As a BetterHelp affiliate, we receive compensation from BetterHelp if you purchase products or services through the links provided
As a concerned parent, it’s essential to recognize potential sleep disorders in your child, including sleep apnea. Sleep apnea is commonly associated with adults but can also affect children, leading to various health and behavioral issues. This article provides an opportunity to learn more about sleep apnea and determine if your child may be at risk by participating in our “Does My Child Have Sleep Apnea Quiz.”
Understanding sleep apnea is the first step to helping your child. Sleep apnea is a disorder in which a person’s breathing repeatedly stops and starts during sleep, and it can manifest in different forms, such as obstructive sleep apnea and central sleep apnea. It can impact your child’s health, leading to poor sleep quality, irritability, decreased attention span, and more. With the assistance of our quiz and other resources, you’ll be better equipped to make informed decisions about your child’s sleep habits and overall well-being.
Our quiz also explores the symptoms, risk factors, and treatments associated with child sleep apnea, guiding you to make the right decisions for your child’s health. This quiz and advice from medical professionals will help you identify the necessary steps to address any sleep issues and improve your child’s overall health.
Key Takeaways
- The quiz helps identify if your child may have sleep apnea by assessing symptoms and risk factors.
- Sleep apnea in children can lead to various health and behavioral issues
- Consult medical professionals for accurate diagnosis and proper treatment options
 Understanding Sleep Apnea
Understanding Sleep Apnea
Sleep apnea is a sleep disorder characterized by repeated interruptions in breathing during sleep. There are two main types of sleep apnea: obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) and central sleep apnea (CSA).
Obstructive sleep apnea occurs when the muscles in the throat relax, causing the airway to narrow or close, restricting breathing for brief periods. Central sleep apnea, on the other hand, stems from the brain’s failure to send the correct signals that control breathing during sleep. Both types of sleep apnea disrupt your sleep quality, leading to daytime sleepiness and potential behavior issues in children.
Some common signs of sleep apnea in children include:
- Loud, persistent snoring
- Choking or gasping for breath during sleep
- Restlessness and difficulty staying asleep
- Bedwetting
- Frequently cranky or sick for seemingly no reason
It’s essential to remember that not every child who snores has sleep apnea, but persistent snoring accompanied by the mentioned symptoms should raise concerns. Early detection and treatment of sleep apnea in children are crucial for their health and well-being.
Treating sleep apnea usually involves lifestyle changes, such as weight management, maintaining a healthy diet, and practicing good sleep hygiene. In some cases, medical interventions, such as using a continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) machine, dental appliances, or even surgery, may be necessary.
So, if you suspect that your child has sleep apnea, don’t hesitate to consult a healthcare professional for evaluation and support.
Symptoms Commonly Associated with Child Sleep Apnea
When determining if your child might have sleep apnea, looking for specific symptoms is essential. Here are some of the most common signs of sleep apnea in children:
- Loud snoring: If your child snores loudly and frequently, this could indicate sleep apnea.
- Daytime sleepiness: Does your child often appear drowsy or have trouble staying awake during the day? Sleep apnea can affect their sleep quality, leaving them tired even after a whole night’s rest.
- Restless sleep: If your child tosses and turns during the night, it might be due to sleep apnea disrupting their sleep.
- Pauses in breathing, gasping, and choking: These are crucial signs of sleep apnea. If you notice your child stopping breathing for intervals, gasping for breath, or choking in their sleep, it’s essential to consult a doctor.
- Bedwetting: Though not specific to sleep apnea, bedwetting can sometimes be associated with the disorder, especially in older children who don’t usually wet the bed.
- Breathing patterns: Pay attention to your child’s breathing patterns during sleep. Snorting and mouth breathing might be symptoms of sleep apnea.
It’s also important to note other signs that could indicate sleep apnea in children:
- Morning headaches: Children with sleep apnea may wake up with headaches because of a lack of oxygen during the night.
- Behavioral problems: Sleep apnea can lead to irritability, difficulty concentrating, and behavioral issues in children due to poor sleep quality.
- Night terrors and insomnia: Sleep apnea may cause night terrors or contribute to insomnia, making it challenging for your child to fall or stay asleep.
In addition to these symptoms, sleep apnea can cause daytime fatigue, making it harder for your child to stay alert and focused. Watch for these signs and consult a doctor if you suspect your child might have sleep apnea. A proper diagnosis and treatment plan can help your child achieve better sleep and overall health.
Behavior and Lifestyle Indicators
When it comes to identifying sleep apnea in your child, there are specific behavioral and lifestyle indicators that you can watch out for. These indicators may hint at the presence of sleep apnea and are worth considering if your child is experiencing sleep disturbances.
One common sign of sleep apnea is a consistent struggle with school performance. If your child suddenly faces difficulties with their academic tasks or has a drop in grades, it could be related to disrupted sleep due to sleep apnea.
Hyperactivity and ADHD (Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder) symptoms can also be linked to sleep apnea. Children with sleep apnea may display signs such as:
- Inattention
- Impulsivity
- Difficulty following instructions
- Excessive talking
These behaviors could be a result of insufficient sleep and frequent nighttime awakenings.
Another aspect to keep an eye on is your child’s lifestyle. Unhealthy habits such as poor diet and lack of exercise may exacerbate sleep apnea symptoms. Encourage your child to maintain a balanced diet and regular physical activity to promote better sleep.
It’s essential to note that sleep apnea can also lead to other behavioral issues, like irritability, mood swings, and aggression. These behaviors could react to the frustration and exhaustion from poor sleep quality.
Sleep apnea might be an underlying factor if your child is experiencing learning problems or difficulties focusing in school. Inadequate sleep may affect your child’s cognitive abilities, making it challenging to process new information, retain knowledge, and concentrate.
In conclusion, paying attention to your child’s behavior and lifestyle can provide valuable insights into their overall health and sleep quality. If you notice any of the mentioned indicators, consider discussing your concerns with a healthcare professional. Early intervention and treatment can help address sleep apnea and improve your child’s sleep, academic performance, and overall well-being.
Medical Assessment and Diagnosis
When you suspect your child might have sleep apnea, it’s essential to consult a pediatrician or sleep specialist for proper assessment and diagnosis. They’ll review your child’s symptoms and medical history and conduct a thorough physical examination, focusing on the head, neck, nose, mouth, and tongue.
In many cases, a sleep study, known as polysomnography, is conducted to diagnose sleep apnea in children. This test records various data while your child is asleep, such as the oxygen level, brain waves, heart rate, and breathing. Sleep studies usually take place at a specialized sleep center, but home sleep tests might be an option in some cases.
During polysomnography, several sensors are attached to your child’s body to monitor their sleep stages, eye movements, muscle activity, and more throughout the night. Here are some critical aspects of the test:
- The test is painless, non-invasive, and safe for children.
- It provides valuable insights into your child’s sleep quality and patterns.
- The sleep specialist will analyze the data to determine whether your child has sleep apnea and its severity.
After the sleep study, your child’s doctor will review the findings and determine the most suitable treatment plan based on the diagnosis. If your child is diagnosed with sleep apnea, early intervention and appropriate treatment can improve their sleep quality, overall health, and daily functioning.
Key takeaway: If you suspect your child has sleep apnea, consult a pediatrician or sleep specialist for a proper assessment and diagnosis, which may include a sleep study (polysomnography). Early detection and treatment can significantly improve your child’s well-being.
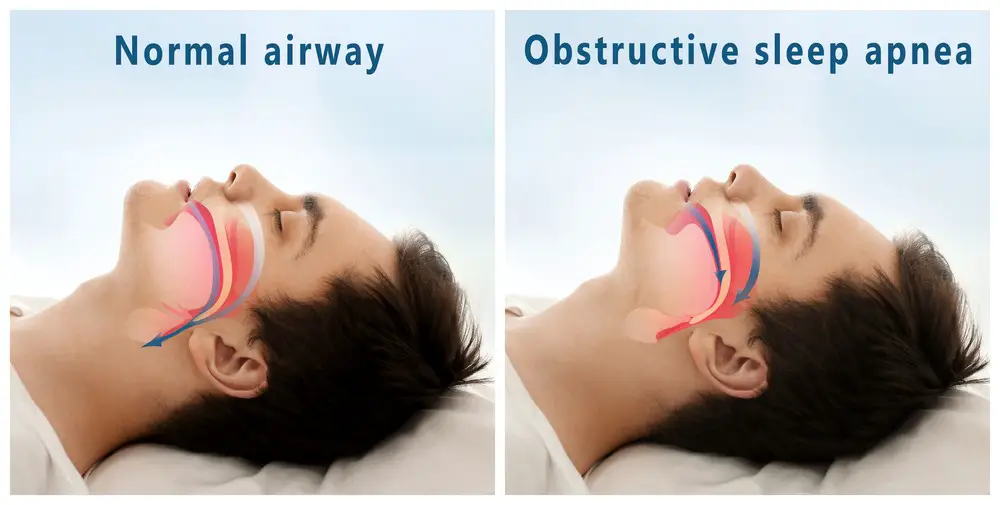
Risk Factors and Complications of Sleep Apnea in Children
Understanding the various factors that can increase the risk of sleep apnea in children. These risk factors often overlap, contributing to the development of this sleep disorder. Some common risk factors include:
- Obesity: Children who are overweight or obese are more likely to develop sleep apnea due to fat accumulation around their upper airway, which can cause it to narrow or collapse during sleep.
- Family history: If a close relative, such as a parent or sibling, has sleep apnea, your child may be more prone to developing the condition.
- Growth: Some children may have sleep apnea due to growth abnormalities, such as a small jaw or enlarged tonsils, that can obstruct their airway.
- Certain medical conditions: Children with Down syndrome, cerebral palsy, neuromuscular disorders, or sickle cell disease have an increased risk of developing sleep apnea.
- Low birth weight: Babies born with low birth weight are more likely to develop sleep apnea later in life.
Not only can these risk factors contribute to the development of sleep apnea, but they can also exacerbate the complications of this disorder. Some potential health problems your child may experience include:
- High blood pressure: Sleep apnea can lead to increased blood pressure during sleep, which in turn can cause strain on the heart.
- Heart problems: Sleep apnea may increase the risk of heart problems, such as an irregular heartbeat or even heart failure, especially if left untreated.
- Stroke: Sleep apnea has been linked to an increased stroke risk in adults and children.
- Lung issues: Sleep apnea can affect your child’s lungs by causing breathing difficulties during sleep, which may lead to respiratory issues.
In summary, knowing the various risk factors and potential health complications associated with sleep apnea in children is essential. By understanding these factors, you can take steps to ensure your child receives appropriate care and treatment if they are experiencing symptoms of this sleep disorder.
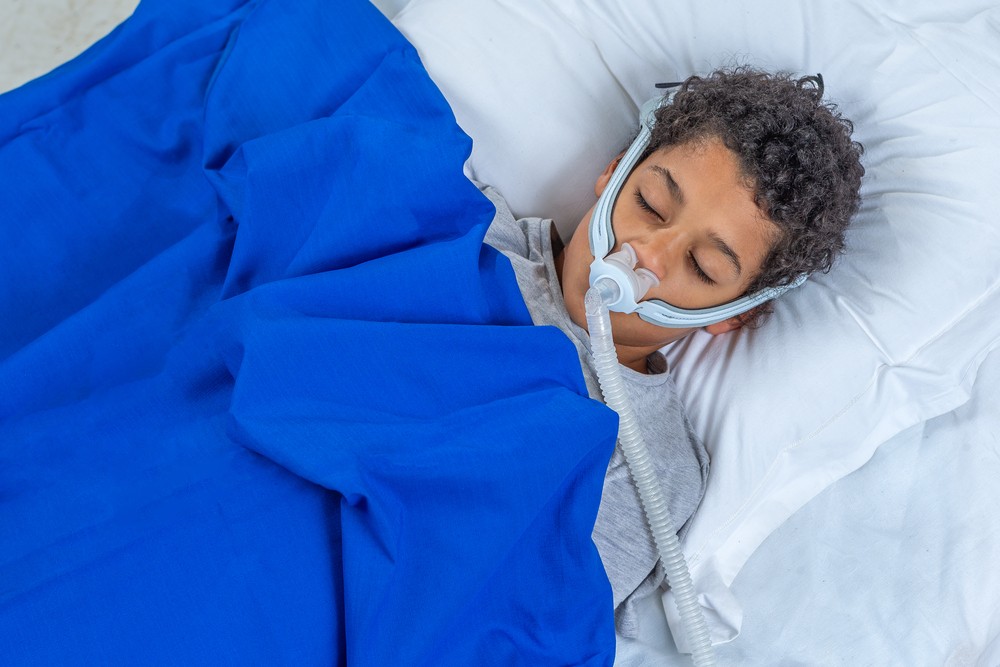
Treatments and Interventions
If your child is diagnosed with sleep apnea, several treatment options are available to help them breathe easier and sleep better. Let’s explore some of the most common and effective treatments:
- Adenotonsillectomy: This surgery removes the tonsils and adenoids, often the primary cause of sleep apnea in children. It’s a relatively straightforward procedure with a high success rate.
- CPAP machine: Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) devices gently blow air through your child’s mask while sleeping. This continuous airflow keeps the airway open, reducing or eliminating the apneas that disrupt their sleep.
- Oral Appliance: These custom-made devices reposition the lower jaw forward, opening the airway and reducing the risk of obstructions. They are less invasive than surgery and might be a suitable option for your child.
- Weight Loss: As obesity is a significant contributor to sleep apnea, following a healthy diet and encouraging physical activity can help reduce the severity of the condition.
- Lifestyle Changes: Ensuring your child has a consistent sleep schedule, a quiet and dark sleeping environment, and avoids caffeine close to bedtime can improve their sleep quality.
- Myofunctional Therapy: This treatment focuses on strengthening the muscles in the mouth and throat that contribute to optimal breathing. A trained therapist works with your child to teach them exercises that can help alleviate sleep apnea symptoms.
Of course, it’s essential to consult with your child’s doctor before implementing any treatment plan. They may need to monitor your child’s oxygen levels or suggest other interventions, like avoiding sedatives and opioids, which can further impact their breathing.
Finally, remember that each child is unique, and it might take some time to find the most effective treatment plan tailored to their needs. Stay patient, supportive, and involved in their journey to better sleep.
Role of Physical Observations in Diagnosis
Physical observations are crucial in diagnosing if your child has sleep apnea. Pay close attention to your child’s sleep patterns and behaviors is essential. Let’s dive into the key points that can help identify the possibility of sleep apnea in your child.
First, monitor your child’s snoring. Occasional snoring is normal, but it can be a sign of sleep apnea if it’s consistent and loud. This is due to obstructions in the upper airway (nose and mouth) that cause breathing pauses during sleep.
Checking for enlarged tonsils and adenoids is another vital observation. Enlarged tonsils and adenoids can block the airway, contributing to sleep apnea. A healthcare professional can examine your child’s mouth to check for these issues.
The position of the tongue plays a part, too. Some children may have an unusually large or displaced tongue that obstructs their airway during sleep. An examination by a healthcare professional will help detect this issue.
Mouth breathing is another indicator of potential sleep apnea. If your child frequently breathes through their mouth during sleep, this can suggest that their nasal passages are blocked, leading to sleep apnea.
Observe if your child experiences nighttime sweating. Excessive sweating during sleep can point to sleep apnea as the body struggles to maintain oxygen levels and keep the airway open.
Another key observation is the use of a mouthpiece. Your doctor might recommend using a mouthpiece that adjusts the jaw and tongue’s position to alleviate sleep apnea symptoms. Monitor how your child adjusts to this device and if it effectively reduces their symptoms.
Remember, these physical observations are a crucial first step in diagnosing sleep apnea in your child. By keeping track of these signs, you can help your healthcare professional make a more accurate diagnosis and recommend appropriate treatment options.
Key takeaway: Pay attention to your child’s snoring, enlarged tonsils, adenoids, tongue position, mouth breathing, and nighttime sweating, as these physical observations can help diagnose sleep apnea.
The Childhood Sleep Apnea Quiz
If you suspect your child might be dealing with sleep apnea, taking a quiz can help determine if further evaluation is needed. Remember that quizzes are not a substitute for professional medical advice, but they can be a helpful starting point to understand your child’s symptoms.
One of the quizzes you can find online consists of a few questions that aim to identify some common signs related to sleep apnea in children. These questions may touch on essential factors such as:
- Snoring: Does your child snore loudly during their sleep?
- Breathing patterns: Have you noticed any abrupt or irregular breathing patterns while your child is asleep?
- Daytime fatigue: Is your child often tired and lethargic, even after a full night?
- Bedwetting or restlessness: Does your child struggle with bedwetting or exhibit restlessness during sleep?
When taking the quiz, being as honest as possible about your child’s symptoms is essential. Remember, early detection and treatment can help prevent long-term complications.
• Seeking Professional Evaluation: – If the quiz results suggest a possibility of sleep apnea, scheduling a visit to a pediatrician or a sleep specialist is imperative. They might recommend a sleep study to get a definitive diagnosis. – Prepare for the appointment by noting down the symptoms you’ve observed and any questions or concerns you might have. It’s always a good idea to be well-prepared.
• Maintaining a Sleep Diary: – Before and after the professional evaluation, keep a sleep diary to track your child’s sleep patterns, snoring frequency, and any other pertinent observations. This diary can be a valuable tool for the healthcare provider.
• Understanding the Treatment Options: – Treatment for sleep apnea in children might include medication, lifestyle modifications, or, in severe cases, surgery. – Understanding and discussing all available treatment options with your healthcare provider is crucial to determining what’s best for your child.
• Educating Yourself and Your Family: – Learn as much as possible about sleep apnea and its implications on your child’s health and daily life. – It’s also beneficial to educate other family members so everyone is on the same page regarding the care and support your child needs.
• Creating a Conducive Sleep Environment: – Ensure your child’s bedroom is comfortable, quiet, and dark to foster better sleep quality. – Establishing a consistent bedtime routine can also promote healthier sleep habits.
This journey might seem daunting initially, but with the proper guidance and support, you can ensure your child receives the necessary care to manage or overcome sleep apnea. Remember, the key to successful management and treatment lies in early detection, proper diagnosis, and a well-rounded approach to care. Your proactive steps today can significantly impact your child’s life.
Frequently Asked Questions

Does your child snore loudly or gasp for air during sleep?
It could indicate sleep apnea if your child snores loudly or gasps for air during sleep. Sleep apnea is a sleep disorder characterized by interrupted breathing during sleep. You must monitor your child’s sleep and seek medical advice if you notice these symptoms.
Is your child often restless or have difficulty staying asleep?
Restlessness and difficulty staying asleep can also indicate sleep apnea in children. If your child tosses and turns, wakes up frequently or appears restless throughout the night, they may be experiencing sleep apnea. Monitor their sleep pattern and consult a healthcare professional if it persists.
Does your child struggle with excessive daytime sleepiness?
Excessive daytime sleepiness in children could be another symptom of sleep apnea. If your child is always tired, falling asleep during the day, or generally lethargic, sleep apnea could be the underlying cause. Seek medical advice if you notice these signs.
Are there pauses in your child’s breathing while asleep?
Pauses in breathing during sleep are a significant indicator of sleep apnea. Monitor your child’s sleep and pay attention to any instances where their breathing stops or becomes shallow for some time before resuming. If you notice these symptoms, consult a healthcare professional.
Has your child experienced bedwetting or night sweats?
While not as common, bedwetting and night sweats could be associated with sleep apnea in children. If your child experiences these and other sleep apnea symptoms like snoring, gasping, restlessness, or daytime sleepiness, discussing these concerns with a healthcare professional is crucial.
Do you notice poor attention or irritability in your child during the day?
Poor attention, irritability, or mood swings during the day might be linked to sleep apnea in children. Sleep is crucial for development and overall health, so disrupted sleep from sleep apnea could impact your child’s daily functioning. If you notice that your child is struggling with focus or mood, alongside other sleep-related symptoms, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional.
- Breaking the Silence: Why Men’s Mental Health Matters More Than Ever - April 15, 2025
- How to Transform a Home’s Patio Space into a Relaxing Space - March 23, 2025
- 5 Strategies to Use a Cell Phone to Help Manage Your Stress - March 23, 2025
This site contains affiliate links to products. We will receive a commission for purchases made through these links.


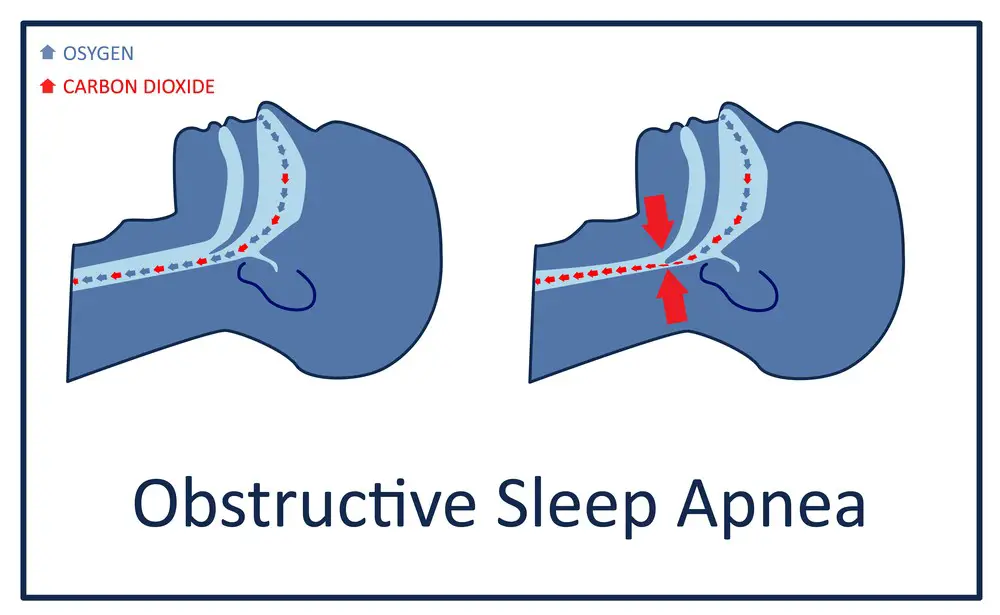 Understanding Sleep Apnea
Understanding Sleep Apnea
