As a BetterHelp affiliate, we receive compensation from BetterHelp if you purchase products or services through the links provided
Adolescent counseling is a specialized field that focuses on supporting and guiding young individuals through the challenges and complexities they may encounter during their formative years. The need for such counseling arises from adolescents’ unique developmental stages, marked by rapid physical, emotional, and cognitive changes. Professional counselors working with adolescents possess the necessary skills and understanding to help these youths navigate the hurdles they face, ultimately guiding them toward healthy growth and personal discovery.
Fundamental to adolescent counseling is the recognition that the issues and concerns faced by adolescents are distinct from those of adults or children. Common issues addressed in counseling can range from family and peer relationships, identity development, and academic struggles to mental health concerns such as anxiety, depression, or substance abuse. Counselors can effectively address these concerns by employing various therapeutic techniques and strategies, providing a crucial support system for adolescents and their families.
Key Takeaways
- Adolescent counseling targets the unique challenges youths encounter during their developmental stage.
- Professional counselors address relationships, identity development, mental health, and adolescent academic struggles.
- Various therapeutic techniques and strategies provide comprehensive support and resources for adolescents and their families.
Fundamentals of Adolescent Counseling
Adolescent counseling mainly focuses on providing support, guidance, and assistance to adolescents during their crucial developmental phase. The fundamentals of adolescent counseling can be divided into three sub-sections: Therapy Approaches, Roles of Mental Health Professionals, and Parent and Family Involvement.
Therapy Approaches
Mental health professionals employ various therapy approaches to address the unique needs of adolescents. Some of the most common methods include:
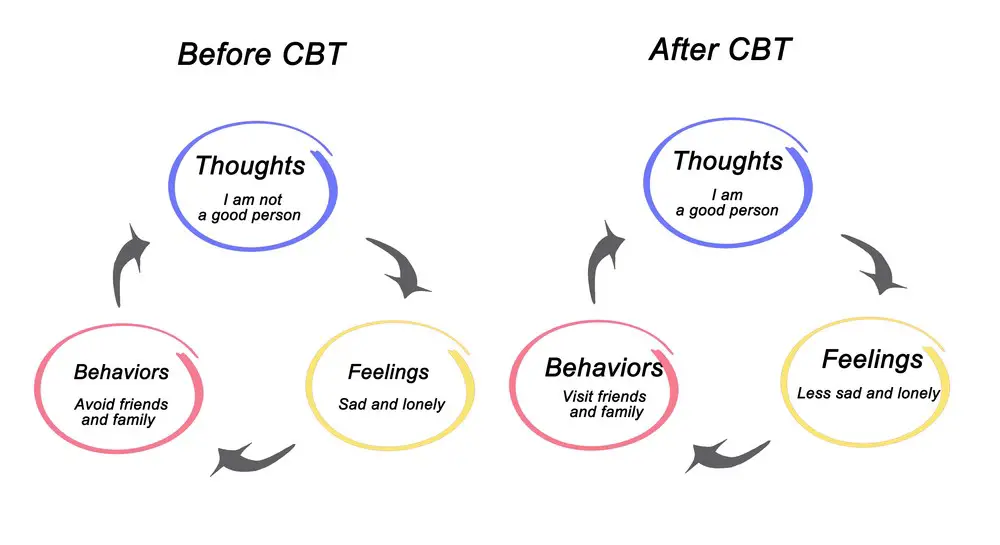
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): CBT helps adolescents identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors. It is particularly useful for those struggling with anxiety, depression, and other mood disorders.
- Family Systems Therapy: This approach targets the entire family unit and addresses family dynamics or communication patterns that may contribute to an adolescent’s issues.
- Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT): DBT is an evidence-based therapy that teaches emotional regulation, distress tolerance, mindfulness, and interpersonal effectiveness skills.
Roles of Mental Health Professionals
Mental health professionals play a crucial role in adolescent counseling. Some of the licensed professionals involved in this field include:
- Therapists: They provide individual, group, or family therapy sessions tailored to the adolescent’s needs.
- Psychologists: Psychologists are trained to administer psychological assessments and provide specialized therapy approaches.
- Psychiatrists specialize in the medical aspect of mental health, prescribing medications when necessary and collaborating with other professionals in the treatment process.
Parent and Family Involvement
The involvement of parents and families is often essential in adolescent counseling. Some of the ways this involvement can be facilitated include:
- Parent education: Providing parents with relevant information and resources helps them better understand their adolescent’s needs and support.
- Family therapy: Regular family sessions can strengthen communication and relationships within the family, addressing any underlying issues contributing to the adolescent’s struggles.
- Collaboration: Mental health professionals should maintain an open line of communication with parents, updating them on their adolescent’s progress and involving them in decision-making.

Get Support for Your Teen
Common Issues Addressed in Counseling
Emotional and Mental Health
Adolescents often face emotional and mental health challenges like anxiety, depression, and trauma. Counseling can help them understand their feelings and develop coping strategies. A common issue is anxiety, which may manifest in various ways, including social, generalized, or separation anxiety. Furthermore, depression is another prevalent issue among teens, resulting from biological, psychological, and social factors. Counseling can offer support and treatment options to address these concerns.
Behavioral Problems
Certain behavioral issues, like ADHD, may arise during adolescence, causing difficulties in everyday life. Counseling can help adolescents develop more effective organizational skills, self-discipline, and impulse control. Additionally, treatment might focus on managing coexisting issues, such as academic struggles. Moreover, eating disorders, like anorexia or bulimia, may emerge during the teenage years, challenging physical and emotional health. Counselors can offer guidance, support, and therapeutic interventions to help adolescents manage these problems.
Family and Relationship Dynamics
Family and relationship dynamics significantly impact adolescent well-being. Conflicts with parents, siblings, and other family members can cause stress and affect emotional health. Counseling can help adolescents improve communication skills and build healthier relationships within their families. Moreover, substance use is a concern that frequently arises within this age group, potentially affecting family dynamics and causing additional issues. Adolescents can learn strategies to prevent or reduce substance use through counseling and find recovery support.
Therapeutic Techniques and Strategies
Start Achieving Goals Together
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is an evidence-based psychotherapy approach. It focuses on identifying and changing negative thought patterns and behaviors in adolescents. CBT helps improve self-esteem by promoting self-awareness and reinforcing positive thoughts. Techniques can include journaling, identifying cognitive distortions, and Socratic questioning. The aim is to help them develop coping skills and effective communication.
Dialectical Behavior Therapy
Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT) is a type of CBT that emphasizes emotional regulation and interpersonal effectiveness. DBT is particularly helpful for adolescents struggling with intense emotions, self-harm, or unstable relationships. Techniques can include mindfulness, distress tolerance, and interpersonal communication skills.
Acceptance and Commitment Therapy
Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT) teaches adolescents to accept and work with uncomfortable emotions and thoughts. They learn to recognize and change unhelpful coping patterns and commit to values-based goals. Techniques can include mindfulness, cognitive defusion, and value clarification.
Interpersonal Therapy
Interpersonal Therapy (IPT) addresses interpersonal issues and helps adolescents improve their relationships. It targets communication, conflict resolution, and adjusting to life transitions. Techniques can include role-playing, active listening, and exploring past relationships to identify patterns.
Mentalization Based Therapy
Mentalization Based Therapy (MBT) aims to improve adolescents’ ability to understand and interpret their and others’ mental states. Doing so helps them build self-esteem, emotional regulation, and secure attachments. Techniques can include exploring mental states through artwork, discussing emotions, and reflecting on interpersonal interactions.
Group and Family Therapy
Group therapy, involving peers facing similar challenges, provides support, fosters communication, and allows for skill-building in a shared environment. Family therapy can help address family dynamics and improve communication within the family unit. Techniques can include psychoeducation, role-playing, and establishing boundaries.

Seek Professional Guidance Today
Support and Resources for Adolescents and Families
Community Programs and Services
There are numerous community programs and services available to support adolescents and families. These programs focus on providing resources, education, and awareness about mental health. Local organizations, such as schools, community centers, and nonprofit organizations, often offer support groups and workshops for adolescents and their families.
Key community resources:
- Mental health clinics
- Youth centers
- Family support groups
Prevention strategies:
- Community-based workshops
- School-sponsored events
- Public awareness campaigns
Discover a brighter future!
Educational Opportunities
Educational opportunities can play a significant role in adolescent mental health. Many schools and community organizations provide classes, presentations, and workshops to educate adolescents and their families about mental health issues. This education can help facilitate early intervention, support, and prevention efforts.
Examples of educational opportunities include:
- Mental health awareness workshops
- Parent-teacher conferences
- School wellness programs
Online and Social Support
In today’s digital age, many online and social support resources are available to adolescents and their families. These resources often include informative websites, forums, and social media platforms where individuals can access support and information from their homes.
Examples of valuable online resources:
- Mental health organizations’ websites
- Online support groups
- Social media forums
By exploring these support and resource options, adolescents and their families can find the help they need in dealing with mental health challenges.
Addressing Specific Adolescent Needs
Gender Identity and Sexual Orientation
During adolescence, many young people experience changes and self-exploration related to their gender identity and sexual orientation. Counselors must create a safe and non-judgmental space where teens can discuss these topics openly. Counselors should be knowledgeable about LGBTQ+ issues and offer resources and guidance to help adolescents navigate their journey to self-discovery and acceptance.
Special Needs and Chronic Conditions
Adolescents with special needs or chronic conditions, such as autism or other developmental disabilities, may face unique challenges during this transitional period. Counselors should be trained to work with individuals with various abilities and consider their specific needs in the counseling process. This may include providing accommodations, collaborating with other professionals or caregivers, and developing customized therapy plans. Additionally, counselors should address concerns around puberty, promoting autonomy, and fostering social skills in this population.
| Special Needs | Strategies |
|---|---|
| Autism | Social skills training, sensory integration therapy |
| Learning Disabilities | Academic support, accommodations, study skills coaching |
| Chronic Health Issues | Coping strategies, medical care coordination |
Coping with Peer Pressure and Social Issues
Peer pressure and social issues are common challenges faced by adolescents. Counselors can help young people develop healthy coping skills and decision-making abilities to navigate these situations. Techniques may include:
- Teaching assertiveness skills
- Fostering positive self-esteem
- Encouraging critical thinking
- Role-playing scenarios to practice responses to challenging situations
Counselors should also be prepared to address substance use, bullying, and suicidal thoughts. Open discussions and education can facilitate prevention and early intervention efforts. Encouraging teens to seek support from trusted adults and peers can help foster resilience and healthy emotional development during adolescence.

Empower yourself with therapy!
FAQs
What is adolescent counseling?
Adolescent counseling is a mental health service for individuals between 12 and 18. It aims to help teenagers cope with and overcome various emotional, behavioral, and developmental problems that may arise during this challenging phase of life.
When should a teenager seek counseling?
There are numerous reasons for a teenager to seek counseling, such as self-esteem, anxiety, depression, bullying or peer pressure, relationship issues, family conflicts, or other behavioral or emotional concerns.
What methods are used in adolescent counseling?
Different counseling approaches can be employed depending on the teenager’s specific needs, such as person-centered, cognitive-behavioral, or family-based therapy. Techniques may include discussing feelings and experiences, identifying patterns that contribute to problems, developing problem-solving or coping strategies, and enhancing communication skills.
How long does a typical counseling session last?
A standard counseling session generally lasts about 50 minutes to one hour. However, the duration of a session may vary depending on the needs and preferences of the teenager and the counselor.
What is the role of parents in adolescent counseling?
Parents play a crucial role in supporting their teenagers throughout the counseling process. This may involve attending sessions regularly, maintaining open communication with the counselor, and helping implement strategies recommended by the counselor.
Is adolescent counseling confidential?
Confidentiality is an essential aspect of the counseling relationship. Counselors must maintain strict confidentiality, with some exceptions involving safety or legal concerns, such as harming oneself or others or abuse or neglect. In such cases, the counselor is mandated to report the situation to the proper authorities to ensure the safety of the adolescent.
- Breaking the Silence: Why Men’s Mental Health Matters More Than Ever - April 15, 2025
- How to Transform a Home’s Patio Space into a Relaxing Space - March 23, 2025
- 5 Strategies to Use a Cell Phone to Help Manage Your Stress - March 23, 2025
This site contains affiliate links to products. We will receive a commission for purchases made through these links.





