As a BetterHelp affiliate, we receive compensation from BetterHelp if you purchase products or services through the links provided
It’s quite common to feel uneasy before an important presentation, a first date, or even a visit to the dentist. However, it’s crucial to differentiate between anxiety and nervousness. In this exploration, we’ll uncover the subtle yet significant differences between these two states of mind. It is essential to recognize when apprehension crosses the line into something more profound. The ability to distinguish between anxiety and nervousness can lead to effective coping strategies and improved mental health management.
Understanding Anxiety
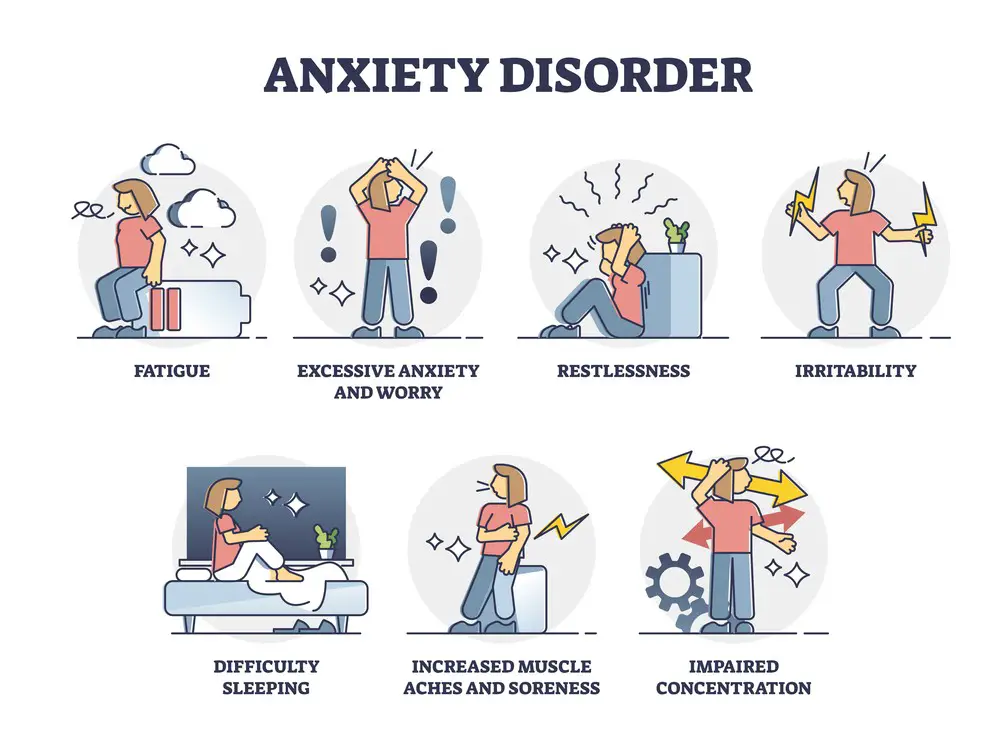
Defining Anxiety
Anxiety, at its core, is a natural emotional response that encompasses a range of feelings like unease, worry, and fear. It’s an intricate interplay of psychological and physiological elements. Psychologically, anxiety often arises from our perception of potential threats or dangers, and it can manifest as excessive, irrational, or uncontrollable worry. It’s rooted in our evolutionary survival mechanisms, where heightened alertness helped our ancestors navigate dangerous situations.
Also Read: Self-Centered vs Selfish: Unraveling the Key Differences
Understanding Anxiety As An Emotional Response
Anxiety is a universal human experience, a response to life’s challenges and uncertainties. Various situations, such as exams, job interviews, or major life changes, can trigger it. In moderation, anxiety can even be adaptive, motivating us to plan and prepare. However, when it becomes chronic or overwhelming, it can significantly impact mental and physical well-being.
Causes And Triggers Of Anxiety
A multitude of factors can trigger anxiety. Common causes include environmental stressors like work pressure, relationship issues, financial concerns, or traumatic events. Biological factors, such as genetics and brain chemistry, also play a role in an individual’s susceptibility to anxiety. Understanding these triggers is vital in addressing and managing anxiety effectively.
Role Of Chronic Stress And Anxiety Disorders
Chronic stress is a significant contributor to anxiety disorders. When stressors persist, the body’s stress response system, including the release of stress hormones like cortisol, can become dysregulated. This, in turn, may lead to various anxiety disorders, such as generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), panic attack, panic disorder, or social anxiety disorder. These conditions are characterized by persistent, excessive worry and fears that can interfere with daily life, necessitating specialized treatment and support.
Understanding Nervousness
Defining Nervousness
Nervousness is a transient emotional state characterized by heightened alertness and anticipation. It often manifests as feelings of unease, butterflies in the stomach, and a racing heart. Unlike anxiety, which tends to be more pervasive and long-lasting, nervousness is typically tied to specific situations or events.

Nervousness As A Natural Response
Nervousness is a natural and adaptive response to various situations. It can arise when individuals face novel or challenging experiences, such as public speaking, job interviews, or taking an important exam. This heightened state of alertness can enhance performance by increasing focus and motivation.
Also Read: Emotional Support Plushie: Your Ultimate Guide to Snuggly Comfort
Situational Nervousness
Nervousness can be triggered by a wide range of situations and factors, varying from person to person. What makes one person nervous may not have the same effect on someone else. However, some instances and scenarios that commonly induce nervousness for many people include:
- Public Speaking: The fear of speaking in front of a large audience is a well-known source of nervousness. It can lead to symptoms like sweaty palms, a shaky voice, and increased heart rate.
- Job Interviews: The pressure to perform well during a job interview can be nerve-wracking. Feeling anxious about presenting oneself in the best light and answering questions effectively is common.
- Exams and Tests: Academic evaluations, such as final exams, standardized tests, or professional certification exams, can induce nervousness due to the fear of failure or poor performance.
- Performance and Auditions: Whether it’s a musician, actor, or athlete preparing for a performance or audition, the pressure to excel can cause nervousness.
- First Dates: Meeting someone new and trying to make a good impression can be nerve-wracking, leading to social anxiety and butterflies in the stomach.
- Medical Procedures: Even routine medical appointments or procedures like dental visits, injections, or surgeries can induce nervousness due to fear of pain, complications, or unknown outcomes.
Tips For Managing Situational Nervousness
Managing situational nervousness involves strategies such as deep breathing exercises, positive self-talk, and visualization. Additionally, preparation and practice can significantly reduce nervousness by increasing confidence and competence. Embracing nervousness as a natural response and reframing it as a source of energy rather than a hindrance can also be empowering.
Key Differences
Emotional Responses
Anxiety is a multifaceted emotional and psychological response to perceived threats or stressors. It involves feelings of fear, worry, restlessness, and irritability and can lead to physical symptoms like increased heart rate and muscle tension. Anxiety affects one’s perception of reality, leads to obsessive thoughts, and negative emotions, and triggers avoidance behaviors. In conditions like obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), anxiety can lead to persistent and intrusive thoughts that cause distress. It may also affect concentration, sleep patterns, and social interactions. When anxious feelings become chronic and significantly impair daily life, it may indicate an anxiety disorder that often requires treatment and management.
Emotional Responses Associated With Nervousness
On the other hand, feeling nervous tends to be a more specific and temporary emotional response. It commonly involves feelings of anticipation, excitement, or mild apprehension. Unlike anxiety, nervousness is often situation-specific and is a normal stress response that is not typically associated with overwhelming fear or intrusive thoughts.
Also Read: What is DMT Meditation: Unlocking the Mind’s Mysteries
Physical Symptoms
Physical Symptoms Of Anxiety
Anxiety often leads to a wide array of physical symptoms, such as increased heart rate, shortness of breath, muscle tension, and sweating. Individuals with anxiety may experience panic attacks characterized by intense physical sensations like chest pain and dizziness. These symptoms are more pervasive and can persist even without an immediate external trigger.
Physical Reactions Associated With Nervousness
Nervousness tends to manifest as milder physical reactions compared to anxiety. It can include butterflies in the stomach, trembling, and a slightly elevated heart rate. These physical responses are generally short-lived and are directly tied to the situation that triggers the nervousness, such as the moments before a presentation or a first date.
Coping With Anxiety
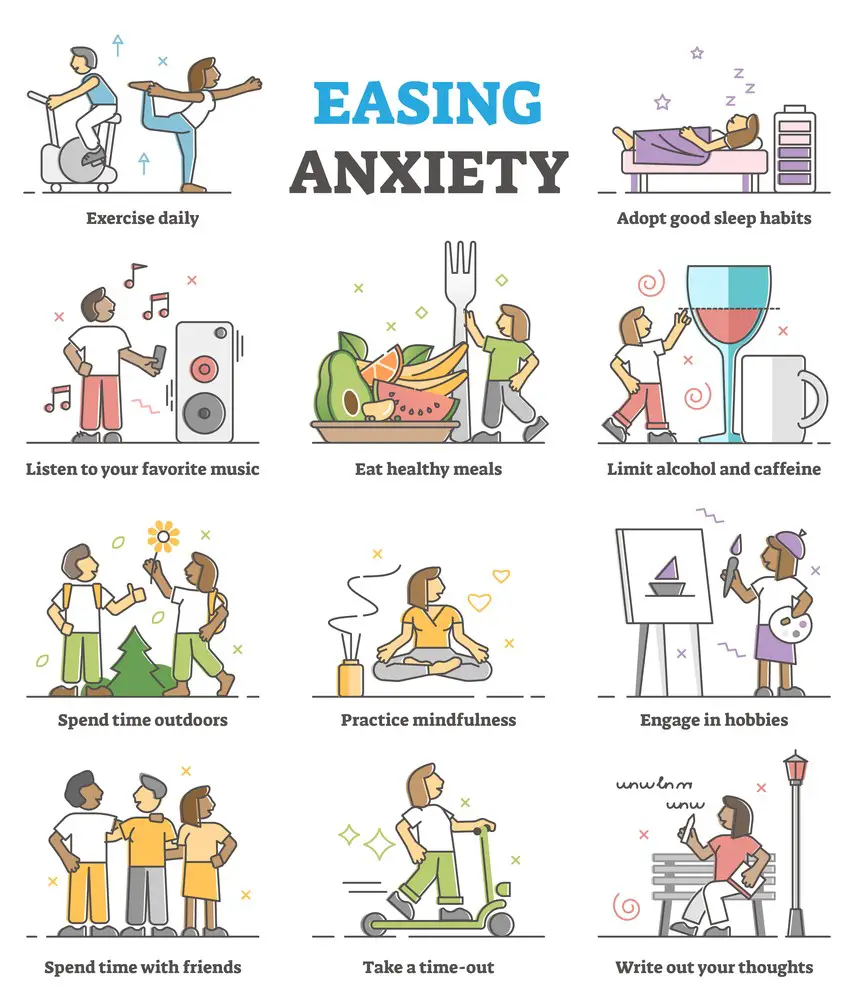
Self-Help Strategies
Coping with anxiety through self-help involves various strategies, including mindfulness, relaxation techniques, exercise, healthy lifestyle choices, stress management, and positive self-talk. It’s essential to prioritize self-care, maintain social connections, and seek professional help when necessary. These strategies can help manage anxiety and promote emotional well-being.
Role Of Mindfulness, Deep Breathing, And Relaxation Methods
Mindfulness practices, deep breathing exercises, and progressive muscle relaxation are effective tools for managing anxiety symptoms. Mindfulness involves staying present and non-judgmentally aware of your thoughts and emotions. Deep breathing and relaxation methods can help calm the body’s stress response, reducing the physical symptoms of anxiety.
Professional Help
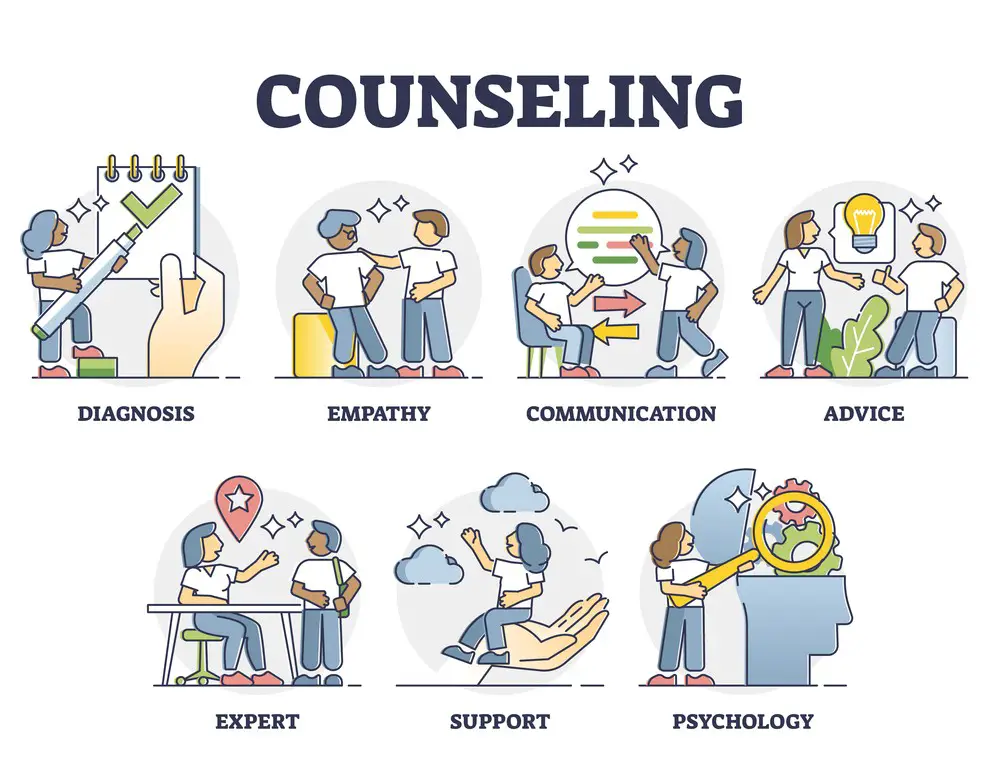
Seeking professional help for anxiety is recommended when it significantly interferes with daily life, becomes chronic, or leads to severe distress. If self-help strategies prove insufficient, or if symptoms are particularly severe, it’s essential to consult a mental health professional, such as a therapist or psychiatrist.
 Types Of Therapy And Medications For Anxiety Treatment
Types Of Therapy And Medications For Anxiety Treatment
There are several types of therapy and medications commonly used in the treatment of anxiety disorders. The choice of treatment depends on the type and severity of anxiety, as well as individual preferences. Here’s an overview of therapy and medication options for anxiety treatment:
Types Of Therapy
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT)
- Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT)
- Exposure Therapy
- Interpersonal Therapy (IPT)
- Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT)
- Psychodynamic Therapy
Medications for Anxiety
- Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs)
- Benzodiazepines
- Serotonin-Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors (SNRIs)
- Buspirone
- Antidepressants
- Beta-Blockers
- Anticonvulsants
The choice between therapy and medication, or a combination of both, should be made in consultation with a mental health professional. Treatment plans are personalized based on the individual’s specific diagnosis, symptoms, and preferences. It’s essential to follow the guidance of a healthcare provider for the most effective anxiety treatment.
Also Read: 4 Ways to Get the Most Out of Your Talk Therapy Sessions
Coping With Nervousness
Situational Management
Managing nervousness in specific situations involves techniques like visualization, positive self-talk, and controlled breathing. Visualizing a successful outcome can boost confidence, while self-affirmations help reframe negative thoughts. Deep, controlled breathing can calm the body’s physical response to nervousness.
Building Confidence And Easing Nervousness
To build confidence and reduce nervousness over time, increase self-awareness and understand your triggers. Set achievable goals, prepare thoroughly for challenging situations, practice regularly, and engage in positive self-talk. Visualization, seeking feedback, embracing failure, maintaining physical health, and using relaxation techniques can also improve your confidence. Gradual exposure to anxiety triggers and professional help when needed are important steps. Surrounding yourself with a supportive network and learning from role models can further boost your confidence. Be patient with yourself and acknowledge your progress as you work towards increased self-assurance.
The Role Of Preparation
Preparation is a potent antidote to nervousness. Thoroughly researching and understanding the subject matter or task at hand, practicing, and having a well-structured plan can significantly reduce the rate at which you feel nervous. Knowing you’ve put in the effort can boost confidence.
Developing Effective Preparation Habits
Effective preparation habits include setting realistic goals, creating a study or practice schedule, seeking feedback from mentors or peers, and staying organized. Additionally, managing time wisely and breaking tasks into smaller, manageable chunks can make preparation more manageable and less anxiety-inducing.
Conclusion
It’s essential to remember that both emotions are natural responses to life’s challenges. While anxiety may require professional help and therapeutic interventions, nervousness can often be managed with practical self-help techniques, situational strategies, and effective preparation. Explore these coping strategies and seek professional guidance when needed. By doing so, you can navigate life’s hurdles with greater resilience, reduce the impact of these emotions, and ultimately lead a more fulfilling and less anxious life.
- Left Arm Pain and Anxiety: Understanding the Relationship - November 23, 2023
- Anxiety Paralysis: Coping with Overwhelming Stress - November 23, 2023
- Anxious vs. Nervous: Differentiating Emotions and Responses - November 15, 2023
This site contains affiliate links to products. We will receive a commission for purchases made through these links.


 Types Of Therapy And Medications For Anxiety Treatment
Types Of Therapy And Medications For Anxiety Treatment
