissism in Different Stages of Life
Narcissism in Different Stages of Life Mental Health and Comorbid Conditions
Mental Health and Comorbid Conditions Family Dynamics with ASD
Family Dynamics with ASD Understanding Narcissism in Modern Psychology
Understanding Narcissism in Modern Psychology

