As a BetterHelp affiliate, we receive compensation from BetterHelp if you purchase products or services through the links provided
We’ve all been there—you’re so exhausted that it feels like you could fall asleep right where you’re standing. But is it possible to catch some Z’s without lying down? In this article, we explore the fascinating question: can you sleep standing up?
While the idea might seem far-fetched, it’s not entirely unheard of. Some animals, like horses and cows, doze off while standing, thanks to a nifty physiological system called the stay apparatus. However, humans are a different story—and we’ll address the factors at play when it comes to upright slumber, as well as potential implications for your health.
Numerous factors contribute to the way we sleep. As we delve into the science of sleeping and the wide range of sleeping positions humans utilize, we’ll also take a look at some of the sleep disorders and medical conditions that affect how we rest. Additionally, we’ll explore the world of innovative sleeping solutions designed for unique situations and discuss the importance of healthy sleep in our day-to-day lives.
Key Takeaways
- Human sleep while standing is rare and usually indicates an underlying issue.
- Proper sleep positions and understanding sleep disorders are crucial for overall health.
- Animals like horses can sleep standing up due to their unique physiological mechanisms.
The Science Behind Sleeping
Sleep is a fascinating and essential part of life. In this section, we will explore the science of sleep and how it relates to the possibility of sleeping while standing up. To better understand this, let’s delve into sleep cycles and gravity’s role in our sleep.
Understanding Sleep Cycles
Sleep is not a static state; it consists of different stages of a complete sleep cycle. There are two primary types of sleep: Rapid Eye Movement (REM) sleep and Non-REM sleep. Non-REM sleep consists of three stages: light sleep (stage 1), intermediate sleep (stage 2), and deep sleep (stage 3). Here’s a brief explanation of each stage:
- Light sleep (stage 1): This is the first stage of sleep, where you’re transitioning from wakefulness to sleep. It’s easy to wake someone during this stage.
- Intermediate sleep (stage 2): This is a slightly deeper stage of sleep. Your heart rate and breathing slow down, and your muscles relax.
- Deep sleep (stage 3): This is the most vital stage of sleep. Your body repairs and regenerates tissues strengthens the immune system, and builds bone and muscle.
Finally, there’s REM sleep, the stage where dreams occur. During this phase, your brain is active, and your body is in near-paralysis to prevent you from physically acting out your dreams.
The Role of Gravity in Sleep
Gravity plays a critical role in our ability to sleep comfortably. When we lie down, our bodies distribute our weight more evenly, reducing pressure points and allowing us to relax. This horizontal position also aids in blood circulation, making it easier for our heart to pump blood.
On the other hand, when you’re standing, gravity works against you. It becomes more challenging to maintain balance, and the pressure on your feet and legs increases. Blood gets pumped to these areas, and if you were to fall asleep standing up, your brain would receive insufficient blood flow, causing you to awaken quickly.
While some animals can sleep standing up due to their unique anatomy, humans can’t do so for an extended period. Your body is designed to experience the various stages of sleep cycles while lying down and allowing gravity to assist in relaxation and blood flow.
In conclusion, sleeping standing up is not a feasible option for humans. To get the best quality sleep, find a comfortable position lying down, and allow your body to benefit from the different sleep stages and the aid of gravity.
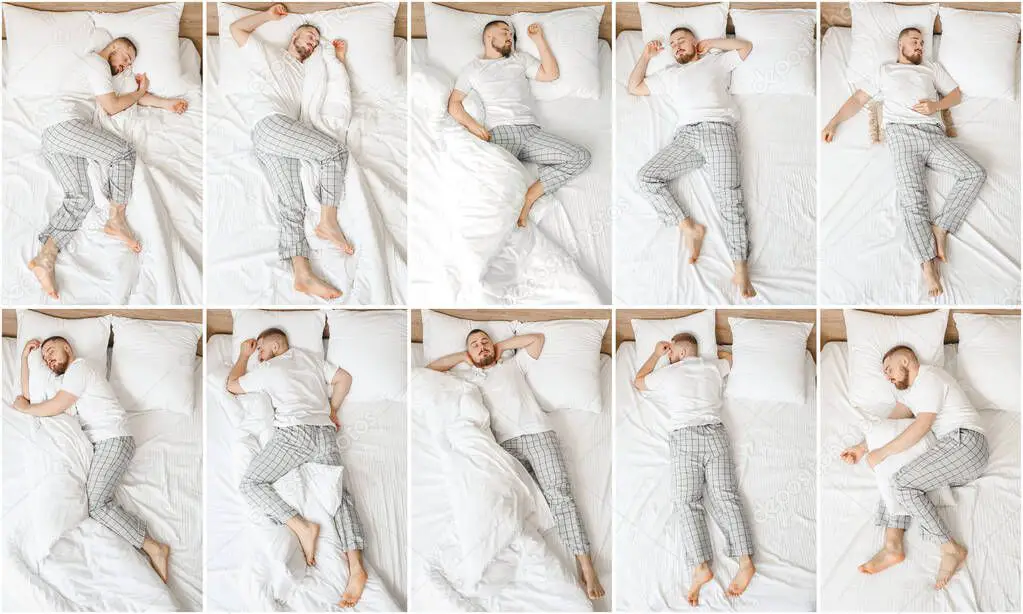
 Sleeping Positions and Their Effects
Sleeping Positions and Their Effects
Effects of Upright Sleeping
Some people claim to sleep better when they’re in an upright position, but is it beneficial? Sleeping upright might help reduce snoring and improve oxygen levels, making it a good option for those with sleep apnea. However, it’s essential to ensure the proper support to prevent neck and back pain. When sleeping upright, use a specialized pillow or a recliner chair to align your spine and maintain comfort throughout the night.
Key takeaway: Upright sleeping may help with snoring and oxygen levels but requires proper support for comfort and spinal alignment.
Repercussions of Prone and Supine Positions
Sleeping on your stomach (prone position) or back (supine position) can also affect your sleep quality. Prone sleepers might experience discomfort and pain due to the unnatural curvature of the spine and the pressure on the rib cage. In the supine position, you might experience increased snoring and potential sleep apnea episodes. Additionally, lying flat on your back can lead to heartburn or acid reflux, especially for those with GERD. To alleviate these issues, use a pillow to elevate your head or consider changing your sleep position.
Key takeaway: Prone and supine positions can cause discomfort, contribute to sleep apnea, and lead to acid reflux. Consider modifying your sleep position for better rest.
Advantages of Lateral Position
The lateral position, or sleeping on your side, is often considered the most comfortable and healthiest option. Side sleeping may help alleviate back and neck pain by maintaining a neutral spinal alignment. It can reduce the likelihood of snoring and sleep apnea episodes as well. If you’re a side sleeper, try placing a pillow between your knees to improve hip alignment and comfort.
Key takeaway: The lateral position is often the most comfortable, can alleviate pain, and helps reduce snoring and sleep apnea episodes. Incorporate a pillow between your knees for optimal comfort and alignment.
 Sleep Disorders and Medical Conditions
Sleep Disorders and Medical Conditions
Understanding Sleep Apnea
Sleep apnea is a common sleep disorder that affects many people. It is characterized by brief interruptions of breathing during sleep. There are two main types: obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) and central sleep apnea. OSA occurs when the muscles in your airway relax, causing it to narrow or close, while central sleep apnea involves the brain not sending proper signals to control your breathing.
Common sleep apnea symptoms include loud snoring, gasping for air during sleep, and daytime fatigue. If you suspect you have sleep apnea, it’s essential to see a doctor for a proper diagnosis and treatment. Untreated sleep apnea can lead to more serious medical conditions, such as diabetes, heart failure, and even pulmonary embolism.
Insights into Insomnia
Insomnia is another common sleep disorder, with many people suffering from difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep. Various factors like stress, anxiety, or medical conditions can trigger this. Chronic insomnia can have a significant impact on your overall health and well-being.
To better manage insomnia, try the following strategies:
- Establish a regular sleep schedule
- Create a comfortable sleep environment
- Limit exposure to screens before bedtime
- Incorporate relaxation techniques, such as meditation or deep breathing exercises
It’s essential to consult with a doctor if your insomnia persists, as it may be linked to an underlying medical condition, such as diabetes or congestive heart failure. Your doctor can help identify the root causes of your sleep difficulties and recommend appropriate treatment options.
Remember, paying attention to your sleep habits and seeking medical advice when necessary can help prevent sleep disorders and maintain your overall well-being.
 Sleeping Solutions for Different Scenarios
Sleeping Solutions for Different Scenarios
In this section, we will explore various sleep solutions that cater to your personal preferences and provide maximum comfort. We’ll focus on three main areas: a selection of mattresses and pillows, adjustable beds, and sleeping upright while sitting.
Selection of Mattresses and Pillows
Your choice of mattress and pillow can have a significant impact on your overall comfort. It is essential to find the perfect balance between these two elements to ensure a restful night’s sleep. Some tips to consider include:
- Personal preference: Pay attention to your preferences when choosing a mattress and pillow. Different people have different comfort levels, so what works for one person may not work for another.
- Firmness: Mattresses come in various firmness levels. Opt for the one that best supports the natural curvature of your spine.
- Pillow types: There are various pillow options available. A wedge pillow, for example, can provide additional support and flexibility.
Exploring Adjustable Beds
Adjustable beds can be a great solution for those who require more flexibility in their sleeping arrangements. They allow you to change the angle of the head and foot sections, which can help alleviate discomfort and accommodate various sleep positions. Key takeaway:
- Flexibility: Adjustable beds allow you to find your most comfortable sleeping position, making them an excellent option for those with specific needs or preferences.
 Sleeping Upright While Sitting
Sleeping Upright While Sitting
Finally, another option to consider is sleeping upright while sitting. This could be useful in certain scenarios, such as when you must sleep in a limited space where lying down isn’t an option. Here are two things to keep in mind:
- Comfort: Ensure that the chair or seat you choose provides adequate support and cushioning to maintain comfort for an extended duration.
- Sleep posture: Utilize a pillow or cushion to support your head and neck, helping maintain proper alignment while sleeping in a seated position.
The Connection Between Sleep and Productivity
Quality Over Position: A Holistic View of Sleep
We’ve all heard the age-old advice: “You must sleep on your back for optimal health.” While sleep positions do matter to an extent, it’s time to zoom out and take a more holistic view. Sleep quality is the real game-changer, not just how you’re angled on your bed.
- Debunking the Horizontal Sleep Myth: No, you don’t have to sleep horizontally to get a good night’s rest. Research shows that it’s the quality—how deep your sleep cycles go—that matters most for rejuvenation. Vertical sleep pods, hammocks, or even reclining chairs can offer great sleep if comfortable for you.
Key Takeaway: It’s all about comfort, consistency, and complete sleep cycles, not merely your orientation in space.
Understanding the Sleep-Productivity Link
If you’ve felt like a zombie after a poor night’s sleep, you’re not alone. But why does it impact your work life so drastically?
- The Sleep-Productivity Equation: Sleep isn’t just a “switch off” period. It’s an active, vital process where your brain and body are hard at work. Poor sleep? Your productivity takes a nosedive.
Tips for Boosting Productivity:
- Prioritize 7-9 hours of sleep per night
- Wind down at least 30 minutes before bedtime
- Keep gadgets away for a tech-free sleep environment
Quality Sleep: A Catalyst for Productivity
Restorative Sleep Principles
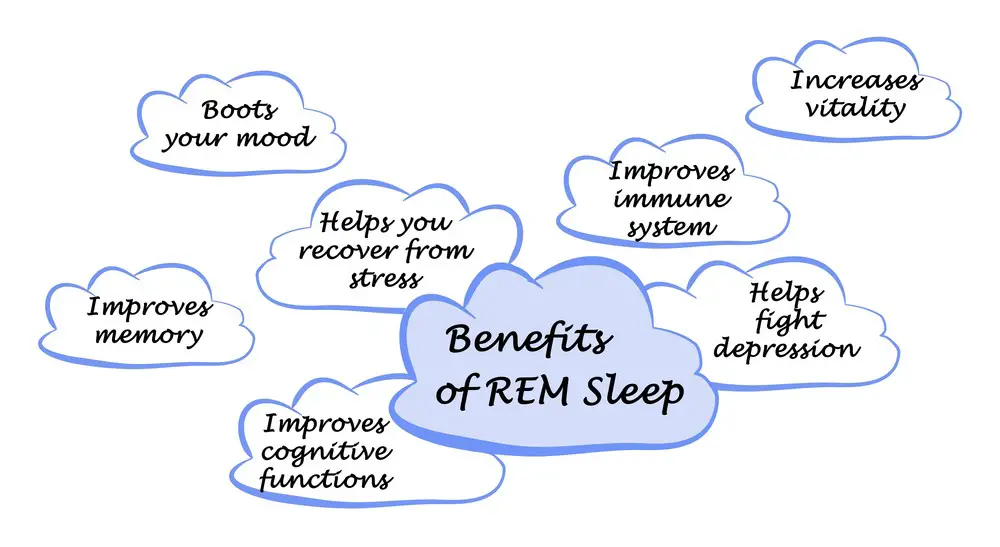
Sleep has a restorative function that goes beyond just “feeling refreshed.”
- Deep Sleep & REM Cycles: These are the bread and butter of quality sleep. Deep sleep helps bodily repair, while REM sleep enhances cognitive functions. Whether sleeping on a futon or in a floating pod, reaching these stages is key.
Takeaway: Both horizontal and unconventional sleep positions can serve the restorative purpose of sleep if they allow you to reach these critical cycles.
 Mental Clarity and Focus: The Cognitive Benefits of Quality Sleep
Mental Clarity and Focus: The Cognitive Benefits of Quality Sleep
Feeling sharp and ready to conquer the day isn’t just a ‘morning person’ thing. It’s a ‘quality sleep’ thing.
- Decision-making & Problem-Solving: If you’ve slept well, your brain has had the time to sift through data and memories, leaving you primed for decision-making.
Quick Tip: Struggling with a complex problem? Sometimes, “sleeping on it” is the best action you can take.
Emotional Well-being: The Unsung Hero
Quality sleep has a secret power: it can make you emotionally resilient.
- Emotional Resilience: Well-rested individuals have a more balanced emotional state. They’re better equipped to handle stress and bounce back from setbacks.
Bottom Line: Great sleep doesn’t just make you smarter; it makes you emotionally stronger too.
So, let’s stop obsessing over sleep positions and focus on what counts: quality, restorative sleep that enhances every aspect of our lives.
Debunking Myths for a Holistic Perspective
Challenging the Horizontal-Only Myth: Healthier Lifestyle Beyond Horizontal Sleep
Let’s cut through the noise: horizontal sleep is not the end-all, be-all. Contrary to popular belief, quality sleep isn’t solely confined to a horizontal plane.
- Sleep Quality Over Position: It’s not so much about the angle of your body as it is about the depth and restfulness of your sleep. If you’re getting solid REM and deep sleep cycles, that’s what truly counts.
Quick Tip: Experiment with sleep positions and settings to find what gives you the most restorative sleep. Listen to your body, not myths.
Sleep Adaptability: Your Body Knows Best
One of the most incredible things about the human body? Its adaptability. We’re designed to thrive in various conditions, including sleep settings.
- Individual Preferences: What works wonders for one person might be a nightmare for another. Whether you’re a side sleeper, back sleeper, or even an inclined sleeper, it’s about personal comfort.
- Flexible Approach: Being flexible about sleep positions opens up possibilities. Focus on quality—like uninterrupted sleep and reaching those beneficial deep and REM stages.
Key Takeaway: Adaptability is your friend. You don’t have to stick to one “correct” sleep position. It’s all about the quality of sleep you’re getting.
Toward a Holistic Perspective on Sleep
The beauty of understanding sleep quality is that it allows us to find what genuinely works for us. And guess what? That might not involve a flat mattress and a strict “sleeping on the back” rule.
- Quality Over Position: It’s the real kingpin here. Quality sleep rejuvenates your body, sharpens your mind, and strengthens your emotional resilience.
- Individual Preferences Matter: One size doesn’t fit all. Personal comfort and sleep quality go hand in hand.
- Holistic Approach: By debunking myths and embracing adaptability, we pave the way for a more comprehensive view on sleep that promotes health and productivity.
When to Seek Medical Help: Red Flags in Sleep Quality
While it’s great to experiment and find what works best for you, there are instances where sleep troubles may indicate a deeper health issue. Here’s when you might want to consult a medical professional:
- Chronic Insomnia: If you’re lying awake night after night, unable to fall or stay asleep, it could indicate an underlying issue.
- Sleep Apnea: Loud snoring accompanied by periods where you stop breathing could be a symptom of sleep apnea, a serious condition that requires medical attention.
- Restless Legs Syndrome: If you experience uncomfortable sensations in your legs that disrupt your sleep, it might be time for a medical check-up.
- Persistent Nightmares or Night Terrors: While the occasional bad dream is normal, recurrent nightmares might be a sign of stress or other mental health conditions.
- Unexplained Daytime Fatigue: If you’re clocking in enough hours of sleep but still feel perpetually drained, there might be an underlying issue affecting sleep quality.
Quick Tip: Keep a sleep diary to track your symptoms. This can provide valuable information for healthcare providers.
Bottom Line: If you’re experiencing any of these symptoms consistently, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare professional for a thorough evaluation and appropriate treatment. Prioritizing your sleep quality is essential, but it should go hand-in-hand with medical guidance when red flags appear.
Sleep Standing Up in Animals
Animals in the animal kingdom display various sleep patterns and positions. Some of them, like horses, have developed specialized mechanisms that enable them to sleep while standing up. In this section, we’ll explore the passive stay apparatus in horses and the unique sleep patterns found in animals.
The Passive Stay Apparatus in Horses
Horses possess a fascinating adaptation that allows them to rest while standing. The passive stay apparatus is a system of ligaments, tendons, and joint locks that enable horses to lock their limbs in place. This mechanism requires minimal muscular effort to maintain an upright posture.
This adaptation is crucial for survival since it allows horses to respond quickly to potential threats. While standing, horses can easily transition from a resting state to a flight response, ensuring their safety in the wild.
Key Takeaway: Horses use the passive stay apparatus to sleep standing up, enabling them to respond quickly to potential dangers.
Animal Sleep Patterns
The sleep cycle in animals varies significantly across the animal kingdom. Horses, for example, have shorter sleep cycles, with REM sleep typically lasting just a few minutes. This enables them to easily transition from sleeping to a heightened state of alertness.
Other animals have distinct sleep patterns:
- Elephants sleep standing up during short power naps but lie down for more extended rest periods.
- Giraffes curl their necks and rest their heads on their bodies, allowing them to stand while sleeping.
- Cows, like horses, can also lock their limbs to rest standing up, although they require lying down for deeper sleep stages.
Key Takeaway: Animals across the animal kingdom have evolved unique sleep patterns and positions that best suit their survival needs.
As you can see, the animal kingdom is full of diverse sleep patterns and ingenious adaptations that allow animals to rest while standing up. From horses with their passive stay apparatus to the varied sleep patterns among other species, these unique abilities demonstrate the incredible adaptability of life on our planet.
So, the next time you hear someone say you have to sleep a certain way for optimal health, remember: it’s not about the position but the quality and what feels suitable for you.
Frequently Asked Questions

Is it possible to sleep while standing?
Yes, it is possible to sleep while standing, but it might not be comfortable for everyone. Some animals, like horses, can sleep standing, but humans usually need a stable support system, like sitting or lying down. In some cases, people working long hours or military personnel have been known to doze off standing up, but it’s not ideal for a restful sleep.
What are the benefits of sleeping upright?
There are a few potential benefits when you sleep upright, such as:
- Easier breathing: Sleeping upright can help reduce nasal congestion and snoring, allowing for easier breathing.
- Improved digestion: Upright sleeping may lead to better digestion, as gravity helps food move through your system and prevents heartburn.
- Relief from orthopedic issues: People with certain back or neck conditions may find relief in sleeping upright.
Can sleeping upright help with sleep apnea?
Yes, sleeping upright can help some people with sleep apnea. Sleep apnea is a condition characterized by interrupted breathing during sleep, often caused by the relaxation of throat muscles. Sleeping upright can help keep your airway open, reducing the risk of sleep apnea episodes. Of course, it’s essential to consult a doctor for proper diagnosis and treatment.
What are the downsides to sleeping upright?
There can be a few downsides to sleeping upright, such as:
- Strain on your body: Sleeping upright can cause muscle strain due to insufficient support.
- Reduced quality of sleep: Upright sleeping might not be as restful, leading to tiredness during the day.
- Circulation issues: Prolonged upright sleeping may cause blood to pool in your legs, potentially leading to swollen feet or ankles.
How can I sleep comfortably sitting up?
To sleep comfortably sitting up, follow these tips:
- Use a supportive chair or recliner that offers proper neck and back support.
- Place a cushion or pillow behind your lower back to maintain the curve of your spine.
- Use a U-shaped travel pillow or a rolled towel to support your neck.
- Keep a blanket nearby to stay warm and comfortable when you sleep.
Are there any health concerns from sleeping while sitting up?
Although there are some benefits to sleeping upright, there are some potential health concerns:
- Strain on muscles: Lack of support can cause discomfort or pain in your neck, shoulders, and lower back.
- Swelling: As mentioned earlier, blood pooling in your legs may lead to swollen feet or ankles.
- Reduced quality of sleep: Discomfort may lead to restlessness, impacting the quality of your sleep.
Safety first: It’s crucial to consult with a healthcare professional before making any significant changes to your sleeping habits.
- Unveiling the Magic: The Ultimate Guide to Sleep Tinctures - November 1, 2023
- Can You Sleep Standing Up? - October 31, 2023
- Taurine for Sleep: Your Natural Ticket to Tranquil Nights - October 10, 2023
This site contains affiliate links to products. We will receive a commission for purchases made through these links.


 Sleeping Positions and Their Effects
Sleeping Positions and Their Effects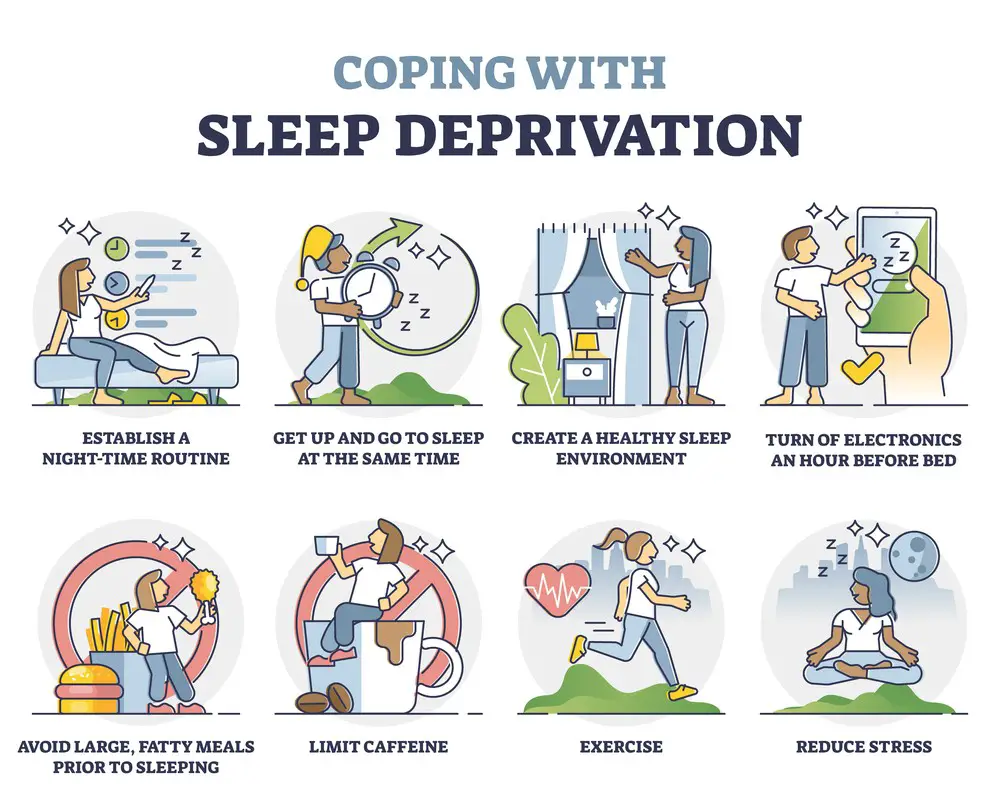 Sleep Disorders and Medical Conditions
Sleep Disorders and Medical Conditions Sleeping Solutions for Different Scenarios
Sleeping Solutions for Different Scenarios Sleeping Upright While Sitting
Sleeping Upright While Sitting
 Mental Clarity and Focus: The Cognitive Benefits of Quality Sleep
Mental Clarity and Focus: The Cognitive Benefits of Quality Sleep
