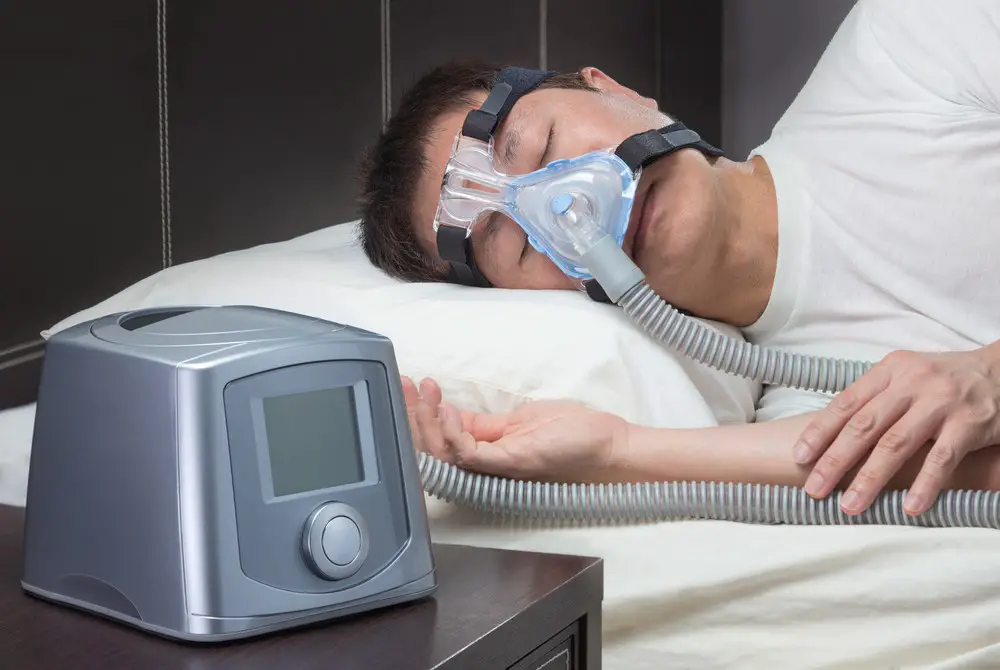
As a BetterHelp affiliate, we receive compensation from BetterHelp if you purchase products or services through the links provided
Sleep apnea is a serious and potentially life-threatening sleep disorder in which an individual’s breathing repeatedly stops and starts during sleep. While various factors contribute to sleep apnea development, research supports the idea that certain dietary choices can exacerbate or possibly trigger the condition. Recognizing these foods and understanding their impact on sleep apnea is essential for those looking to adjust their eating habits and reduce the severity of the disorder.
A well-balanced diet is crucial for maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and its impact on sleep cannot be underestimated. Specific foods and eating patterns have been linked to developing or worsening sleep apnea symptoms. Individuals need to pay attention to the type of food and beverages they consume, particularly those that can potentially induce inflammation, cause weight gain, or obstruct the airway during sleep.
Key Takeaways
- Certain foods and eating patterns can contribute to sleep apnea development and worsen symptoms.
- A well-balanced diet is essential for maintaining a healthy lifestyle and improving sleep quality.
- Paying attention to food choices and recognizing their impact on sleep apnea is crucial for those experiencing the disorder.
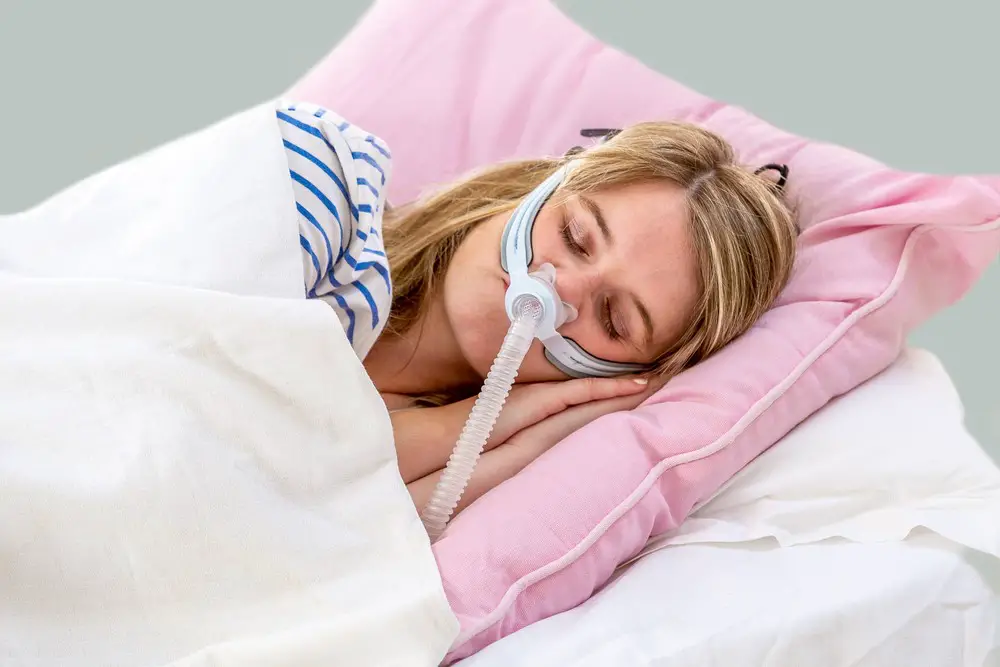

Understanding Sleep Apnea
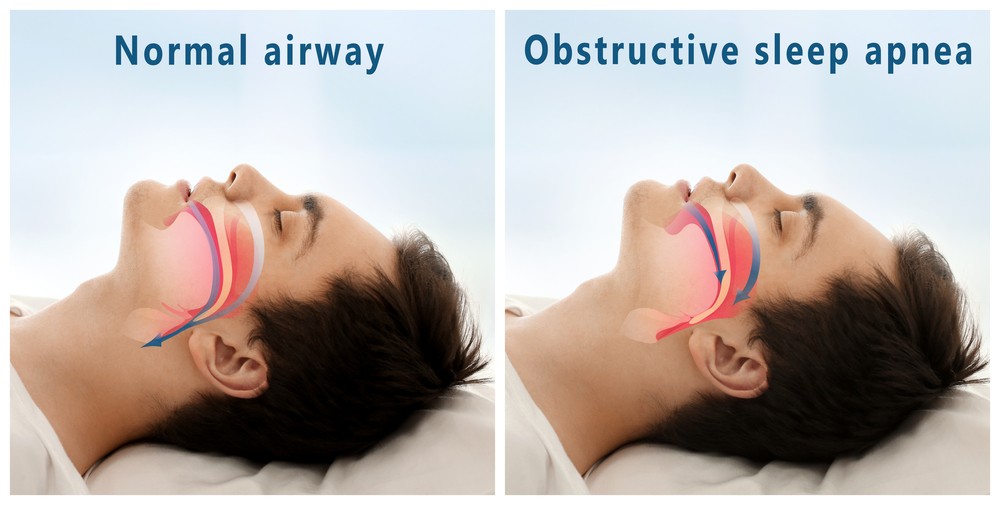
Sleep apnea is a sleep disorder characterized by pauses in breathing or shallow breaths during sleep. There are three main types of sleep apnea, but the most common form is Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA).
Obstructive Sleep Apnea
Obstructive Sleep Apnea occurs when the muscles in the back of the throat fail to keep the airway open during sleep, despite the effort to breathe. This causes the brain to briefly awaken the person to reopen the airway, resulting in fragmented and poor-quality sleep. Repeated awakenings often go unnoticed but significantly impact the body and overall health.
Some symptoms of OSA include snoring, gasping for air during sleep, and excessive daytime sleepiness. Sleep apnea can affect anyone, but certain factors increase the risk of developing the condition.
Causes and Risk Factors
There are multiple causes and risk factors associated with Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Some of the most common include:
- Excess weight: Obesity, particularly around the neck, can pressure the upper airway, narrowing it and making it more susceptible to collapse during sleep. An increase in fatty tissue also increases the risk of obstructions.
- Age: Sleep apnea is more common in middle-aged and older adults, as muscle tone in the upper airway may decrease over time.
- Genetics: A family history of sleep apnea increases the likelihood of developing the condition, as it can be linked to inherited physical traits such as a narrow throat or large tonsils.
- Alcohol and sedative use: Drinking alcohol before bedtime or using sedatives can relax the throat muscles, increasing the chance of an obstructed airway during sleep.
- Smoking: Smoking increases inflammation and fluid retention in the upper airway, potentially contributing to sleep apnea.
Addressing the causes and risk factors associated with sleep apnea is important to maintain overall health. In some cases, making lifestyle changes or receiving medical treatment can greatly alleviate the symptoms and consequences of this sleep disorder.
Dietary Factors and Sleep Apnea
Foods That Worsen Sleep Apnea
Research indicates certain dietary factors can contribute to obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) development and progression. Foods high in saturated fats, added sugars and refined carbohydrates have been linked to inflammation, obesity, heart disease, and diabetes, all of which can exacerbate sleep apnea symptoms. Examples of such foods include:
- Processed meats: sausages, hot dogs, and bacon
- Fried foods: french fries, fried chicken, and doughnuts
- Sugary snacks: cookies, candy, and pastries
- Refined carbohydrates: white bread, pasta, and white rice
Individuals with sleep apnea must reduce their consumption of these harmful foods to improve their sleep quality and overall health.
Foods That Improve Sleep Apnea
Conversely, a healthy diet can help reduce the severity of sleep apnea symptoms and promote better sleep quality. A well-balanced diet should include a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Foods that are rich in fiber and antioxidants can help reduce inflammation, which can alleviate OSA symptoms. Such beneficial foods include:
- Fruits and vegetables: berries, leafy greens, and cruciferous vegetables
- Whole grains: brown rice, quinoa, and whole-grain bread
- Lean proteins: chicken, turkey, and fish
- Healthy fats: avocado, nuts, and seeds
In addition to these specific food choices, maintaining a healthy weight is crucial for managing sleep apnea symptoms. Obesity, a common risk factor for OSA, can be addressed through a balanced diet and regular exercise. By incorporating the foods as mentioned earlier and lifestyle changes, individuals with sleep apnea can improve their sleep quality and reduce the risk of related health complications.
Lifestyle Factors and Sleep Apnea
Alcohol and Sleep Apnea
Consuming alcohol before bedtime can significantly increase the risk of sleep apnea. Alcohol relaxes the muscles in the throat and mouth, leading to increased snoring and a greater likelihood of temporary airway obstructions during sleep. Furthermore, alcohol disrupts normal sleep patterns, causing an individual to experience daytime sleepiness and fatigue.
It is important to note that regular consumption of alcohol could cause weight gain, which might further exacerbate sleep apnea symptoms. Reducing alcohol intake, particularly in the evening, is crucial in managing sleep apnea and improving overall sleep quality.
Weight Loss and Sleep Apnea
Excess weight, especially around the neck and upper airway, is a major contributor to sleep apnea. The additional fat tissue can cause the airway to narrow, making it difficult to breathe while sleeping. This results in episodes of partial or complete airway blockages, leading to loud snoring, interrupted breathing, and frequent awakenings.
Weight loss can significantly improve sleep apnea symptoms. Reducing body weight reduces the pressure on the airway and allows for easier air passage during sleep. Benefits of weight loss for sleep apnea sufferers include:
- Decreased snoring: A narrower airway results in louder and more frequent snoring. Weight loss can help reduce snoring by easing the constriction in the airway.
- Reduced daytime sleepiness: Sleep apnea causes interrupted sleep, leading to feelings of daytime fatigue. Weight loss can improve sleep quality and decrease daytime sleepiness.
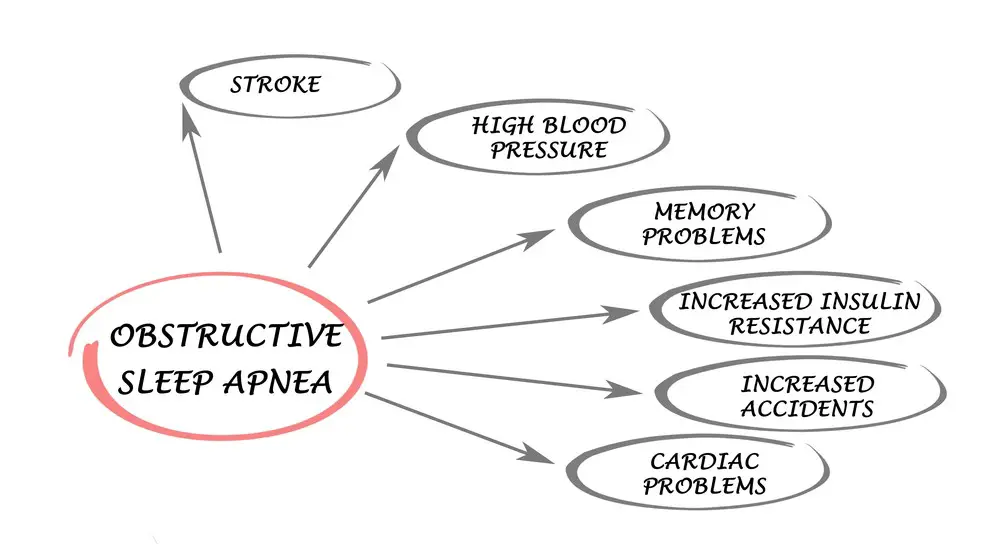
- Lower risk of health complications: Sleep apnea is associated with an increased risk of heart disease, high blood pressure, and stroke. Achieving a healthy weight can lower these risks.
Implementing healthy lifestyle changes, such as incorporating exercise and a balanced diet, are key factors in achieving weight loss and alleviating sleep apnea symptoms.
Anatomy and Sleep Apnea
The Role of the Mouth and Tongue
The mouth and tongue play essential roles in sleep apnea. During sleep, the muscles in the mouth, including the tongue, can relax excessively, resulting in the tongue falling backward towards the throat. This can block the airway, reducing oxygen intake and causing sleep apnea episodes. Furthermore, the size and position of the tongue can impact the severity of sleep apnea.
Tonsils
Enlarged tonsils are a common contributor to sleep apnea, particularly in children. When tonsils become swollen, they can obstruct the airway, leading to disruptions in breathing during sleep. Removing the tonsils, known as a tonsillectomy, can help alleviate sleep problems caused by enlarged tonsils.
Lower Jaw
The lower jaw’s position affects the airway’s size and openness. A smaller or recessed lower jaw can result in a narrow upper airway, increasing the risk of sleep apnea. Treatment options like oral appliances or surgery may be necessary to adjust the lower jaw’s position, expand the airway, and reduce the chances of sleep apnea.
Sleep Apnea and Sleep Problems
Sleep apnea and other sleep problems are often interconnected. The interruptions in breathing disrupt the sleep cycle, affecting melatonin production, a sleep-regulating hormone. Identifying and treating the underlying anatomical issues contributing to sleep apnea can improve overall sleep quality, enhancing physical and mental well-being.
Preventing Sleep Apnea
Optimizing Nutrition and Hydration
A well-balanced diet plays a significant role in preventing sleep apnea and other sleep disorders. According to the American Academy of Sleep Medicine, incorporating certain foods and vitamins into one’s daily intake can help alleviate sleep apnea symptoms and improve sleep quality. Consuming various vegetables and fruits, which are high in essential vitamins and antioxidants.
The Mediterranean diet is particularly beneficial for individuals who suffer from sleep apnea, as it emphasizes consuming whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. This dietary approach has been linked to reduced impaired breathing episodes during sleep, contributing to decreased heart failure risk.
Staying well-hydrated throughout the day is crucial for optimal health and sleep quality. The human body relies on sufficient water intake to support numerous physiological processes, including regulating mood and breathing. Drinking adequate water daily is an effective way to combat dehydration, which can worsen sleep apnea symptoms.
Importance of Physical Activity
In addition to optimizing nutrition and hydration, regular physical activity is essential for preventing sleep apnea. Exercise has been shown to improve sleep quality, decrease the severity of sleep apnea symptoms, and promote overall health.
A sleep specialist or MD may recommend a combination of aerobic activities and strength training exercises tailored to an individual’s physical capabilities and preferences. By maintaining a consistent exercise routine, individuals with sleep apnea can reduce their risk of related health complications, such as heart failure.
In conclusion, adopting a balanced diet and staying physically active are crucial components in preventing and managing sleep apnea. While proper nutrition and hydration are essential for overall health, regular exercise can further improve sleep quality and reduce symptoms of sleep disorders. Individuals experiencing sleep apnea should consult a sleep specialist to determine the most effective strategies for their unique needs.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Sleep Apnea
Speaking to Your Doctor
If you suspect you have sleep apnea, speaking to your healthcare provider or doctor is essential. They will evaluate your symptoms and may refer you for a sleep study to confirm the diagnosis. Your doctor will consider risk factors, such as excessive daytime sleepiness, a high body mass index (BMI), and smoking, which can contribute to the development of sleep apnea. During a sleep study, the airflow at the back of the throat and blood pressure are monitored to diagnose the condition accurately.
Treatment Options and Therapies
Once diagnosed, various treatment options can be considered, depending on the severity of your sleep apnea:
- Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP): CPAP is the most common treatment for severe obstructive sleep apnea. It delivers positive pressure through a mask to keep the airways open during sleep, improving airflow and reducing the risk of complications.
- Oral appliance: An oral appliance may be recommended for mild to moderate sleep apnea. This device is custom-made by a dental professional to keep the airway open and prevent collapse during sleep.
- Positional therapy: Sometimes, sleep apnea occurs when sleeping in specific positions. In such cases, positional therapy helps to find the most suitable sleeping position, reducing the risk of sleep apnea.
- Surgery: In some cases, surgery may be required to address structural issues that cause sleep apnea. This can involve procedures to remove tissue from the throat or to stimulate the hypoglossal nerve, improving airflow.
- Inspire therapy is a relatively new treatment option involving an implanted device that stimulates the hypoglossal nerve during sleep, promoting optimal airflow.
Beyond treating sleep apnea, it is vital to address concurrent risk factors, such as obesity, smoking, and high blood pressure, to improve overall health and reduce potential complications.
COVID-19 and Sleep Apnea
During the COVID-19 pandemic, people diagnosed with sleep apnea need to continue their prescribed treatment, as sleep apnea may exacerbate the severity of COVID-19 symptoms. Furthermore, maintaining good cognitive health is vital, as untreated sleep apnea has been associated with an increased risk of dementia and other cognitive health issues.
Frequently Asked Questions
Which foods aggravate sleep apnea?
Foods with unhealthy fats, sodium, and added sugars can aggravate sleep apnea. Processed and fried foods, fast foods, and alcohol can also worsen sleep apnea symptoms. Consuming these foods may lead to weight gain and inflammation, increasing the risk of sleep apnea.
Are there specific foods to avoid for sleep apnea?
Individuals with sleep apnea should avoid high-fat foods like fatty meats, fried foods, and full-fat dairy products. Additionally, high-sodium foods like canned soups, processed snacks, and fast foods should be limited. Sugary foods and beverages, as well as alcohol, should be consumed in moderation.
How does eating before bed impact sleep apnea?
Eating a large meal or consuming certain foods close to bedtime can increase sleep apnea symptoms. Lying down soon after eating can cause acid reflux, worsening sleep apnea. It is best to avoid heavy meals and reflux-triggering foods such as spicy dishes, citrus, and caffeine within a few hours before bedtime.
Do certain food types worsen sleep apnea?
Consuming unhealthy fats, high sodium, and sugary foods can increase the risk of sleep apnea. Highly processed and fast foods may also contribute to weight gain, inflammation, and poor overall health, exacerbating sleep apnea symptoms.
What is the link between diet and sleep apnea?
A healthy diet plays a crucial role in managing sleep apnea. Eating a balanced diet can help maintain a healthy weight, reduce inflammation, and improve overall health, resulting in better sleep quality. A poor diet can contribute to weight gain and other negative health outcomes, increasing the risk of sleep apnea.
Can certain foods improve sleep apnea symptoms?
Incorporating nutrient-dense, whole foods into the diet can help alleviate sleep apnea symptoms. Fresh fruits and vegetables, lean proteins, whole grains, and healthy fats, such as those found in nuts, seeds, and fish, can improve sleep quality. Staying hydrated by drinking water throughout the day can also help improve sleep apnea symptoms.
This site contains affiliate links to products. We will receive a commission for purchases made through these links.



