As a BetterHelp affiliate, we receive compensation from BetterHelp if you purchase products or services through the links provided
Sleep apnea is a serious condition that affects millions of people each year. It can cause severe health issues, including fatigue and difficulty concentrating. But many don’t realize genetics are essential in determining if someone will develop sleep apnea: Is Sleep Apnea Genetic? The answer may surprise you. In this blog post, we’ll explore the causes of sleep apnea, how it’s diagnosed and treated, potential complications associated with untreated cases, and prevention and management techniques for those at risk of developing the disorder. Read on to learn more about this common yet potentially life-threatening condition!
Table of Contents:
What is Sleep Apnea?
Sleep apnea is a sleep disorder characterized by pauses in breathing during sleep. It can cause significant disruptions to standard sleeping patterns and lead to serious health complications if left untreated.
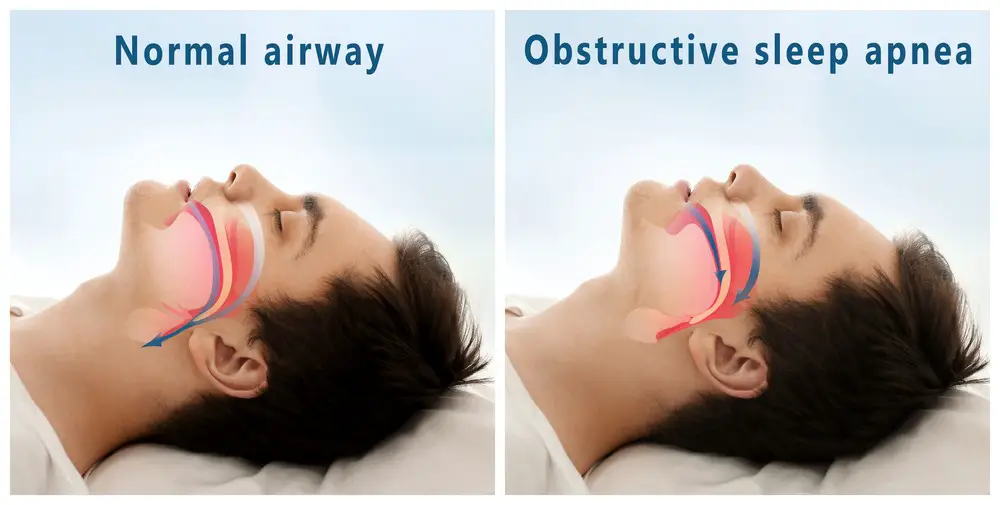
Definition of Sleep Apnea: Sleep apnea is a common condition affecting millions worldwide. It occurs when the airway becomes blocked or partially blocked during sleep, causing pauses in breathing that last for at least 10 seconds. These pauses are called “apneic events,” They can occur hundreds of times per night, resulting in poor quality sleep and excessive daytime fatigue.
The most common symptoms associated with sleep apnea include loud snoring, gasping or choking sounds while sleeping, frequent awakenings throughout the night, morning headaches, dry mouth upon waking up, difficulty concentrating during the day due to lack of restful sleep, irritability or mood swings due to lack of restful sleep and depression due to feeling tired all the time.
Types of Sleep Apnea: There are three main types of sleep apnea – obstructive (OSA), central (CSA), and complex (mixed). Obstructive is caused by an obstruction in the upper airway, such as enlarged tonsils or tongue; central involves problems with how signals from your brain reach your muscles responsible for controlling your breathing; mixed involves both obstructive and central components. Treatment will depend on which type you have been diagnosed with, so getting tested is essential if you think you may be suffering from this condition.
Risk factors for developing OSA include being overweight or obese; having large tonsils or adenoids; smoking cigarettes; drinking alcohol excessively; having certain facial features such as a narrow throat opening or small jawbone structure; using sedatives before bedtime; taking medications that relax muscles including opioids or opiates like codeine, etc.; and having allergies that block nasal passages.
Some studies suggest that genetic factors may be involved in the development of sleep apnea, as some families seem more prone than others. However, further research needs to be done before any definitive conclusions can be made about this link between genetics and OSA risk factors.
Sleep apnea is a severe sleep disorder that can significantly impact health and quality of life. Therefore, understanding the causes of this condition, including genetic and environmental factors, is essential to take appropriate steps for diagnosis and treatment.
Causes of Sleep Apnea
Risk Factors for Sleep Apnea: Several risk factors can increase the likelihood of developing sleep apnea. These include being overweight or obese, having large tonsils, smoking, drinking alcohol excessively, and using sedatives or sleeping pills. People with narrow airways may also be at an increased risk for sleep apnea due to their anatomy. Additionally, older adults and men are more likely to develop this condition than younger people and women.
Genetic Factors in Sleep Apnea: Genetics can also play a role in the development of sleep apnea. Specific genes have been linked to an increased risk for this disorder, such as those related to obesity or craniofacial structure abnormalities, which can lead to narrower airways. Additionally, family history is often considered when diagnosing someone with sleep apnea since it’s possible that multiple members of the same family could have similar genetic predispositions toward developing this condition.
Environmental factors such as changes in altitude or climate can also contribute to the development of sleep apnea by causing the narrowing of the upper airway passages during periods when there are low oxygen levels present in the environment, such as high altitudes. This environmental factor is known as hypoxia-induced obstructive sleep apnea (HIOSA). It has been observed among specific populations living at higher elevations compared to sea level locations where oxygen levels are typically higher.
Although the exact cause of sleep apnea is unknown, research has identified several potential risk factors and environmental influences that may contribute to its development. Next, we’ll discuss how sleep apnea is diagnosed and what treatments are available.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Sleep Apnea
Diagnostic Tests for Sleep Apnea: Diagnosing sleep apnea requires a physical examination, medical history review, and an overnight sleep study. During the physical exam, your doctor will check for enlarged tonsils or other anatomical abnormalities contributing to the problem. Your doctor will also ask about any symptoms you have been experiencing, such as snoring or daytime fatigue. The overnight sleep study measures oxygen levels in your blood while sleeping and can help determine if you have obstructive sleep apnea (OSA).
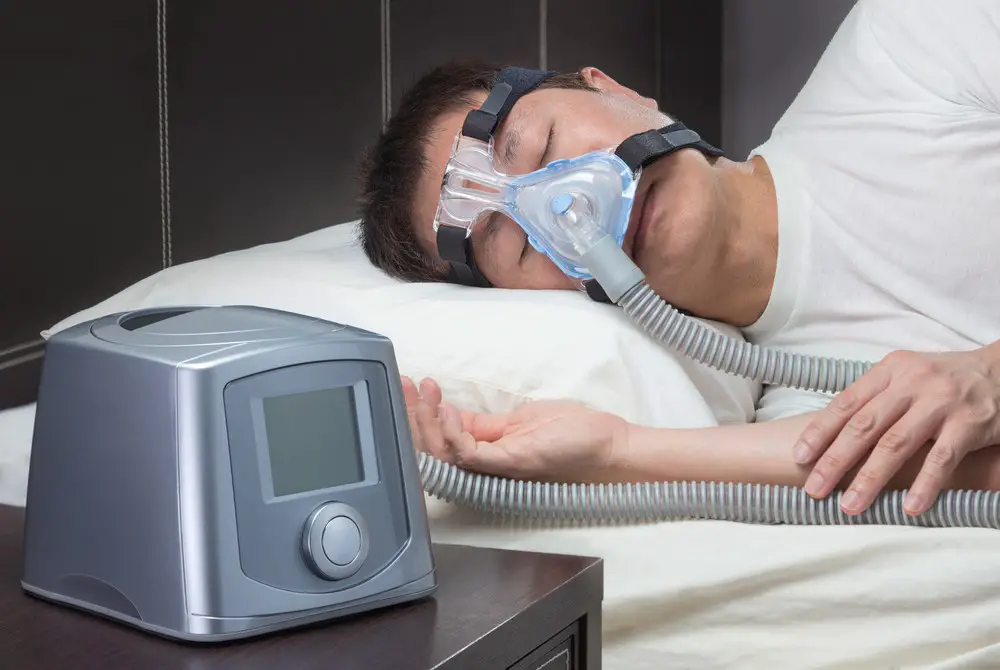
Treatments for Sleep Apnea: Treatment options for OSA include lifestyle changes such as avoiding alcohol before bedtime, losing weight if necessary, and using nasal decongestants or antihistamines to reduce congestion in the airways. Continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) machines are also commonly prescribed to treat OSA by providing a steady stream of pressurized air through a mask worn during sleep which helps keep the airways open throughout the night. In addition, surgery may be recommended depending on the underlying cause of OSA.
Diagnosing and treating sleep apnea is crucial to reduce the risk of serious complications. Next, we will explore the potential complications associated with untreated sleep apnea.
Complications Associated with Untreated Sleep Apnea
Cardiovascular Complications from Untreated Sleep Apnea: Sleep apnea can lead to severe cardiovascular complications, including an increased risk of high blood pressure, stroke, and heart attack. This is because the pauses in breathing during sleep apnea cause a decrease in oxygen levels in the body. As a result, the heart has to work harder to pump enough oxygen-rich blood throughout the body. Over time, this can damage the arteries and other parts of the cardiovascular system.
Cognitive Complications from Untreated Sleep Apnea: People with untreated sleep apnea may experience mental issues such as difficulty concentrating or remembering things due to a lack of quality sleep. In addition, they may be more prone to mood swings or depression due to chronic fatigue caused by their condition. Therefore, people with untreated sleep apnea need adequate rest so their brains can function properly and avoid any long-term cognitive impairments associated with poor sleeping habits.
Not only does untreated sleep apnea increase your risk for cardiovascular problems, but it also puts you at greater risk for respiratory illnesses like asthma or COPD (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease). The pauses in breathing caused by sleep apnea can weaken your lungs over time, making them more susceptible to infections and inflammation-related respiratory illnesses. Additionally, those who suffer from severe sleep apnea may experience hypoxia (lack of oxygen), which can lead to lung damage and other respiratory complications if left untreated for an extended period.
Left untreated, sleep apnea can cause a variety of severe health complications. Fortunately, several methods to prevent and manage the condition will be discussed in the next section.
Prevention and Management of Sleep Apnea
It is characterized by pauses in breathing during sleep, which can lead to poor sleep quality and daytime fatigue. Fortunately, several lifestyle changes and medical interventions are available to manage or prevent this condition.
Lifestyle Changes to Manage or Prevent Sleep Apnea: Making simple lifestyle changes such as losing weight, avoiding alcohol before bedtime, sleeping on your side instead of your back, quitting smoking, and avoiding sedatives can help reduce the severity of symptoms associated with sleep apnea. Also, maintaining good sleeping habits, such as going to bed at the same time each night and getting enough restful sleep, will help reduce symptoms.
Medical Interventions to Manage or Prevent Sleep Apnea: In some cases, more aggressive treatment may be necessary for managing or preventing sleep apnea. Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) machines are commonly used to treat moderate-to-severe obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) cases. These machines use air pressure delivered through a mask worn over the nose while sleeping to keep the airways open throughout the night. Other treatments include oral appliances designed to hold the jaw forward during sleep; surgery; medications; and oxygen therapy. Depending on individual needs, these treatments may be used alone or in combination with one another for optimal results.
It is crucial for those suffering from OSA or other types of sleep apnea to seek professional medical advice to develop an appropriate treatment plan based on their individual needs and preferences. With proper management and prevention strategies, it is possible for individuals living with this condition to experience improved quality of life without compromising their overall health outcomes.
FAQs
Are you born with sleep apnea, or do you develop it?
Sleep apnea is a condition that can be either congenital (present at birth) or acquired. It occurs when the airway becomes blocked during sleep, causing pauses in breathing and reduced oxygen levels in the blood. Congenital sleep apnea is caused by physical abnormalities present from birth, such as an abnormally small jaw or enlarged tonsils. Lifestyle factors like obesity, smoking, alcohol use and certain medications usually cause acquired sleep apnea. Treatment for both types of sleep apnea may include lifestyle changes, medical devices, or surgery to open up the airways.
What is the root cause of sleep apnea?
Sleep apnea is a sleep disorder in which breathing repeatedly stops and starts during sleep. It occurs when the muscles in the back of your throat relax too much, causing your airway to become blocked. This can lead to decreased oxygen levels in the blood, resulting in loud snoring, pauses between breaths, and frequent awakenings throughout the night. Treatment for sleep apnea may include lifestyle changes such as weight loss or avoiding alcohol before bedtime, using a continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) machine while sleeping, or undergoing surgery to open up your airways.
What age does sleep apnea start?
Sleep apnea can start at any age, but it is most commonly seen in adults over 40. It is also more common in men than women. Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) occurs when the airway collapses or becomes blocked during sleep, causing pauses in breathing and a decrease in oxygen levels. If left untreated, this can lead to daytime fatigue, snoring, and other health problems. Treatment options include lifestyle changes such as weight loss, avoiding alcohol before bedtime, using devices such as CPAP machines, or surgery for more severe cases.
Can a healthy person have sleep apnea?
Yes, a healthy person can have sleep apnea. Sleep apnea is a disorder that causes pauses in breathing during sleep. It can occur in people of any age and health status, although it is more common among those who are overweight or obese. Symptoms include snoring, frequent awakenings throughout the night, excessive daytime fatigue, and morning headaches. Sleep apnea can lead to serious health problems such as high blood pressure and heart disease if left untreated. Treatment options vary depending on the severity of the condition but may include lifestyle changes like weight loss or CPAP therapy.
Conclusion
It is essential to be aware of the signs and symptoms of sleep apnea and the potential causes to ensure early diagnosis and treatment. While certain risk factors are associated with sleep apnea, such as age, gender, family history, or obesity, it is still unclear whether or not genetics play a role in its development. Therefore, more research needs to be done into this area before any definitive conclusions can be made about whether or not sleep apnea is genetic.
Are you or someone you know suffering from sleep apnea? Genetics can play a role in this condition, but other factors are also at work. Take the first step towards finding relief and understanding your diagnosis by exploring our website for helpful information about therapy options and stress-reducing techniques that may help improve your symptoms. Don’t wait any longer – take control of your health today!
Sleep Apnea Resources
Regarding sleep apnea, many resources are available to help you get the treatment and support you need. From lifestyle changes to medical treatments, here are some of the most helpful resources for managing your condition.
Lifestyle Changes: Making healthy lifestyle changes can be an effective way to reduce symptoms of sleep apnea.
This includes avoiding alcohol and caffeine before bedtime, quitting smoking if applicable, exercising regularly, maintaining a healthy weight, and sleeping on your side instead of your back.
CPAP Machines: Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) machines provide air pressure through a mask worn while sleeping to keep the airways open during sleep.
A doctor can prescribe CPAP machines or purchase them online from reputable retailers such as Amazon or Walmart.
Oral Appliances: Oral appliances are another option for treating mild-to-moderate cases of sleep apnea.
These devices fit inside the mouth like a retainer or mouthguard and work by moving the lower jaw forward slightly to keep the airway open during sleep.
They can be custom-made by dentists specializing in dental sleep medicine or purchased over the counter at pharmacies or online retailers such as Amazon or Walmart.
Surgery: In severe obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) cases, surgery may be recommended as an option for the treatment depending on what is causing the blockage in the upper airway area (e.g., enlarged tonsils).
Common surgeries used for OSA include uvulopalatopharyngoplasty (UPPP), maxillomandibular advancement (MMA), and tracheostomytracheotomy procedures, which involve making incisions into either the throat area or neck region to widen blocked sites so that breathing is easier during sleep time hours.
Sleep Studies & Diagnosis Tests: If you suspect that you have Obstructive Sleep Apnea, you must consult with your primary care physician before seeking other treatments.
Your doctor will likely refer you for further testing, such as overnight polysomnography, home oximetry tests, multiple wakefulness tests, etc. All these tests help diagnose whether someone has OSA and how severe their case might be.
Sleep Apnea Tips
Diet and Exercise
Maintaining a healthy diet and exercise routine is essential when living with sleep apnea. Eating nutritious foods like fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, whole grains, and low-fat dairy can help improve your overall health.
Additionally, regular physical activity can reduce stress levels which may help you get better quality sleep at night. Try to incorporate 30 minutes of moderate exercise into your daily routine.
Avoid Stimulants
Stimulants like caffeine or nicotine should be avoided if you have sleep apnea since they can interfere with your ability to fall asleep and stay asleep throughout the night.
Caffeine has been known to increase alertness, so it’s best not to consume any after lunchtime so it not to disrupt your sleeping pattern.
It’s also recommended that you avoid drinking alcohol before bed as this can worsen sleep apnea symptoms by causing the throat muscles to relax more than usual while sleeping.
Sleep Positioning
When dealing with sleep apnea, you must find a comfortable position that helps keep your airways open during the night, such as on one side or propped up on pillows in an elevated position instead of lying flat on your back.
This will allow for easier breathing while sleeping and prevent snoring from occurring due to obstructed airways caused by gravity pulling down on them while lying flat on one’s back.
- 3 Ways Wearing a Hat Can Help Lower Your Stress Levels - April 19, 2025
- Breaking the Silence: Why Men’s Mental Health Matters More Than Ever - April 15, 2025
- How to Transform a Home’s Patio Space into a Relaxing Space - March 23, 2025
This site contains affiliate links to products. We will receive a commission for purchases made through these links.